
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




Bài 2:
\(A=\dfrac{2}{-x^2-2x-2}=\dfrac{-2\left(-x^2-2x-2\right)-2x^2-4x-2}{-x^2-2x-2}\) \(=-2+\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)^2}{-x^2-2x-2}\ge-2\)
Dấu bằng xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy \(A_{Min}=-2\) khi \(x=-1\)
Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2x^2-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=3\)
hay \(x\in\left\{\sqrt{3};-\sqrt{3}\right\}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\sqrt{3};-\sqrt{3}\right\}\)

\(PT< =>x^4+5x^3-6x^2-6x+5x^2-6x-6=0\)
\(< =>x^4+5x^3-x^2-12x-6=0\)
\(< =>\left(x^2-x-1\right)\left(x^2+6x+6\right)=0\)
<=>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\\x=\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{cases}}\)hay \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3+\sqrt{3}\\x=-3-\sqrt{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2};\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2};-3+\sqrt{3};-3-\sqrt{3}\right\}\)

b) 5x(x-2000)-x+2000=0
\(\Rightarrow5x\left(x-2000\right)-\left(x-2000\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-2000\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2000=0\\5x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0+2000\\5x=0+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2000\\5x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2000\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)


2x3 + 5x2 – 3x = 0
⇔ x(2x2 + 5x – 3) = 0
⇔ x.(2x2 + 6x – x – 3) = 0
⇔ x. [2x(x + 3) – (x + 3)] = 0
⇔ x.(2x – 1)(x + 3) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc 2x – 1 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
+ 2x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 2x = 1 ⇔ x = 1/2.
+ x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 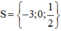

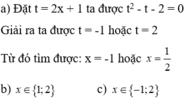
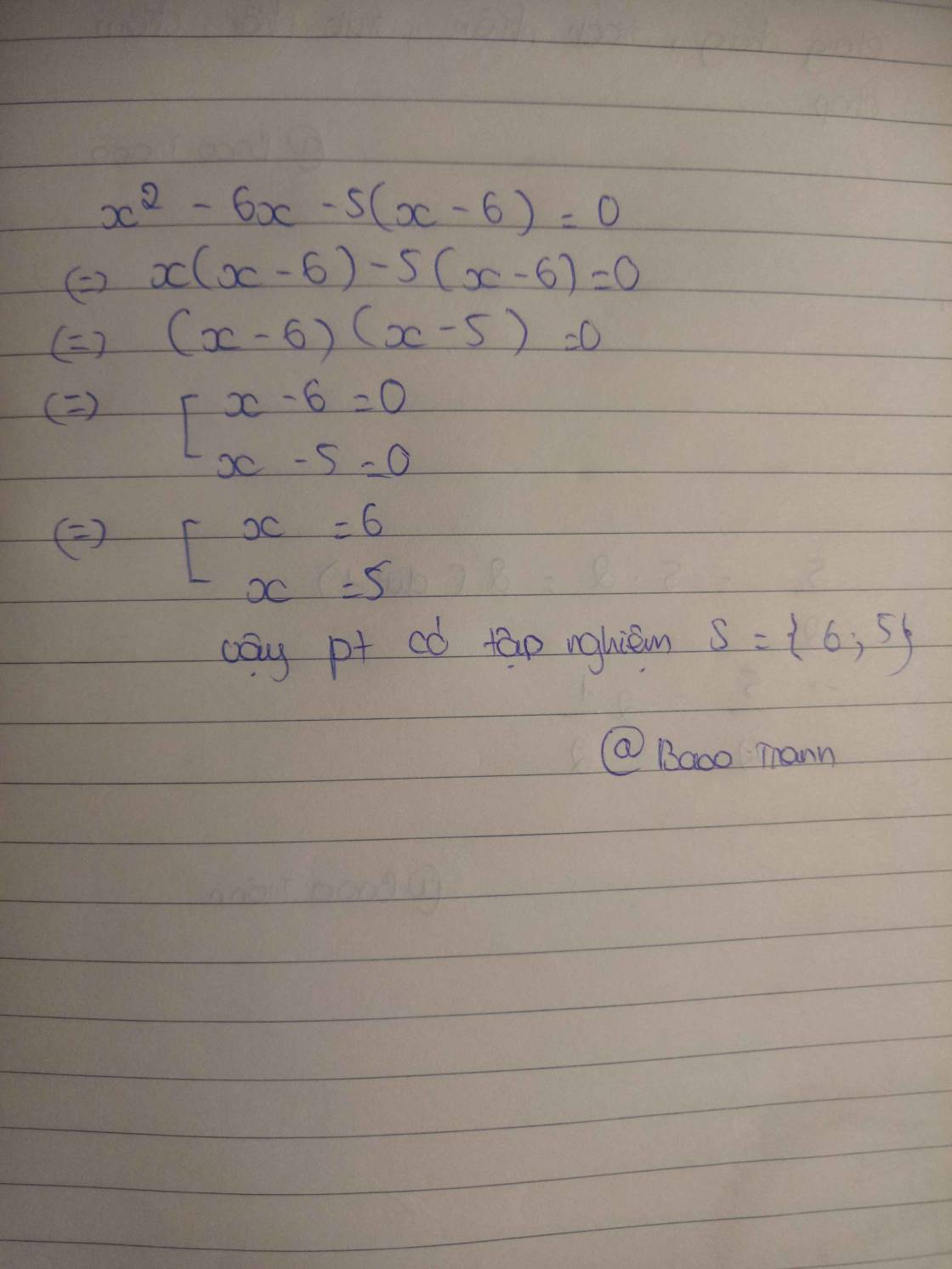
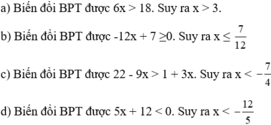

\(x^4+\left(x+1\right)\left(5x^2-6x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+5x^3-x^2-12x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^3+6x^3-x^2-6x^2+6x^2\)
\(-6x-6x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4-x^3-x^2\right)+\left(6x^3-6x^2-6x\right)+\)
\(\left(6x^2-6x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-x-1\right)+6x\left(x^2-x-1\right)+\)
\(6\left(x^2-x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+6x+6\right)\left(x^2-x-1\right)=0\)
\(TH1:x^2+6x+6=0\)
Ta có: \(\Delta=6^2-4.6=12\sqrt{\Delta}=\sqrt{12}\)
pt có 2 nghiệm:
\(x_1=\frac{-6+\sqrt{12}}{2}=-3+\sqrt{3}\)
\(x_2=\frac{-6-\sqrt{12}}{2}=-3-\sqrt{3}\)
\(TH2:x^2-x-1=0\)
Ta có: \(\Delta=1^2+4.1=5,\sqrt{\Delta}=\sqrt{5}\)
pt có 2 nghiệm:
\(x_1=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\)và \(x_2=\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
Vậy pt có 4 nghiệm \(x_1=\frac{-6+\sqrt{12}}{2}=-3+\sqrt{3}\);\(x_2=\frac{-6-\sqrt{12}}{2}=-3-\sqrt{3}\);
\(x_3=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\);\(x_4=\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
Làm tốt rồi nhưng mà lớp 8 chưa học cách giải pt bậc 2 \(\Delta\). Thì chúng ta có thể:
VD TH1: \(x^2+6x+6=0\)
<=> \(x^2+6x+9-9+6=0\)
<=> \(\left(x+3\right)^2=3\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+3=\sqrt{3}\\x+3=-\sqrt{3}\end{cases}}\)<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3+\sqrt{3}\\x=-3-\sqrt{3}\end{cases}}\)
tương tự Th2.