Tổng tấ cả của m để hàm số \(y=\frac{1}{5}m^2x^5-\frac{1}{3}mx^3+10x^2-\left(m^2-m-20\right)x+1\) đồng biến trên R bằng
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(f'\left(x\right)=m^2x^4-mx^2+20x-\left(m^2-m-20\right)\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên \(ℝ\)thì \(f'\left(x\right)\ge0,\)với mọi \(x\inℝ\).
Mà ta thấy \(f'\left(-1\right)=m^2-m-20-\left(m^2-m-20\right)=0\)
do đó \(x=-1\)là một điểm cực trị của hàm số \(f'\left(x\right)\).
Ta có: \(f''\left(x\right)=4m^2x^3-2mx+20\)
\(f''\left(-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow-4m^2+2m+20=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m=\frac{5}{2}\\m=-2\end{cases}}\).
Thử lại.
Với \(m=\frac{5}{2}\): \(f''\left(x\right)=25x^3-5x+20\)
\(f''\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
\(f'\left(-1\right)=0\)
do đó \(f'\left(x\right)\ge0\)thỏa mãn.
Với \(m=-2\): \(f''\left(x\right)=16x^3+4x+20\)
\(f''\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\).
\(f'\left(-1\right)=0\)
do đó \(f'\left(x\right)\ge0\)thỏa mãn.
Vậy tổng các giá trị của \(m\)là: \(\frac{5}{2}+\left(-2\right)=\frac{1}{2}\).
Chọn D.

Theo mình:
để hàm số đồng biến, đk cần là y'=0.
a>0 và \(\Delta'< 0\)
nghịch biến thì a<0
vì denta<0 thì hầm số cùng dấu với a
mình giải được câu a với b
câu c có hai cực trị thì a\(\ne\)0, y'=0, denta>0 (để hàm số có hai nghiệm pb)
câu d dùng viet
câu e mình chưa chắc lắm ^^

Ta có : \(y'=-x^2+2mx+m-2\Rightarrow\Delta'=m^2+m-2\)
Hàm số đồng biến trên đoạn có độ dài bằng 4 <=> phương trình y' =0 có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1;x_2\) và thỏa mãn :
\(\left|x_1-x_2\right|=4\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}\Delta'>0\\\left|x_1-x_2\right|=4\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}m^2+m-2>0\\\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1.x_2=16\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}m^2+m-2>0\\4m^2+4\left(m-2\right)=16\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=2\) hoặc \(m=-3\)
Kết luận \(m=2\) hoặc \(m=-3\) thì hàm số đồng biến trên đoạn có độ dài bằng 4

\(y'=m^2x^4-mx^2+20x-m^2+m+20\)
\(y'=\left(x+1\right)\left(m^2x^3-m^2x^2+\left(m^2-m\right)x-m^2+m+20\right)\)
Để \(y'\ge0\) \(\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=m^2x^3-m^2x^2+\left(m^2-m\right)x-m^2+m+20=0\) có nghiệm bội lẻ \(x=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-1\right)=0\Rightarrow-m^2-m^2-m^2+m-m^2+m+20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m^2+2m+20=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-2\\m=\frac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thử lại:
Thay \(m=-2\) vào \(f\left(x\right)=4x^3-4x^2+6x+14=\left(x+1\right)\left(4x^2-8x+14\right)\)
Do \(4x^2-8x+14>0\) \(\forall x\Rightarrow y'=\left(x+1\right)^2\left(4x^4-8x+14\right)\ge0\) (t/m)
Thay \(m=\frac{5}{2}\)
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{25}{4}x^3-\frac{25}{4}x^2+\frac{15}{4}x+\frac{65}{4}=\frac{5}{4}\left(x+1\right)\left(5x^2-10x+13\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\frac{5}{4}\left(x+1\right)^2\left(5x^2-10x+13\right)\ge0\) (t/m)
Vậy \(m=\left\{-2;\frac{5}{2}\right\}\)

a: \(y=-x^3-3x^2+\left(5-m\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-3\cdot2x+5-m\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-6x+5-m\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(-6\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-3\right)\left(5-m\right)< =0\\-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(36+12\left(5-m\right)< =0\)
=>\(36+60-12m< =0\)
=>\(-12m+96< =0\)
=>-12m<=-96
=>m>=8
b: \(y=x^3+\left(2m-2\right)\cdot x^2+mx\)
=>\(y'=3x^2+2\left(2m-2\right)\cdot x+m\)
=>\(y'=3x^2+\left(4m-4\right)x+m\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên R thì y'>=0 với mọi x
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3>0\\\left(4m-4\right)^2-4\cdot3\cdot m< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(16m^2-32m+16-12m< =0\)
=>\(16m^2-44m+16< =0\)
=>\(4m^2-11m+4< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{11-\sqrt{57}}{8}< =m< =\dfrac{11+\sqrt{57}}{8}\)

B1a) m khác 5, khác -2
b) m khác 3, m < 3
B2a) vì căn 5 -2 luôn lớn hơn 0 nên hsố trên đồng biến
b) h số trên là nghịch biến vì 2x > căn 3x
c) bạn hãy đưa h số về dạng y=ax+b là y= 1/6x+1/3 mà 1/6 >0 => h số đồng biến

Để hàm số là hàm số bậc nhất thì hệ số \(a\ne0\)
a) Cm : \(\sqrt{3-m}\ne0\Rightarrow m\ne3\)
b) \(\frac{m-5}{m+2}\ne0\Rightarrow m\ne5\)
Bài 2 :
Để hàm số đồng biến thì hệ số \(a>0\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến thì hệ số \(a< 0\)
Gợi ý z tư làm nha

a: \(y=-x^3-\left(m+1\right)x^2+3\left(m+1\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-\left(m+1\right)\cdot2x+3\left(m+1\right)\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2+x\cdot\left(-2m-2\right)+\left(3m+3\right)\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(-2m-2\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-3\right)\left(3m+3\right)< =0\\-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+8m+4+12\left(3m+3\right)< =0\)
=>\(4m^2+8m+4+36m+36< =0\)
=>\(4m^2+44m+40< =0\)
=>\(m^2+11m+10< =0\)
=>\(\left(m+1\right)\left(m+10\right)< =0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1>=0\\m+10< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=-1\\m< =-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1< =0\\m+10>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< =-1\\m>=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-10<=m<=-1
b: \(y=-\dfrac{1}{3}x^3+mx^2-\left(2m+3\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2+m\cdot2x-\left(2m+3\right)\)
=>\(y'=-x^2+2m\cdot x-\left(2m+3\right)\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1< 0\\\left(2m\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-1\right)\cdot\left(-2m-3\right)< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+4\left(-2m-3\right)< =0\)
=>\(m^2-2m-3< =0\)
=>(m-3)(m+1)<=0
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3>=0\\m+1< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=3\\m< =-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3< =0\\m+1>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< =3\\m>=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-1<=m<=3

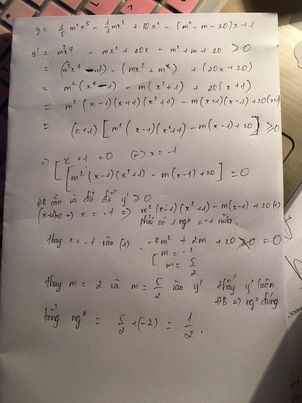

\(y'=m^2x^4-mx^2+20x-m^2+m+20\ge0\) ; \(\forall x\in R\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2\left(x^4-1\right)-m\left(x^2-1\right)+20\left(x+1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-m\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+20\left(x+1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left[m^2\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)-m\left(x-1\right)+20\right]\ge0\) ;\(\forall x\in R\)
Do pt trên luôn có nghiệm \(x=-1\) nên nó phải là nghiệm bội chẵn
\(\Rightarrow m^2\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)-m\left(x-1\right)+20=0\) có nghiệm bội lẻ \(x=-1\) (1)
Thay \(x=-1\) vào pt trên ta được:
\(-4m^2+2m+20=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-2\\m=\frac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay ngược 2 giá trị m vào (1) để kiểm tra xem có thể phân tích \(y'=\left(x+1\right)^2\left(ax^2+bx+c\right)\) thỏa mãn \(ax^2+bx+c\ge0\) với mọi x hay ko