
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 13:
Ta có: \(f\left(x\right)>0\Leftrightarrow3x-m>0\Leftrightarrow3x>m\)
Mà x>1 hay 3x>3
Vậy \(m\le3\)
Đáp án C
Câu 14:
(d): x-2y+1=0 hay \(\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{1}{2}=y\)
Gọi phương trình đường thẳng cần tìm là: y=ax+b
Phương trình cần tìm đi qua A nên ta có: 2=-2a+b
Để phương trình cần tìm vuông góc với (d) thì: \(a.\dfrac{1}{2}=-1\Rightarrow a=-2\)\(\Rightarrow b=-2\)
Vậy phương trình cần tìm là: \(y=-2x-2\)
Đáp án C

Đường thẳng d có 1 vtpt là \(\left(1;-2\right)\)
Đường thẳng \(d'\) vuông góc d nên có 1 vtpt là (2;1) (đảo thứ tự tọa độ vtpt của d và đảo dấu 1 trong 2 vị trí tùy thích)
Phương trình d':
\(2\left(x+1\right)+1\left(y-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow2x+y+1=0\)

c/Theo công thức pascal trong Nhị Thức Newton ta có: \(C_{n-1}^{n-1}\) + \(C_{n-1}^k\) = \(C_n^k\)
C = \(C_{19}^0\) + \(C_{19}^1\) + \(C_{19}^2\) + ....+ \(C_{19}^{18}\) + \(C_{19}^{19}\)
C = (1+1)19 = 524288
còn câu d hình như đề sai

Câu 2:
\(a,\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(1-m\right)^2-\left(m^2-m\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2+m>0\\ \Leftrightarrow1-m>0\Leftrightarrow m< 1\\ b,\text{Áp dụng Viét: }\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(1-m\right)\\x_1x_2=m^2-m\end{matrix}\right.\\ \left(2x_1-1\right)\left(2x_2-1\right)-x_1x_2=1\\ \Leftrightarrow2x_1x_2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1-x_1x_2=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1x_2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-m-4\left(1-m\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2+3m-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)\left(m+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\left(ktm\right)\\m=-4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy m=-4
Câu 1:
\(1,\Leftrightarrow2x-2=3\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\ 2,ĐK:x\ne\pm1\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2+2x-1}{x^2-1}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x-1=2x^2-2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\\ 3,\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=2x-1\\3x-2=1-2x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{3}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(4,\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=2-x\left(x\ge\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\\3x-1=x-2\left(x< \dfrac{1}{3}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{4}\left(tm\right)\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ 5,\Leftrightarrow4x^2-2x+10=9x^2-6x+1\left(x\le\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow5x^2-4x-9=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9}{5}\left(ktm\right)\\x=-1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(6,\Leftrightarrow3x^2-9x+1=x^2-4x+4\left(x\ge2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-5x-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(tm\right)\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ 7,\Leftrightarrow2x^2+3x-4=7x+2\left(x\ge-\dfrac{2}{7}\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(tm\right)\\x=-1\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: (2x-1)(x+3)<=0
nên -3<=x<=1/2
b: \(\left(2x-7\right)\left(4-5x\right)>=0\)
=>(2x-7)(5x-4)<=0
=>4/5<=x<=7/2
i: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3-x+2}{x-2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-5}{x-2}< 0\)
=>2<x<5







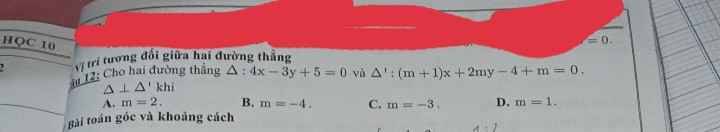


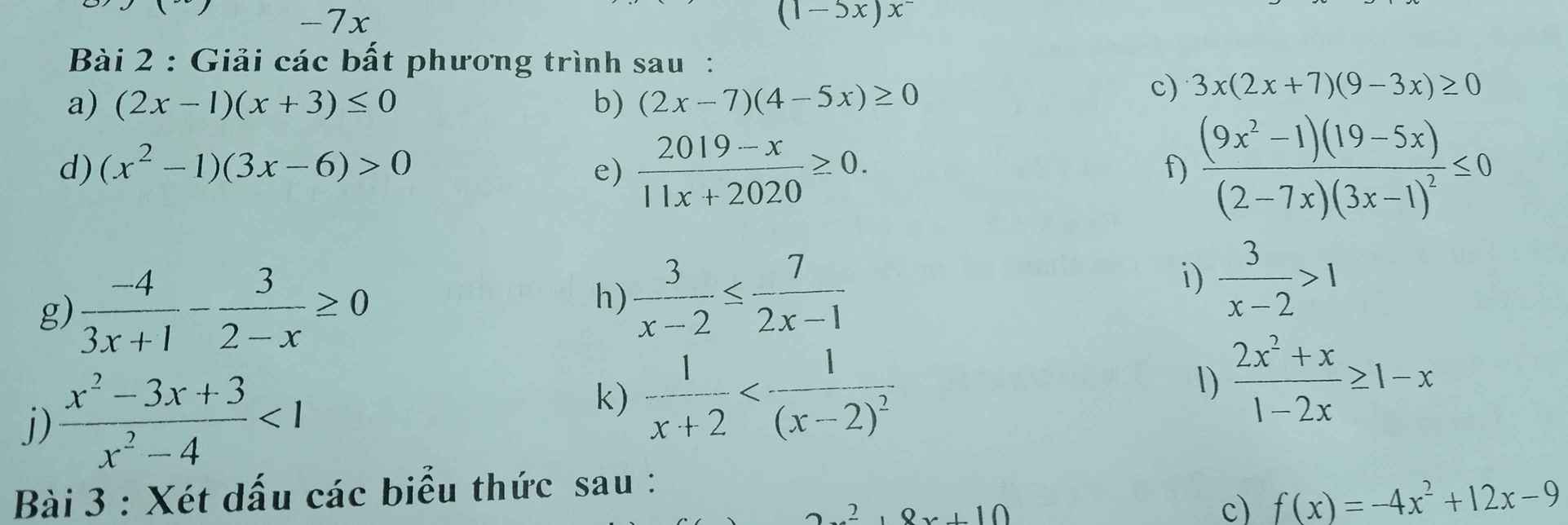

1:
a: x^2+y^2-2x-2y-2=0
=>x^2-2x+1+y^2-2y+1-4=0
=>(x-1)^2+(y-1)^2=4
=>R=2 và I(1;1)
b:x^2+y^2-6x+4y-12=0
=>x^2-6x+9+y^2+4y+4-25=0
=>(x-3)^2+(y+2)^2=25
=>R=5 và I(3;-2)
4:
a: \(R=d\left(I;\text{Δ}\right)=\dfrac{\left|3\cdot4+4\cdot\left(-3\right)+15\right|}{\sqrt{4^2+\left(-3\right)^2}}=3\)
(C) có phương trình là:
(x-3)^2+(y-4)^2=3^2=9
b: \(R=d\left(I;\text{Δ}\right)=\dfrac{\left|2\cdot5+3\cdot\left(-12\right)-7\right|}{\sqrt{5^2+\left(-12\right)^2}}=\dfrac{33}{13}\)
(C) có phương trình là;
(x-2)^2+(y-3)^2=R^2=1089/169