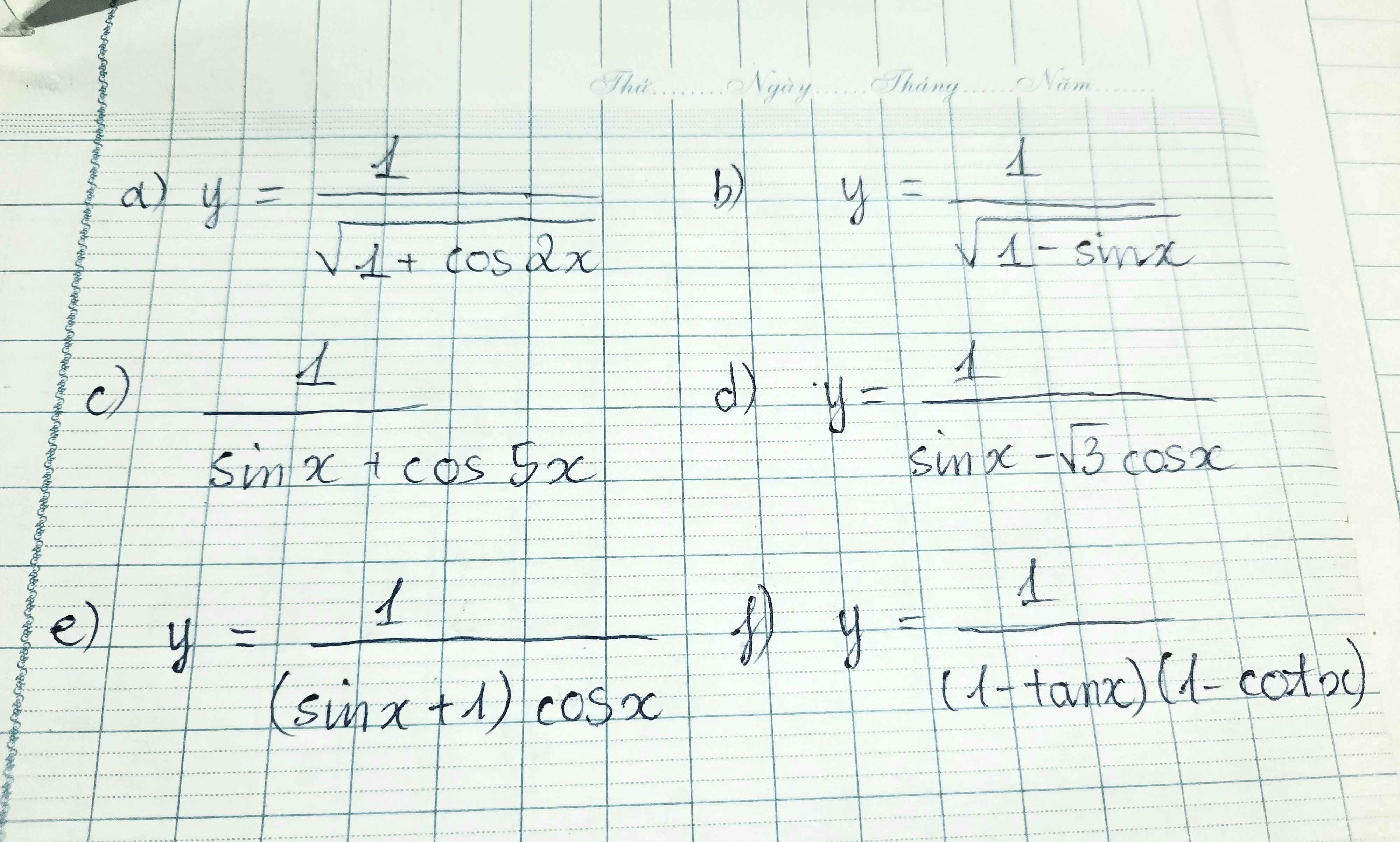Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(y'=2\cdot\left(sinx\right)'\cdot sinx+3\cdot\left(-2x\right)\cdot sin2x\)
\(=2cosx\cdot sinx-6x\cdot sin2x=sin2x\cdot\left(1-6x\right)\)

a) Hàm số xđ <=> \(1+cos2x>0\) \(\Leftrightarrow cos2x\ne-1\) \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(2cos^2x-1\ne-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx\ne0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\left(k\in Z\right)\)
b)Hàm số xđ <=> \(1-sinx>0\) \(\Leftrightarrow sinx\ne1\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\left(k\in Z\right)\)
c) Hàm số xđ <=> \(sinx+cos5x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx\ne-cos5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-x\right)\ne cos\left(\pi-5x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{\pi}{2}-x\ne\pi-5x+k2\pi\\\dfrac{\pi}{2}-x\ne-\pi+5x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) (\(k\in Z\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{8}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}-\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))
d) Hàm số xđ <=> \(sinx-\sqrt{3}cosx\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2.sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\ne0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\left(k\in Z\right)\)
e) Hàm số xđ <=> \(\left(sinx+1\right).cosx\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sinx\ne-1\\cosx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) (\(k\in Z\)) \(\Rightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\) (Hai họ nghiệm trùng nhau nên e tổng hợp lại, e nghĩ thế)
f) Hàm số xđ <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(1-tanx\right)\left(1-cotx\right)\ne0\\sinx\ne0\\cosx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}tanx\ne1\\cotx\ne1\\sinx.cosx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sinx\ne cosx\\\dfrac{1}{2}.sin2x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sinx\ne sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-x\right)\\2x\ne k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}-x+k2\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+x+k2\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\0\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\)) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))
Tìm đạo hàm của hàm số \(y=\dfrac{a^3}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}}\) (a là hằng số)
Giúp mình với ạ, mình cảm ơnn

\(y'=\dfrac{\left(a^3\right)'.\sqrt{a^2-x^2}-\left(\sqrt{a^2-x^2}\right)'.a^3}{a^2-x^2}=\dfrac{-\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{a^2-x^2}}\left(a^2-x^2\right)'.a^3}{a^2-x^2}\)
\(y'=\dfrac{x.a^3}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}\left(a^2-x^2\right)}\)


Đáp án B
+ Xét hàm y = f(x) = cos (x + π)
TXĐ: D = R
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và f(-x) = cos (-x + π) = -cos x = cos (x + π) = f(x)
Do đó y = cos (x + π) là hàm số chẵn .
+ Xét hàm y = g(x) = tan2016x
TXĐ: D = R\{π/2 + kπ, k ∈ Z}
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và g(-x) = tan2016(-x) = (-tan x)2016 = tan2016x = g(x)
Do đó: y = tan2016x là hàm chẵn trên tập xác định của nó.
+Xét hàm y = cot2x
f(-x) = cot(-2x) = - cot 2x = -f(x) nên đây là hàm số lẻ.
+ Xét hàm số y = 1-sinx
f(-x) = 1- sin(-x) = 1+ sin x
Nên hàm số không chẵn không lẻ

\(y=cos^2x-cosx=\left(cosx-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\ge-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(y=cos^2x-cosx-2+2=\left(cosx+1\right)\left(cosx-2\right)+2\le2\)
\(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{1}{4}\le y\le2\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Có 3 giá trị nguyên \(y=\left\{0;1;2\right\}\)

tham khảo:
a)\(y'=xsin2x+sin^2x\)
\(y'=sin^2x+xsin2x\)
b)\(y'=-2sin2x+2cosx\\ y'=2\left(cosx-sin2x\right)\)
c)\(y=sin3x-3sinx\)
\(y'=3cos3x-3cosx\)
d)\(y'=\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}-\dfrac{1}{sin^2x}\)
\(y'=\dfrac{sin^2x-cos^2x}{sin^2x.cos^2x}\)

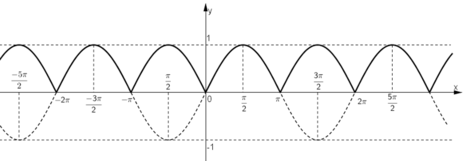
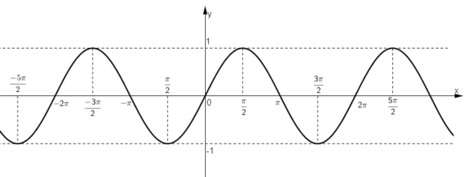
+ Đồ thị hàm số y = sin x.
+ Ta có:
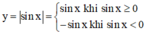
Vậy từ đồ thị hàm số y = sin x ta có thể suy ra đồ thị hàm số y = |sin x| bằng cách:
- Giữ nguyên phần đồ thị nằm phía trên trục hoành (sin x > 0).
- Lấy đối xứng phần đồ thị nằm phía dưới trục hoành qua trục hoành.
Ta được đồ thị hàm số y = |sin x| là phần nét liền hình phía dưới.