Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) \( AH \bot BC\) và \(BH \bot CA\)
\( \Rightarrow \left( {\overrightarrow {AH} ,\overrightarrow {BC} } \right) = {90^o} \Leftrightarrow \cos \left( {\overrightarrow {AH} ,\overrightarrow {BC} } \right) = 0\) . Do đó \(\overrightarrow {AH} .\overrightarrow {BC} = \overrightarrow 0 \)
Tương tự suy ra \(\overrightarrow {BH} .\overrightarrow {CA} = \overrightarrow 0 \).
b) Gọi H có tọa độ (x; y)
\( \Rightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AH} = (x - ( - 1);y - 2) = (x + 1;y - 2)\\\overrightarrow {BH} = (x - 8;y - ( - 1)) = (x - 8;y + 1)\end{array} \right.\)
Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {AH} .\overrightarrow {BC} = \overrightarrow 0 \) và \(\overrightarrow {BC} = (8 - 8;8 - ( - 1)) = (0;9)\)
\((x + 1).0 + (y - 2).9 = 0 \Leftrightarrow 9.(y - 2) = 0 \Leftrightarrow y = 2.\)
Lại có: \(\overrightarrow {BH} .\overrightarrow {CA} = \overrightarrow 0 \) và \(\overrightarrow {CA} = ( - 1 - 8;2 - 8) = ( - 9; - 6)\)
\(\begin{array}{l}(x - 8).( - 9) + (y + 1).( - 6) = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow - 9x + 72 + 3.( - 6) = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow - 9x + 54 = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow x = 6.\end{array}\)
Vậy H có tọa độ (6; 2)
c) Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {AB} = (8 - ( - 1); - 1 - 2) = (9; - 3)\)\( \Rightarrow AB = \left| {\overrightarrow {AB} } \right| = \sqrt {{9^2} + {{( - 3)}^2}} = 3\sqrt {10} \)
Và \(\overrightarrow {BC} = (0;9) \Rightarrow BC = \left| {\overrightarrow {BC} } \right| = \sqrt {{0^2} + {9^2}} = 9\);
\(\overrightarrow {CA} = ( - 9; - 6)\)\( \Rightarrow AC = \left| {\overrightarrow {CA} } \right| = \sqrt {{{( - 9)}^2} + {{( - 6)}^2}} = 3\sqrt {13} .\)
Áp dụng định lí cosin cho tam giác ABC, ta có:
\(\cos \widehat A = \frac{{{b^2} + {c^2} - {a^2}}}{{2bc}} = \frac{{{{\left( {3\sqrt {13} } \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3\sqrt {10} } \right)}^2} - {{\left( 9 \right)}^2}}}{{2.3\sqrt {13} .3\sqrt {10} }} \approx 0,614\)\( \Rightarrow \widehat A \approx 52,{125^o}\)
\(\cos \widehat B = \frac{{{a^2} + {c^2} - {b^2}}}{{2ac}} = \frac{{{{\left( 9 \right)}^2} + {{\left( {3\sqrt {10} } \right)}^2} - {{\left( {3\sqrt {13} } \right)}^2}}}{{2.9.3\sqrt {10} }} = \frac{{\sqrt {10} }}{{10}}\)\( \Rightarrow \widehat B \approx 71,{565^o}\)
\( \Rightarrow \widehat C \approx 56,{31^o}\)
Vậy tam giác ABC có: \(a = 9;b = 3\sqrt {13} ;c = 3\sqrt {10} \); \(\widehat A \approx 52,{125^o};\widehat B \approx 71,{565^o};\widehat C \approx 56,{31^o}.\)

Có vẻ không đúng.
Giả sử \(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MA}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{MB}+\left(\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{AB}\right)=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MB}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\overrightarrow{MB}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M\equiv B\) (Vô lí)

a)
\(\overrightarrow{AK}=\overrightarrow{AI}+\overrightarrow{IK}=\overrightarrow{AI}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{IB}=\overrightarrow{AI}+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{AB}\right)\)
\(=\overrightarrow{AI}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{IA}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}\)\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AI}\).
b) Theo câu a:
\(\overrightarrow{AK}=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AI}=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{4}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{4}\overrightarrow{AC}=\dfrac{3}{4}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{4}\overrightarrow{AC}\).

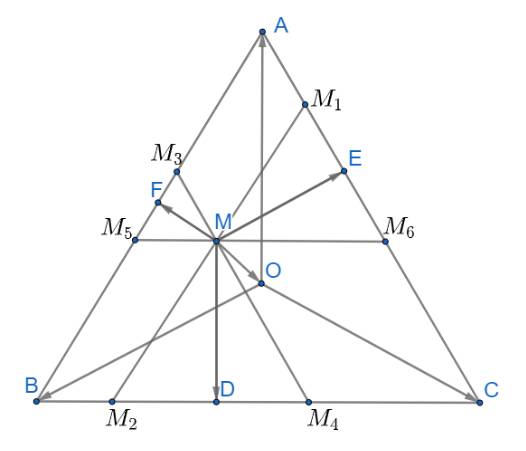
\(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OD} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OE} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OF} } \right)\)
Qua M kẻ các đường thẳng \({M_1}{M_2}//AB;{M_3}{M_4}//AC;{M_5}{M_6}//BC\)
Từ đó ta có: \(\widehat {M{M_1}{M_6}} = \widehat {M{M_6}{M_1}} = \widehat {M{M_4}{M_2}} = \widehat {M{M_2}{M_4}} = \widehat {M{M_3}{M_5}} = \widehat {M{M_5}{M_3}} = 60^\circ \)
Suy ra các tam giác \(\Delta M{M_3}{M_5},\Delta M{M_1}{M_6},\Delta M{M_2}{M_4}\) đều
Áp dụng tính chất trung tuyến \(\overrightarrow {AM} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} } \right)\)(với M là trung điểm của BC) ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {ME} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right);\overrightarrow {MD} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right);\overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
Ta có: các tứ giác \(A{M_3}M{M_1};C{M_4}M{M_6};B{M_2}M{M_5}\) là hình bình hành
Áp dụng quy tắc hình bình hành ta có
\(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_3}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_4}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MA} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MC} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OA} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OB} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OC} } \right)} \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {3\overrightarrow {MO} + \left( {\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} } \right)} \right) = \frac{3}{2}\overrightarrow {MO} \) (đpcm)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{3}{2}\overrightarrow {MO} \)

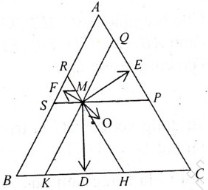
Qua M kẻ các đường thẳng song song với các cạnh của tam giác
A1B1 // AB; A2C2 // AC; B2C1 // BC.
Dễ thấy các tam giác MB1C2; MA1C1;MA2B2 đều là các tam giác đều. Ta lại có MD  B1C2 nên MD cũng là trung điểm thuộc cạnh B1C2 của tam giác MB1C2
B1C2 nên MD cũng là trung điểm thuộc cạnh B1C2 của tam giác MB1C2
Ta có 2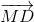 =
= 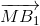 +
+ 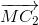
Tương tự: 2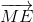 =
= 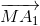 +
+ 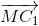
2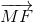 =
= 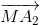 +
+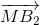
=> 2( 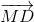 +
+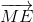 +
+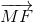 ) = (
) = (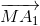 +
+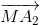 ) + (
) + (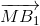 +
+ 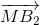 ) + (
) + (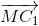 +
+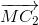 )
)
Tứ giác là hình bình hành nên
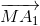 +
+ 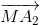 =
= 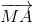
Tương tự: 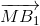 +
+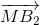 =
= 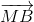
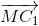 +
+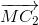 =
= 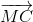
=> 2( 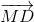 +
+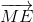 +
+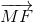 ) =
) = 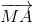 +
+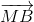 +
+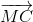
vì O là trọng tâm bất kì của tam giác và M là một điểm bất kì nên
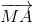 +
+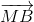 +
+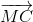 = 3
= 3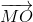 .
.
Cuối cùng ta có:
2( 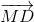 +
+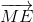 +
+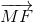 ) = 3
) = 3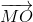 ;
;
=> 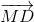 +
+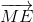 +
+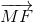 =
= 
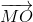




Có \(\overrightarrow{MH}=-\overrightarrow{HM}=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{HB}+\overrightarrow{HC}\right)\);
\(\overrightarrow{MA}=-\overrightarrow{AM}=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}\right)\).
Vì vậy:
\(\overrightarrow{MH}.\overrightarrow{MA}=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{HB}+\overrightarrow{HC}\right).\dfrac{-1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\overrightarrow{HB}.\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{HB}.\overrightarrow{AC}+\overrightarrow{HC}.\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{HC}.\overrightarrow{AC}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\overrightarrow{CH}.\overrightarrow{AC}+\overrightarrow{BH}.\overrightarrow{AB}\right)\) (Do H là trực tâm tam giác ABC).
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left[\overrightarrow{CH}\left(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BC}\right)+\overrightarrow{BH}\left(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BC}\right)\right]\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\overrightarrow{CH}.\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{CH}.\overrightarrow{BC}+\overrightarrow{BH}.\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BH}.\overrightarrow{BC}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\overrightarrow{CH}.\overrightarrow{BC}+\overrightarrow{BH}.\overrightarrow{BC}\right)\) ( do H là trực tâm tam giác ABC).
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\overrightarrow{BC}\left(\overrightarrow{BH}+\overrightarrow{HC}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\overrightarrow{BC}.\overrightarrow{BC}=\dfrac{1}{4}BC^2\).
2 cái dòng do H là trực tâm mk ko hiểu. Bn vón thể giải thích rõ đc ko ak