
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


24.
\(cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\le1\Rightarrow y\le3.1+1=4\)
\(y_{max}=4\)
26.
\(y=\sqrt{2}cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
Do \(cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\le1\Rightarrow y\le\sqrt{2}\)
\(y_{max}=\sqrt{2}\)
b.
\(\dfrac{1}{2}sinx+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cosx=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

a.
Tìm min:
$y=(4\sin ^2x-4\sin x+1)+2=(2\sin x-1)^2+2$
Vì $(2\sin x-1)^2\geq 0$ với mọi $x$ nên $y=(2\sin x-1)^2+2\geq 0+2=2$
Vậy $y_{\min}=2$
----------------
Mặt khác:
$y=4\sin x(\sin x+1)-8(\sin x+1)+11$
$=(\sin x+1)(4\sin x-8)+11$
$=4(\sin x+1)(\sin x-2)+11$
Vì $\sin x\in [-1;1]\Rightarrow \sin x+1\geq 0; \sin x-2<0$
$\Rightarrow 4(\sin x+1)(\sin x-2)\leq 0$
$\Rightarrow y=4(\sin x+1)(\sin x-2)+11\leq 11$
Vậy $y_{\max}=11$
b.
$y=\cos ^2x+2\sin x+2=1-\sin ^2x+2\sin x+2$
$=3-\sin ^2x+2\sin x$
$=4-(\sin ^2x-2\sin x+1)=4-(\sin x-1)^2\leq 4-0=4$
Vậy $y_{\max}=4$.
---------------------------
Mặt khác:
$y=3-\sin ^2x+2\sin x = (1-\sin ^2x)+(2+2\sin x)$
$=(1-\sin x)(1+\sin x)+2(1+\sin x)=(1+\sin x)(1-\sin x+2)$
$=(1+\sin x)(3-\sin x)$
Vì $\sin x\in [-1;1]$ nên $1+\sin x\geq 0; 3-\sin x>0$
$\Rightarrow y=(1+\sin x)(3-\sin x)\geq 0$
Vậy $y_{\min}=0$

a.
\(y=\dfrac{3}{2}sin2x-2\left(cos^2x-sin^2x\right)+5=\dfrac{3}{2}sin2x-2cos2x+5\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(\dfrac{3}{5}sin2x-\dfrac{4}{5}cos2x\right)+5=\dfrac{5}{2}sin\left(2x-a\right)+5\) (với \(cosa=\dfrac{3}{5}\))
\(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{5}{2}+5\le y\le\dfrac{5}{2}+5\)
b.
\(\Leftrightarrow y.sinx-2y.cosx+4y=3sinx-cosx+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(y-3\right)sinx+\left(1-2y\right)cosx=1-4y\)
Theo điều kiện có nghiệm của pt lượng giác bậc nhất:
\(\left(y-3\right)^2+\left(1-2y\right)^2\ge\left(1-4y\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow11y^2+2y-9\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1\le y\le\dfrac{9}{11}\)
c.
Do \(x^2+y^2=1\Rightarrow\) đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=sina\\y=cosa\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2\left(sin^2a+6sina.cosa\right)}{1+2sina.cosa+cos^2a}=\dfrac{1-cos2a+6sin2a}{1+sin2a+\dfrac{1+cos2a}{2}}=\dfrac{2-2cos2a+12sin2a}{3+2sin2a+cos2a}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3y+2y.sin2a+y.cos2a=2-2cos2a+12sin2a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2y-12\right)sin2a+\left(y+2\right)cos2a=2-3y\)
Theo điều kiện có nghiệm của pt bậc nhất theo sin2a, cos2a:
\(\left(2y-12\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2\ge\left(2-3y\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2+8y-36\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow-4-2\sqrt{13}\le y\le-4+2\sqrt{13}\)

a) Dễ thấy cosx = 0 không thỏa mãn phương trình đã cho nên chiaw phương trình cho cos2x ta được phương trình tương đương 2tan2x + tanx - 3 = 0.
Đặt t = tanx thì phương trình này trở thành
2t2 + t - 3 = 0 ⇔ t ∈ {1 ; ![]() }.
}.
Vậy ![]()
b) Thay 2 = 2(sin2x + cos2x), phương trình đã cho trở thành
3sin2x - 4sinxcosx + 5cos2x = 2sin2x + 2cos2x
⇔ sin2x - 4sinxcosx + 3cos2x = 0
⇔ tan2x - 4tanx + 3 = 0
⇔ ![]()
⇔ x = ![]() + kπ ; x = arctan3 + kπ, k ∈ Z.
+ kπ ; x = arctan3 + kπ, k ∈ Z.
c) Thay sin2x = 2sinxcosx ; ![]() =
= ![]() (sin2x + cos2x) vào phương trình đã cho và rút gọn ta được phương trình tương đương
(sin2x + cos2x) vào phương trình đã cho và rút gọn ta được phương trình tương đương
![]() sin2x + 2sinxcosx -
sin2x + 2sinxcosx - ![]() cos2x = 0 ⇔ tan2x + 4tanx - 5 = 0 ⇔
cos2x = 0 ⇔ tan2x + 4tanx - 5 = 0 ⇔ ![]()
⇔ x = ![]() + kπ ; x = arctan(-5) + kπ, k ∈ Z.
+ kπ ; x = arctan(-5) + kπ, k ∈ Z.
d) 2cos2x - 3√3sin2x - 4sin2x = -4
⇔ 2cos2x - 3√3sin2x + 4 - 4sin2x = 0
⇔ 6cos2x - 6√3sinxcosx = 0 ⇔ cosx(cosx - √3sinx) = 0
⇔ 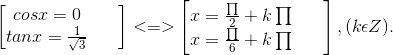

a.
\(-1\le sin\left(1-x^2\right)\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow y_{min}=-1\) khi \(1-x^2=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\) \(\Rightarrow x^2=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+1+k2\pi\) (\(k\ge0\))
\(y_{max}=1\) khi \(1-x^2=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\Rightarrow x^2=1-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\) (\(k\ge1\))
b.
Đặt \(\sqrt{2-x^2}=t\Rightarrow t\in\left[0;\sqrt{2}\right]\subset\left[0;\pi\right]\)
\(y=cost\) nghịch biến trên \(\left[0;\pi\right]\Rightarrow\) nghịch biến trên \(\left[0;\sqrt{2}\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow y_{max}=y\left(0\right)=cos0=1\) khi \(x^2=2\Rightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{2}\)
\(y_{min}=y\left(\sqrt{2}\right)=cos\sqrt{2}\) khi \(x=0\)

