
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(1,ĐK:x\ge2\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3x-6}+x-2-\left(\sqrt{2x-3}-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\sqrt{3x-6}}+\left(x-2\right)-\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3x-6}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3x-6}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}+1=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(x>2\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}>-\dfrac{2}{1+1}=-1\left(3x-6\ne0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1\right)>0-1+1=0\left(vn\right)\)
Vậy \(x=2\)
\(2,ĐK:x\ge-1\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x+1}=a\\\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=b\end{matrix}\right.\left(a,b\ge0\right)\Leftrightarrow a^2+b^2=x^2+2\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow2a^2+2b^2-5ab=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(a-2b\right)\left(2a-b\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=2b\\b=2a\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(a=2b\Leftrightarrow x+1=4x^2-4x+4\left(vn\right)\)
Với \(b=2a\Leftrightarrow4x+4=x^2-x+1\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-3=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{2}\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...

a: Xét tứ giác MAOB có
\(\widehat{MAO}+\widehat{MBO}=180^0\)
Do đó: MAOB là tứ giác nội tiếp

Bài 2:
a) Để hàm số đồng biến thì m+1>0
hay m>-1
b) Để hàm số đi qua điểm A(2;4) thì
Thay x=2 và y=4 vào hàm số, ta được:
\(\left(m+1\right)\cdot2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m+1=2\)
hay m=1
c) Để hàm số đi qua điểm B(2;-4) thì
Thay x=2 và y=-4 vào hàm số, ta được:
\(2\left(m+1\right)=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m+1=-2\)
hay m=-3
Bài 1:
b) Ta có: \(5\cdot\sqrt{25a^2}-25a\)
\(=5\cdot5\cdot\left|a\right|-25a\)
\(=-25a-25a=-50a\)

2\(\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}\) - 3\(\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{27}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{3\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{16}{2\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{2\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{11}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{11\sqrt{3}}{6}\)
f, 2\(\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\)- \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{5\sqrt{2}}{4}\)
(1 + \(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}\)).(1- \(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}+1}\))
= \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1+3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}\).\(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1-3+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}-1}\).\(\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{3}+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{-4}{3-1}\)
= \(\dfrac{-4}{2}\)
= -2

Bài 1:
Vì (d)//y=-2x+1 nên a=-2
Vậy: y=-2x+b
Thay x=1 và y=2 vào (d),ta được:
b-2=2
hay b=4


a) (d) cắt trục hoành tại điểm có hoành độ bằng 2
\(\Rightarrow\) tọa độ điểm đó là \(\left(2;0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow0=2a-3\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{3}{2}\Rightarrow\left(d\right):y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-3\)
b) Vì (d) song song với đồ thị của hàm \(y=2x+1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\-3\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow a=2\Rightarrow\left(d\right):y=2x-3\)
c) Gọi A là giao điểm của (d) và (d')
\(\Rightarrow x_A=1\Rightarrow y_A=2+3=5\Rightarrow A\left(1;5\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow5=a-3\Rightarrow a=8\Rightarrow\left(d\right):y=8x-3\)




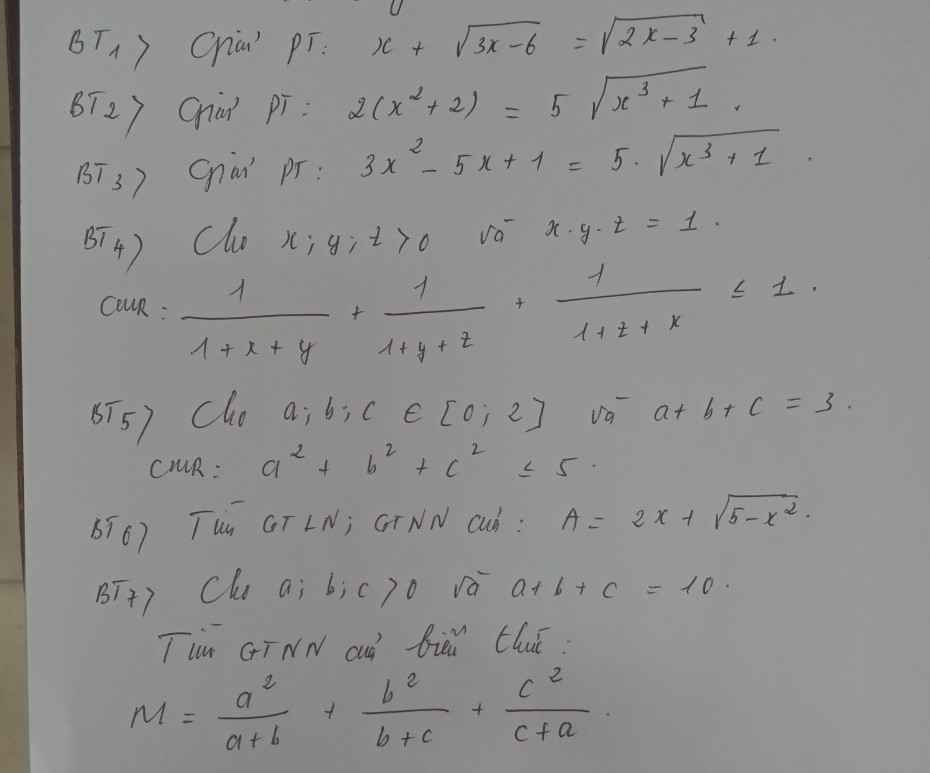


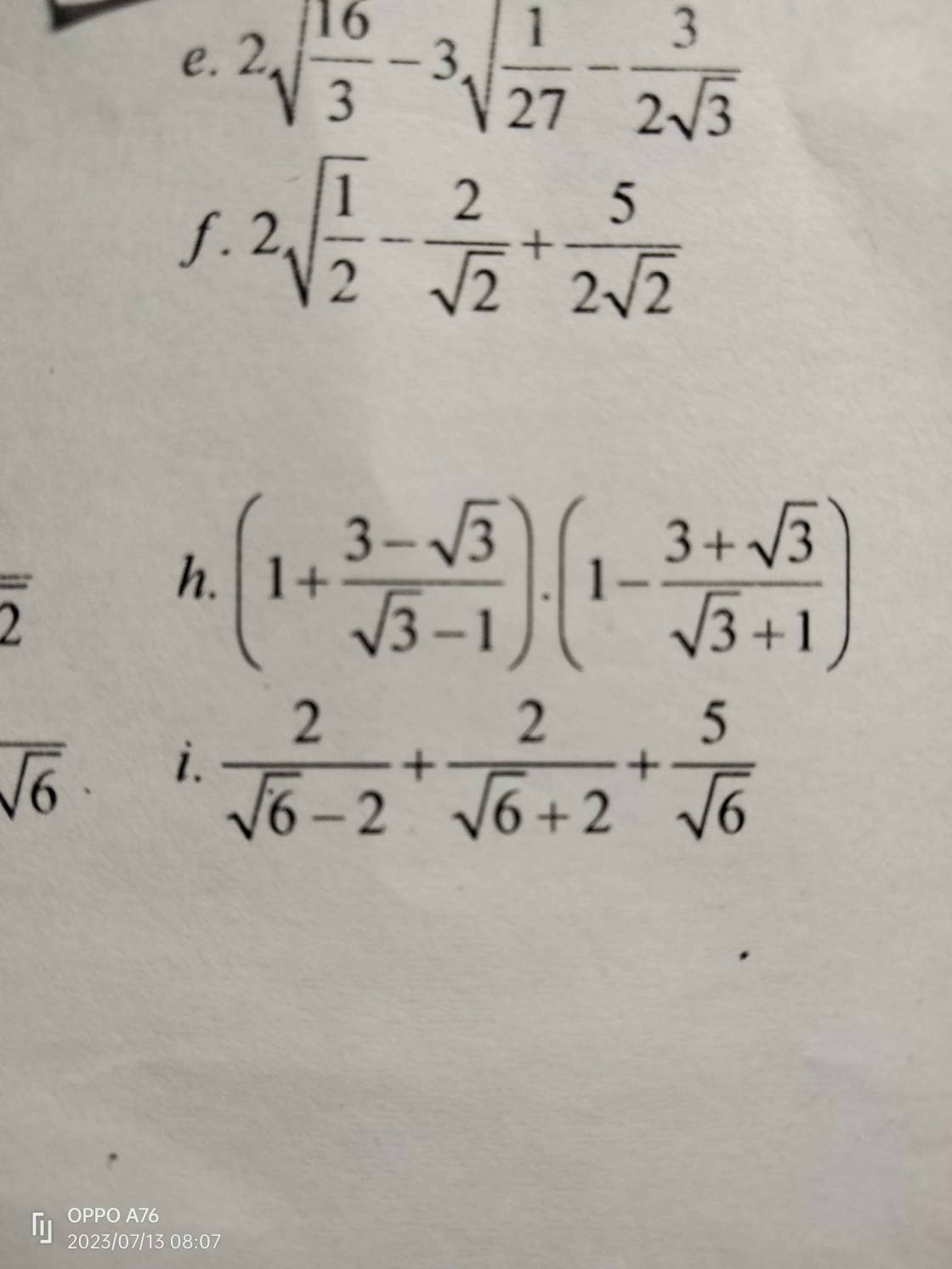





a, Xét tam giác ABC vuông tại A, đường cao AH
Áp dụng định lí Pytago cho tam giác ABC vuông tại A
\(BC^2=AB^2+AC^2=\dfrac{81}{4}+36=\dfrac{225}{4}\Rightarrow BC=\dfrac{15}{2}\)cm
* Áp dụng hệ thức : \(AB^2=BH.BC\Rightarrow BH=\dfrac{AB^2}{BC}=\dfrac{\dfrac{81}{4}}{\dfrac{15}{2}}=\dfrac{27}{10}\)cm
=> \(CH=BC-BH=\dfrac{15}{2}-\dfrac{27}{10}=\dfrac{24}{5}\)cm
* Áp dụng hệ thức : \(AH.BC=AB.AC\Rightarrow AH=\dfrac{AB.AC}{BC}\)
\(=\dfrac{4,5.6}{\dfrac{15}{2}}=\dfrac{18}{5}\)cm
tam giác ABC vuông tại A nên áp dụng Py-ta-go
\(\Rightarrow BC^2=AB^2+AC^2=\left(4,5\right)^2+6^2=\dfrac{225}{4}\Rightarrow BC=\dfrac{15}{2}=7,5\left(cm\right)\)
tam giác ABC vuông tại A có đường cao AH nên áp dụng hệ thức lượng
\(\Rightarrow AB^2=BH.BC\Rightarrow BH=\dfrac{AB^2}{BC}=\dfrac{\left(4,5\right)^2}{7,5}=\dfrac{27}{10}=2,7\left(cm\right)\)
tam giác ABC vuông tại A có đường cao AH nên áp dụng hệ thức lượng
\(\Rightarrow AC^2=CH.BC\Rightarrow CH=\dfrac{AC^2}{BC}=\dfrac{6^2}{7,5}=\dfrac{24}{5}=4,8\left(cm\right)\)