
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(c,\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{y+1}=3\\\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{y+1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{4}{x-2}+\dfrac{2}{y+1}=6\\\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{y+1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{y+1}+\dfrac{3}{y+1}=5\\\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{y+1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5}{y+1}=5\\\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{y+1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y+1=1\\\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{y+1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\left(2\right)\\\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{y+1}=1\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay \(\left(2\right)\) vào \(\left(1\right)\) :
\(\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{0+1}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{4}{x-2}-3=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{4}{x-2}=4\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(3;0\right)\)
c: =>4/x-2+2/y+1=6 và 4/x-2-3/y+1=1
=>5/y+1=5 và 2/x-2+1/y+1=3
=>y+1=1 và 2/x-2+1=3
=>y=0 và x-2=1
=>x=3 và y=0

Câu 3:
2: Xét tứ giác OKEH có
\(\widehat{OKE}=\widehat{OHE}=\widehat{KOH}=90^0\)
Do đó: OKEH là hình chữ nhật
mà đường chéo OE là tia phân giác của \(\widehat{KOH}\)
nên OKEH là hình vuông

\(1,ĐK:x\ge2\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3x-6}+x-2-\left(\sqrt{2x-3}-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\sqrt{3x-6}}+\left(x-2\right)-\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3x-6}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3x-6}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}+1=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(x>2\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}>-\dfrac{2}{1+1}=-1\left(3x-6\ne0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1\right)>0-1+1=0\left(vn\right)\)
Vậy \(x=2\)
\(2,ĐK:x\ge-1\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x+1}=a\\\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=b\end{matrix}\right.\left(a,b\ge0\right)\Leftrightarrow a^2+b^2=x^2+2\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow2a^2+2b^2-5ab=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(a-2b\right)\left(2a-b\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=2b\\b=2a\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(a=2b\Leftrightarrow x+1=4x^2-4x+4\left(vn\right)\)
Với \(b=2a\Leftrightarrow4x+4=x^2-x+1\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-3=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{2}\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...


Bài 2:
a: Thay x=-2 và y=-1 vào (d), ta được:
-2(m+1)+m+2=-1
=>-2m-2+m+2=-1
=>-m=-1
=>m=1
b: (d): y=2x+3
Tọa độ A là:
y=0 và 2x+3=0
=>x=-3/2 và y=0
=>OA=1,5
Tọa độ B là:
x=0 và y=2*0+3=3
=>OB=3
\(AB=\sqrt{1.5^2+3^2}=1.5\sqrt{5}\)
=>\(C=1.5+3+1.5\sqrt{5}=1.5\sqrt{5}+4.5\)
\(S=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB=2.25\)

a: Khi m=1 thì hệ sẽ là x+y=1 và x-y=2
=>x=1,5; y=0,5
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1-y\\m\left(1-y\right)-y=2m\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1-y\\m-my-y=2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=1-y và y(-m-1)=m
=>x=1-y và y=-m/m+1
=>x=1+m/m+1=2m+1/m+1 và y=-m/m+1
Để x,y nguyên thì 2m+1 chia hết cho m+1 và -m chia hết cho m+1
=>\(m+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(m\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)

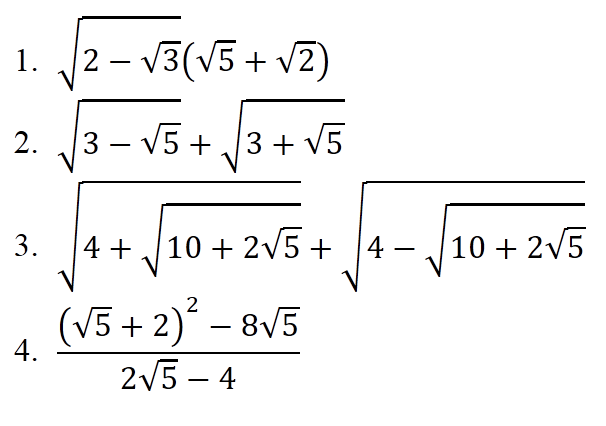












1) \(\sqrt{2-\sqrt{3}}\left(\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\right)=\sqrt{\dfrac{4-2\sqrt{3}}{2}}\left(\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\right)\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)^2}{2}}\left(\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{15}+\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
theo mình nghĩ thì đề nên là \(\sqrt{2-\sqrt{3}}\left(\sqrt{6}+\sqrt{2}\right)\)
như thế thì sẽ \(=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1}{\sqrt{2}}.\sqrt{2}\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)=\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)=2\) đẹp hơn,đó là mình nghĩ vậy thôi,còn nếu đề bạn đúng thì mình làm ở trên đó
2) \(\sqrt{3-\sqrt{5}}+\sqrt{3+\sqrt{5}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{6-2\sqrt{5}}{2}}+\sqrt{\dfrac{6+2\sqrt{5}}{2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)^2}{2}}+\sqrt{\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)^2}{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}-1}{\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{10}\)
3) Đặt \(A=\sqrt{4+\sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}}}+\sqrt{4-\sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}}}\)
\(\Rightarrow A^2=8+2\sqrt{\left(4+\sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}}\right)\left(4-\sqrt{10+2\sqrt{5}}\right)}\)
\(=8+2\sqrt{16-\left(10+2\sqrt{5}\right)}=8+2\sqrt{6-2\sqrt{5}}\)
\(=8+2\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)^2}=8+2\sqrt{5}-2=6+2\sqrt{5}=\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\sqrt{5}+1\left(A\ge0\right)\)
4) \(\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{5}+2\right)^2-8\sqrt{5}}{2\sqrt{5}-4}=\dfrac{9+4\sqrt{5}-8\sqrt{5}}{2\left(\sqrt{5}-2\right)}=\dfrac{9-4\sqrt{5}}{2\left(\sqrt{5}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{5}-2\right)^2}{2\left(\sqrt{5}-2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Cảm ơn ban ạ