Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(VT=4\overrightarrow{MA}-4\overrightarrow{MC}+\overrightarrow{MB}-\overrightarrow{MC}\)
\(=4\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{CB}\)

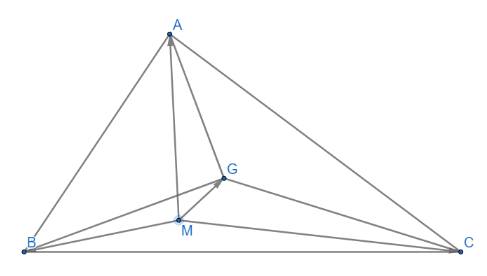
\(\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} = 3\overrightarrow {MG} \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {MG} + \overrightarrow {GA} + \overrightarrow {MG} + \overrightarrow {GB} + \overrightarrow {MG} + \overrightarrow {GC} = 3\overrightarrow {MG} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow \left( {\overrightarrow {MG} + \overrightarrow {MG} + \overrightarrow {MG} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {GA} + \overrightarrow {GB} + \overrightarrow {GC} } \right) = 3\overrightarrow {MG} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow 3\overrightarrow {MG} = 3\overrightarrow {MG} \) (đpcm) ( Vì G là trọng tâm của tam giác ABC nên \(\overrightarrow {GA} + \overrightarrow {GB} + \overrightarrow {GC} = \overrightarrow 0 \))

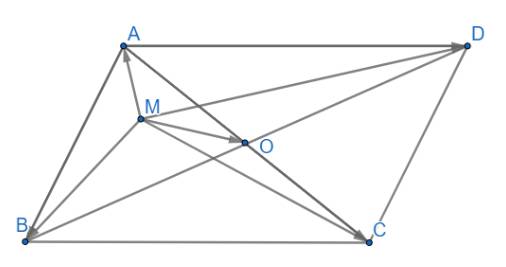
a) \(\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} + \overrightarrow {MD} = 4\overrightarrow {MO} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OB} + \overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OC} + \overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OD} = 4\overrightarrow {MO} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow 4\overrightarrow {MO} + \left( {\overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {OB} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {OC} + \overrightarrow {OD} } \right) = 4\overrightarrow {MO} \)
\( \Leftrightarrow 4\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow 0 + \overrightarrow 0 = 4\overrightarrow {MO} \\ \Leftrightarrow 4\overrightarrow {MO} = 4\overrightarrow {MO} \) (luôn đúng)
(vì O là giao điểm 2 đường chéo nên là trung điểm của AB, CD)
b) ABCD là hình bình hành nên ta có \(\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} = \overrightarrow {AC} \)
Suy ra \(\)\(\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} + \overrightarrow {AD} = \left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} } \right) + \overrightarrow {AC} = \overrightarrow {AC} + \overrightarrow {AC} = 2\overrightarrow {AC} \) (đpcm)

Có \(\overrightarrow{v}=\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{MB}-2\overrightarrow{MC}=\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{MB}+2\overrightarrow{CM}\)
\(=\left(\overrightarrow{CM}+\overrightarrow{MA}\right)+\left(\overrightarrow{CM}+\overrightarrow{MB}\right)=\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{CB}\) (Không phụ thuộc vào vị trí điểm M).
b) Dựng hình bình hành BCAD. Theo quy tắc hình bình hành:
\(\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{CB}=\overrightarrow{CD}\).
Vậy \(\overrightarrow{CD}=\overrightarrow{v}\).
\(\overrightarrow{v}=\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{MB}-2\overrightarrow{MC}\)
\(=2\overrightarrow{ME}-2\overrightarrow{MC}\) (E là trung điểm cạnh AB)
\(=\left(\overrightarrow{ME}-MC\right)=2\overrightarrow{CE}\)
vậy \(\overrightarrow{v}\) không phụ thuộc vị trí của điểm M
\(\overrightarrow{CD}=\overrightarrow{v}=2\overrightarrow{CE}\) thì E là trung điểm của CD
\(\Rightarrow\) ta dựng được điểm D

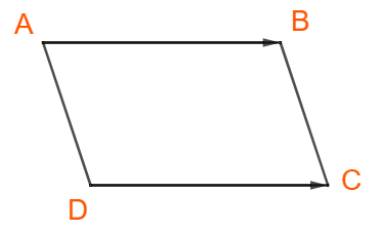
a) ABCD là hình bình hành nên \(\overrightarrow {DC} = \overrightarrow {AB} \)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {DC} = \overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {AB} = \overrightarrow {BB} = \overrightarrow 0 \)
b) \(\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MC} = \left( {\overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {BA} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {DC} } \right)\)
\(= \left( {\overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MD} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {DC}} \right)\)
\(= \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MD} \) (Vì \(\overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {DC} = \overrightarrow {0} \))

2) ∣ MG+ GA+ MG+ GB+ MG+ GC∣=∣BA∣
∣3MG∣= ∣BA∣
∣MG∣=1/3∣BA∣
=> M thuộc đường tròn tâm G, bán kính = 1/3BA

Có vẻ không đúng.
Giả sử \(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MA}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{MB}+\left(\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{AB}\right)=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MB}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\overrightarrow{MB}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M\equiv B\) (Vô lí)

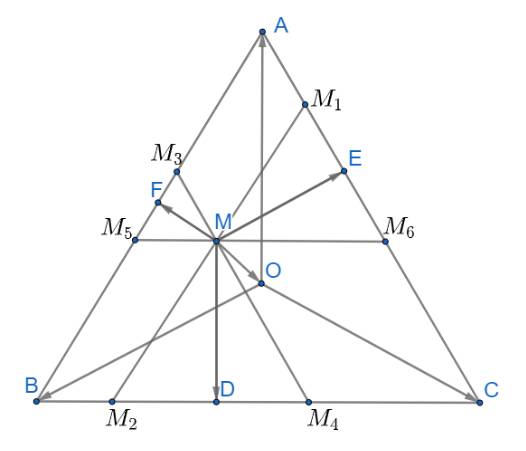
\(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OD} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OE} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OF} } \right)\)
Qua M kẻ các đường thẳng \({M_1}{M_2}//AB;{M_3}{M_4}//AC;{M_5}{M_6}//BC\)
Từ đó ta có: \(\widehat {M{M_1}{M_6}} = \widehat {M{M_6}{M_1}} = \widehat {M{M_4}{M_2}} = \widehat {M{M_2}{M_4}} = \widehat {M{M_3}{M_5}} = \widehat {M{M_5}{M_3}} = 60^\circ \)
Suy ra các tam giác \(\Delta M{M_3}{M_5},\Delta M{M_1}{M_6},\Delta M{M_2}{M_4}\) đều
Áp dụng tính chất trung tuyến \(\overrightarrow {AM} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} } \right)\)(với M là trung điểm của BC) ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {ME} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right);\overrightarrow {MD} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right);\overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
Ta có: các tứ giác \(A{M_3}M{M_1};C{M_4}M{M_6};B{M_2}M{M_5}\) là hình bình hành
Áp dụng quy tắc hình bình hành ta có
\(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_3}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_4}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MA} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MC} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OA} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OB} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OC} } \right)} \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {3\overrightarrow {MO} + \left( {\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} } \right)} \right) = \frac{3}{2}\overrightarrow {MO} \) (đpcm)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{3}{2}\overrightarrow {MO} \)