Giải phương trình : m²x +6m=4x-12, m là tham số. Tìm m. Giải chi tiết giúp mình
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: Để phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất thì \(\left(m-3\right)\left(m+2\right)< >0\)
hay \(m\notin\left\{3;-2\right\}\)
Để phương trình vô nghiệm thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(m-3\right)\left(m+2\right)=0\\\left(m-3\right)\left(m-1\right)< >0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=-2\)
Để phương trình có vô số nghiệm thì m=3

Bài 1:
a) Thay m=3 vào (1), ta được:
\(x^2-4x+3=0\)
a=1; b=-4; c=3
Vì a+b+c=0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(x_1=1;x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{3}{1}=3\)
Bài 2:
a) Thay m=0 vào (2), ta được:
\(x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
hay x=1

\(x^2-2x+m=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-2\right)^2-4m=4-4m\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\) thì \(\Delta>0\Leftrightarrow4-4m>0\Leftrightarrow-4m>-4\Leftrightarrow m< 1\)
Theo Vi-ét, ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có : \(2\left(x_1x_2\right)^2-x_1=6+x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x_1x_2\right)^2-x_1-x_2-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x_1x_2\right)^2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2-2-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2\left(ktm\right)\\m=-2\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(m=-2\) thì thỏa mãn đê bài.
Giải thích giúp em chỗ dấu tương tương thứ hai tại sao x1-x2 lại chuyển thành (x1+x2) được không ạ

\(x^2+6x+6m-m^2=0\left(1\right)\)
Áp dụng định lý Viet ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=-6\\P=x_1.x_2=6m-m^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Delta'=9-6m+m^2=\left(m-3\right)^2\ge0,\forall m\in R\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt[]{\Delta'}=\left|m-3\right|\)
Phương trình \(\left(1\right)\) có 2 nhiệm phân biệt
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=-3+\left|m-3\right|\\x_2=-3-\left|m-3\right|\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x_1-x_2=2\left|m-3\right|\)
Theo đề bài ta có :
\(x^3_1-x^3_2+2x^2_1+12x_1+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)\left(x^2_1+x^2_2+x_1.x_2\right)+2x^2_1+12x_1+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-x_1.x_2\right]+2x^2_1+12x_1+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left|m-3\right|\left(36-6m+m^2\right)+2\left[-3+\left|m-3\right|\right]^2+12\left[-3+\left|m-3\right|\right]+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left|m-3\right|\left(9-6m+m^2+27\right)+2\left[-3+\left|m-3\right|\right]^2+12\left[-3+\left|m-3\right|\right]+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left|m-3\right|\left[\left(m-3\right)^2+27\right]+2\left[-3+\left|m-3\right|\right]^2+12\left[-3+\left|m-3\right|\right]+72=0\left(a\right)\)
- Với \(m>3\)
\(\left(a\right)\Leftrightarrow2\left(m-3\right)\left[\left(m-3\right)^2+27\right]+2\left[-3+m-3\right]^2+12\left[-3+m-3\right]+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(m-3\right)\left[\left(m-3\right)^2+27\right]+2\left(m-6\right)^2+12\left(m-6\right)+72=0\)
Đặt \(t=m-3>0\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow2t\left(t^2+27\right)+2\left(t-3\right)^2+12\left(t-3\right)+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2t^3+54t+2t^2-12t+18+12t-36+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2t^3+2t^2+54t+54=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2t^2\left(t+1\right)+54\left(t+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+1\right)\left(2t^2+54\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t+1=0\left(2t^2+54>0,\forall t\in R\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t=-1\left(ktm\right)\)
- Với \(m< 3\)
\(\left(a\right)\Leftrightarrow2\left(3-m\right)\left[\left(3-m\right)^2+27\right]+2\left[-3-m+3\right]^2+12\left[-3-m+3\right]+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(3-m\right)\left[\left(3-m\right)^2+27\right]+2m^2-12m+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(3-m\right)\left[\left(3-m\right)^2+27\right]-2m\left(6-m\right)+72=0\)
Đặt \(t=3-m< 0\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow2t\left(t^2+27\right)-2\left(3-t\right)\left(3+t\right)+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2t^3+54t-18+2t^2+72=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2t^3+2t^2+54t+54=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2t^2\left(t+1\right)+54\left(t+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+1\right)\left(2t^2+54\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t+1=0\left(2t^2+54>0,\forall t\in R\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-m=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=4\left(ktm\right)\)
- Với \(m=3\)
\(\left(a\right)\Leftrightarrow0+2.9-36+72=54=0\left(vô.lý\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m=3\left(loại\right)\)
Vậy không có m nào để thỏa yêu cầu đề bài.

1.
\(2x+1\ge0\Rightarrow x\ge-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Khi đó pt đã cho tương đương:
\(x^2+2x+2m=\left(2x+1\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+2m=4x^2+4x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+2x+1=2m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=3x^2+2x+1\) trên \([-\dfrac{1}{2};+\infty)\)
\(-\dfrac{b}{2a}=-\dfrac{1}{3}< -\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(f\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{3}{4}\) ; \(f\left(\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Pt đã cho có 2 nghiệm pb khi và chỉ khi \(\dfrac{2}{3}< 2m\le\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{3}< m\le\dfrac{3}{8}\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
3.
Đặt \(x^2=t\ge0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{t}\\x=-\sqrt{t}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Pt trở thành: \(t^2-3mt+m^2+1=0\) (1)
Pt đã cho có 4 nghiệm pb khi và chỉ khi (1) có 2 nghiệm dương pb
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta=9m^2-4\left(m^2+1\right)>0\\t_1+t_2=3m>0\\t_1t_2=m^2+1>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow m>\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\)
Ta có:
\(M=x_1+x_2+x_3+x_4+x_1x_2x_3x_4\)
\(=-\sqrt{t_1}-\sqrt{t_2}+\sqrt{t_1}+\sqrt{t_2}+\left(-\sqrt{t_1}\right)\left(-\sqrt{t_2}\right)\sqrt{t_1}.\sqrt{t_2}\)
\(=t_1t_2=m^2+1\) với \(m>\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\)

Giả sử điểm M(a,b) là điểm mà đường thẳng d luôn đi qua ta có
\(b=2a\left(m-1\right)-m+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(2a-1\right)+1-2a-b=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2a-1=0\\1-2a-b=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=0,5\\b=0\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy đường thẳng luôn đi qua điểm cố định M(0,5; 0)
Cho x, y là các số dương thỏa mãn: xy + \(\sqrt{\left(1+x^2\right)\left(1+y^2\right)}=\sqrt{2008}\). Tính giá trị của biểu thức S=\(x\sqrt{1+y^2}=y\sqrt{1+x^2}\)

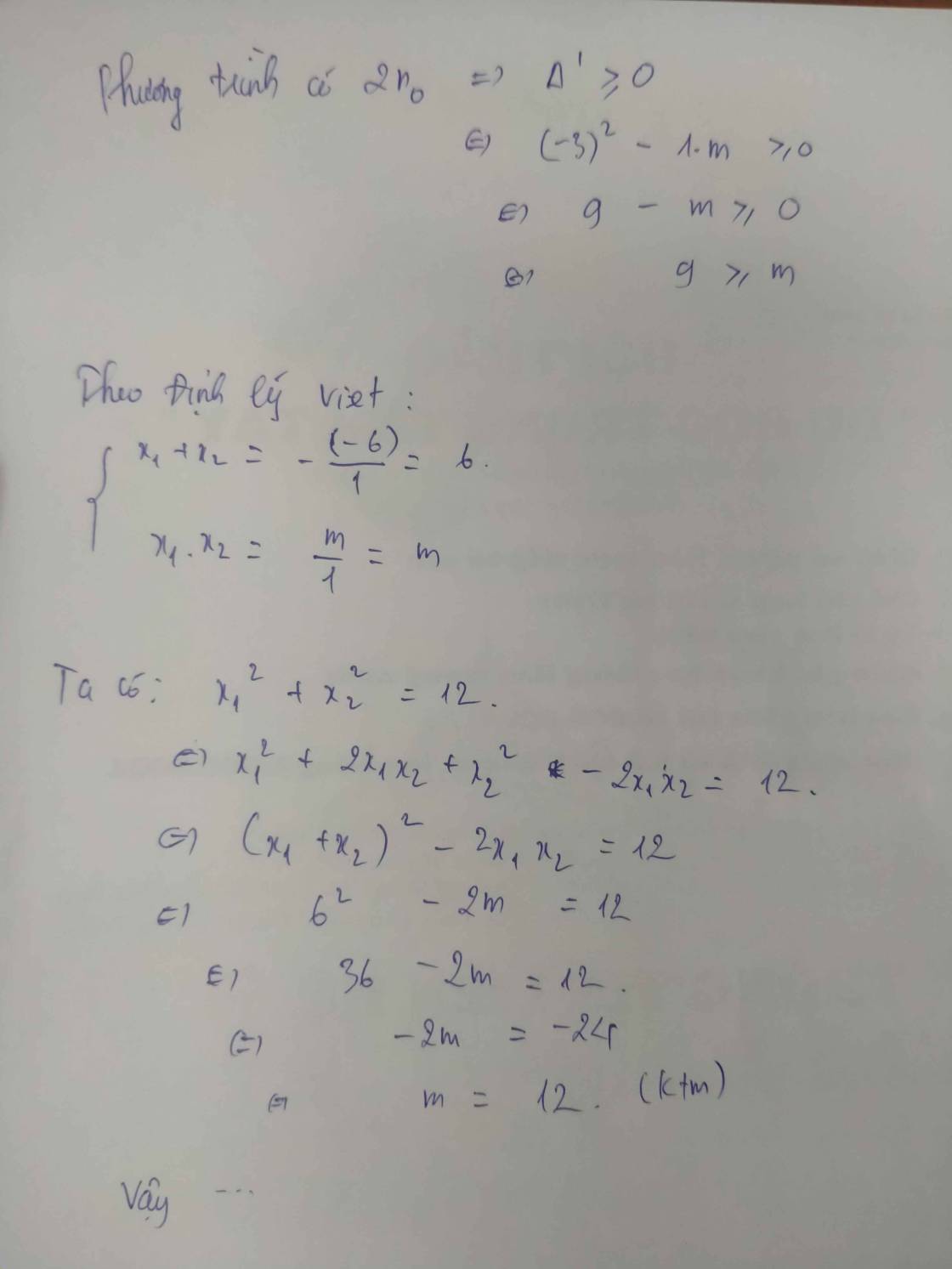

\(m^2x+6m=4x-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2x-4x=-6m-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m^2-4\right)x=-6\left(m+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-2\right)\left(m+2\right)x=-6\left(m+2\right)\)
- Nếu \(m=-2\Leftrightarrow m+2=0\) pt trở thành:
\(0.x=-6.0\Leftrightarrow0=0\) (luôn đúng)
Phương trình có vô số nghiệm
- Nếu \(m=2\Rightarrow m-2=0\) pt trở thành:
\(0.x=-6.4\Leftrightarrow0=-24\) (vô lý)
Phương trình vô nghiệm
- Nếu \(m\ne\pm2\Rightarrow\left(m-2\right)\left(m+2\right)\ne0\) ta được:
\(\left(m-2\right)\left(m+2\right)x=-6\left(m+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-6\left(m+2\right)}{\left(m-2\right)\left(m+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{6}{m-2}\)
Vậy:
Nếu \(m=2\) pt vô nghiệm
Nếu \(m=-2\) pt có vô số nghiệm
Nếu \(m\ne\pm2\) pt có nghiệm duy nhất: \(x=-\dfrac{6}{m-2}\)