
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


2: Thay x=1 và y=-4 vào (d), ta được:
2m+2=-4
hay m=-3

\(d,ĐK:x\ge1\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=2+\sqrt{x+1}\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=2+x+1+4\sqrt{x+1}\\ \Leftrightarrow4\sqrt{x+1}=-4\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\left(4\sqrt{x+1}\ge0\right)\\ g,ĐK:x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow x+\sqrt{2x-1}+x-\sqrt{2x-1}+2\sqrt{\left(x+\sqrt{2x-1}\right)\left(x-\sqrt{2x-1}\right)}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x+2\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{2-2x}{2}=1-x\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|=1-x\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1-x\left(x\ge1\right)\\x-1=x-1\left(x< 1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(tm\right)\\x\in R\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bài 3:
a: Gọi OK là khoảng cách từ O đến AB
Suy ra: K là trung điểm của AB
hay \(AK=BK=\dfrac{AB}{2}=\dfrac{8}{2}=4\left(cm\right)\)
Áp dụng định lí Pytago vào ΔOKA vuông tại K, ta được:
\(OA^2=OK^2+KA^2\)
hay OK=3(cm)

Xét ΔOHA vuông tại H và ΔOKA vuông tại K có
OA chung
OH=OK
Do đó: ΔOHA=ΔOKA
Suy ra: AH=AK
hay AB=AC


c: \(f\left(5-2\sqrt{3}\right)=f\left(2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}}+m\left(5-2\sqrt{3}\right)+2=\sqrt{2-1}+2m+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3}+1+m\left(5-2\sqrt{3}\right)=2m+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(3-2\sqrt{3}\right)=2-\sqrt{3}\)
hay \(m=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\)

Bài 2:
Thay x=3 và y=-5 vào (d), ta được:
b-6=-5
hay b=1

\(x^2-2\left(m-2\right)x+m^2+2m-3=0\left(1\right)\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì Δ' > 0
\(\Rightarrow\left(m-2\right)^2-m^2-2m+3>0\Leftrightarrow m^2-4m+4-m^2-2m+3>0\Leftrightarrow-6m+7>0\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{7}{6}\)\)
Theo viét : \(\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-2\right)\\x_1x_2=m^2+2m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)\)
Lại có :\( \dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)\left(x_1x_2\right)=5\left(x_1+x_2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-4\right)\left(m^2+2m-3\right)=5\left(2m-4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^3+4m^2-6m-4m^2-8m+12=10m-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^3-24m+32=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-4\left(n\right)\\m=2\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(m=-4\) thì thỏa điều kiện



 , mình đang cần giải gấp. Cảm ơn mn nhiều.
, mình đang cần giải gấp. Cảm ơn mn nhiều.


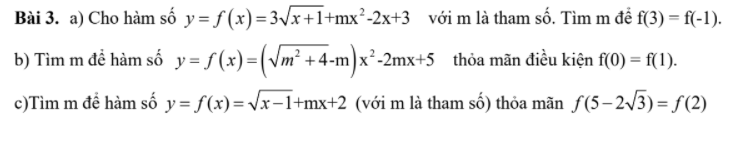



a: Khi m=2 thì (1) se là x^2-2x-3=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=-1
b: Vì a*c<0 nên (1) luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt