Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


f: \(3ab-6a+b-2\)
\(=3a\left(b-2\right)+\left(b-2\right)\)
\(=\left(b-2\right)\left(3a+1\right)\)

a: AN+CN=AC
=>AN=20-15=5cm
Xét ΔABC có AM/AB=AN/AC
nên MN//BC
b: Xét ΔAMN và ΔNPC có
góc AMN=góc NPC(=góc B)
góc ANM=góc NCP)
=>ΔAMN đồng dạng với ΔNPC

a: Xét tứ giác HMKN có
I là trung điểm của HK
I là trung điểm của MN
Do đó: HMKN là hình bình hành

Mọi người giải giúp mình bài này với ạ, cảm ơn mn nhiều, chỉ cần câu c ý chứng minh góc 90 độ thôi ạ

a: Xét tứ giác ABQN có
\(\widehat{BQN}=\widehat{QNA}=\widehat{NAB}=90^0\)
=>ABQN là hình chữ nhật
b: Xét ΔCAD có
DN,CH là các đường cao
DN cắt CH tại M
Do đó: M là trực tâm của ΔCAD
=>AM\(\perp\)CD
c: Xét ΔHAB vuông tại H và ΔHCA vuông tại H có
\(\widehat{HAB}=\widehat{HCA}\left(=90^0-\widehat{ABC}\right)\)
Do đó: ΔHAB đồng dạng với ΔHCA
=>\(\dfrac{HA}{HC}=\dfrac{HB}{HA}\)
=>\(HA^2=HB\cdot HC\)
=>\(HA=\sqrt{HB\cdot HC}\)

câu a, \(\dfrac{x}{x+1}\); \(\dfrac{x^2}{1-x}\); \(\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\) (đk \(x\)≠ -1; 1)
\(x^2\) - 1 = ( \(x\) - 1).(\(x\) + 1)
\(\dfrac{x}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{x.\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right).\left(x-1\right)}\);
\(\dfrac{x^2}{1-x}\) = \(\dfrac{-x^2}{x-1}\)= \(\dfrac{-x^2.\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
b, \(\dfrac{10}{x+2}\); \(\dfrac{5}{2x-4}\); \(\dfrac{1}{6-3x}\) (đk \(x\) ≠ -2; 2)
2\(x-4\) = 2.(\(x\) - 2); 6 - 3\(x\) = - 3.(\(x\) - 2)
\(\dfrac{10}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{10.2.3\left(x-2\right)}{2.3\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{60\left(x-2\right)}{6\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{2x-4}\) = \(\dfrac{5.3\left(x+2\right)}{2.3\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{15.\left(x+2\right)}{6.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{6-3x}\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{3.\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-1.\left(x+2\right)}{3.2.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-2.\left(x+2\right)}{6.\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\)
c, \(\dfrac{x}{2x-4}\); \(\dfrac{1}{2x+4}\) và \(\dfrac{3}{4-x^2}\) đk \(x\) ≠ 2; -2
\(\dfrac{x}{2x-4}\) = \(\dfrac{x}{2.\left(x-2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{x.\left(x+2\right)}{2.\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{2x+4}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2.\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{2.\left(x+2\right).\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\dfrac{3}{4-x^2}\) = \(\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{-6}{2.\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)


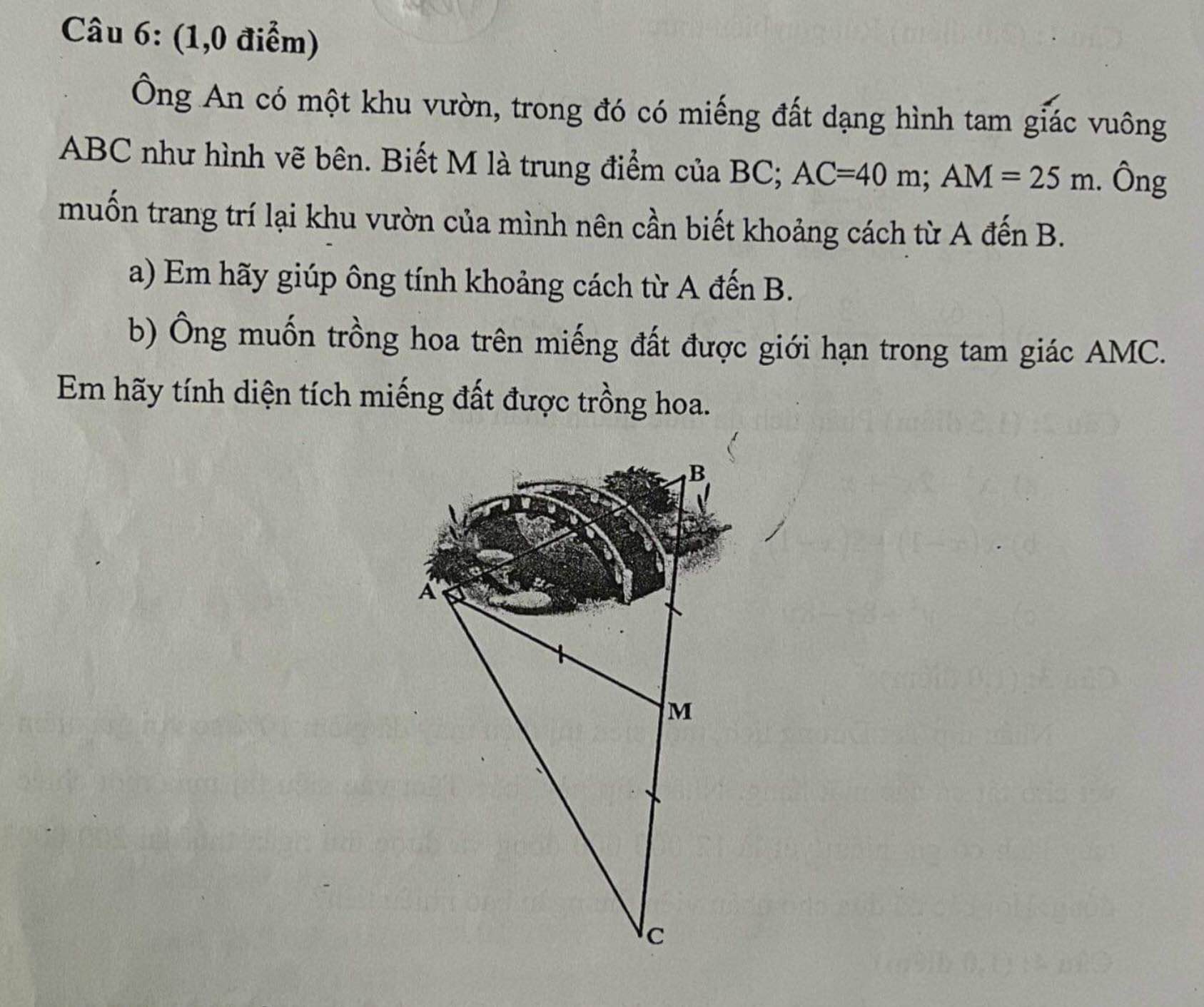
Tam giác ABC vuông tại A có AM là trung tuyến ứng với cạnh huyền
\(\Rightarrow AM=\dfrac{1}{2}BC\Rightarrow BC=2AM=50\left(m\right)\)
a. Áp dụng định lý Pitago:
\(AB=\sqrt{BC^2-AC^2}=30\left(m\right)\)
b. Kẻ \(MH\perp AC\Rightarrow MH||AB\) (cùng vuông góc AC)
Mà M là trung điểm BC \(\Rightarrow MH\) là đường trung bình tam giác ABC
\(\Rightarrow MH=\dfrac{1}{2}AB=15\left(m\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow S_{AMC}=\dfrac{1}{2}MH.AC=\dfrac{1}{2}.15.40=300\left(m^2\right)\)


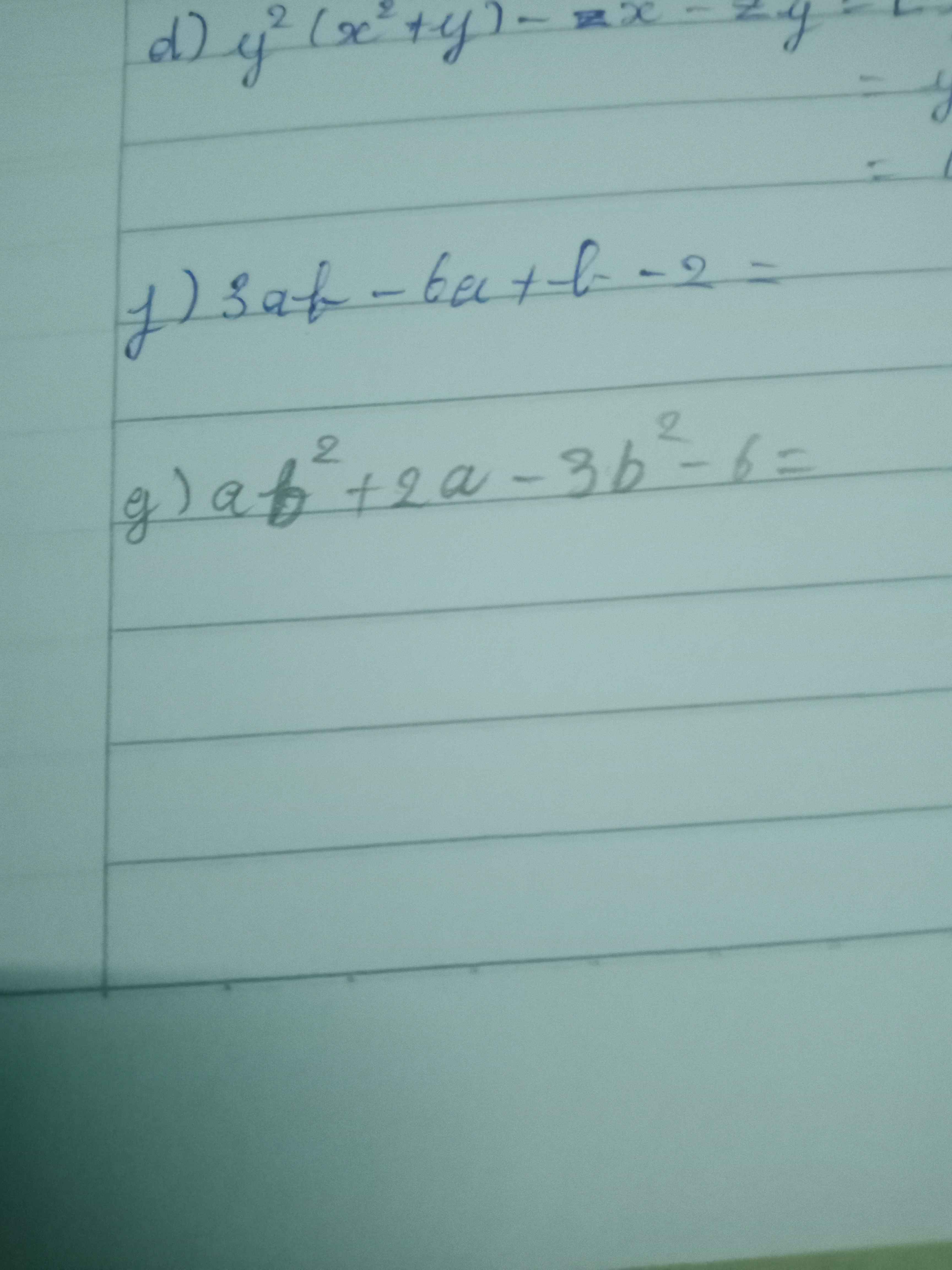

 Mn giải giúp mik vs ạ 🥺 mình đang cần gấp. Cảm ơn mn nhiều
Mn giải giúp mik vs ạ 🥺 mình đang cần gấp. Cảm ơn mn nhiều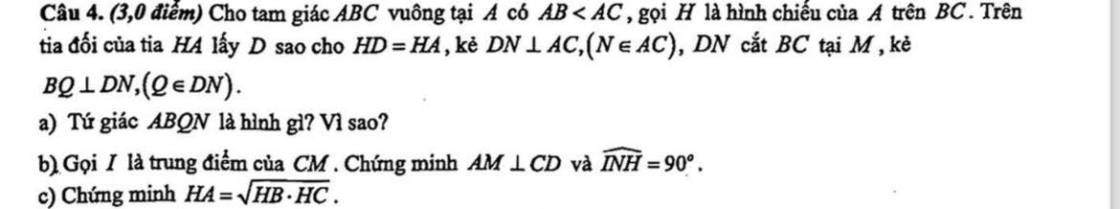
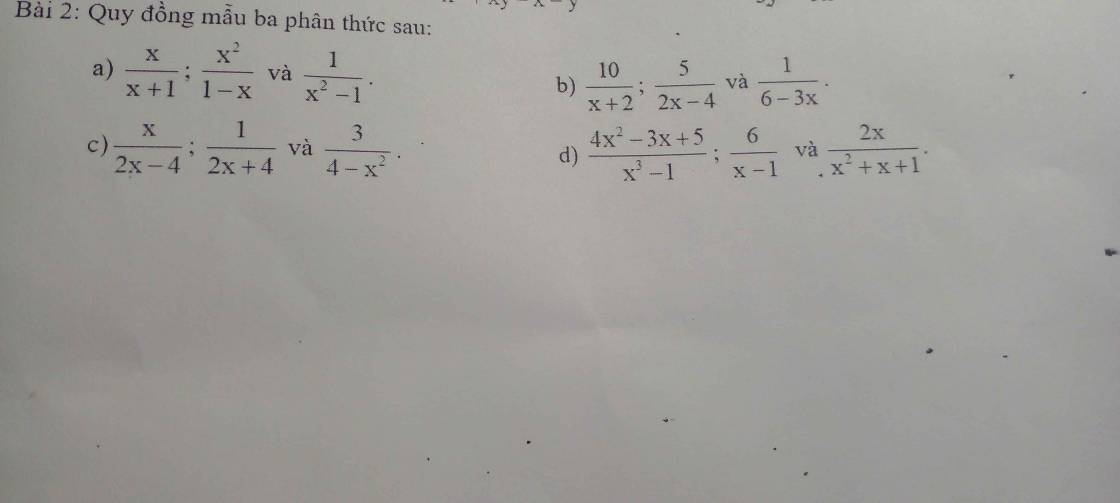
 ai giải giùm em câu 6 vs ạ cho em lời giải chi tiết và vẽ hình giúp em vs ạ cảm ơn mn
ai giải giùm em câu 6 vs ạ cho em lời giải chi tiết và vẽ hình giúp em vs ạ cảm ơn mn