giai phuong trinh :
(x^2+x+1)^2=3(x^4+x^2+1)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(\left(9x^2-4\right)-\left(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(9x^2-4-\left(3x^2-x-2\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(9x^2-4-3x^2+x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)=0;3x^2+x-2=0\)
=> x=-1
với \(3x^2+x-2=0\)
ta sử dụng công thức bậc 2 suy ra : \(x=\dfrac{2}{3};x=-1\)
Vậy ghiệm của pt trên \(S\in\left\{-1;\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1-1+x^2=x+3-x^2-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x=-x^2-2x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2=3\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left[\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(x+5\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x-3-x^2-3x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(-5x+7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;-2;\dfrac{7}{5}\right\}\)

Ta có: x 4 + 2 x 2 – x + 1 = 15 x 2 – x – 35
⇔ x 4 + 2 x 2 – x + 1 - 15 x 2 + x + 35 = 0
⇔ x 4 – 13 x 2 + 36 = 0
Đặt m = x 2 . Điều kiện m ≥ 0
Ta có: x 4 – 13 x 2 + 36 = 0 ⇔ m 2 – 13m + 36 = 0
∆ = - 13 2 – 4.1.36 = 169 – 144 = 25 > 0
∆ = 25 = 5
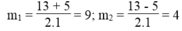
Ta có: x 2 = 9 ⇒ x = ± 3
x 2 = 4 ⇒ x = ± 2
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 4 nghiệm: x 1 = 3; x 2 = -3; x 3 = 2; x 4 = -2

Ta có: 2 x 4 + x 2 – 3 = x 4 + 6 x 2 + 3
⇔ 2 x 4 + x 2 – 3 – x 4 – 6 x 2 – 3 = 0
⇔ x 4 – 5 x 2 – 6 = 0
Đặt m = x 2 . Điều kiện m ≥ 0
Ta có: x 4 – 5 x 2 – 6 = 0 ⇔ m 2 – 5m – 6 = 0
∆ = - 5 2 – 4.1.(-6) = 25 + 24 = 49 > 0
∆ = 49 = 7
![]()
Ta có: x 2 = 6 ⇒ x = ± 6
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 2 nghiệm: x 1 = 6 , x 2 = - 6

1: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(-4x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;\dfrac{1}{4}\right\}\)
2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1-x^2+2x-16\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-15\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;5\right\}\)
3: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+4\right)-9\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;3;-3\right\}\)
5: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+5=x-1\\3x+5=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=-6\\4x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3\right)^2-\left(2x-10\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(6x+3-2x+10\right)\left(6x+3+2x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+13\right)\left(8x-7\right)=0\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{13}{4};\dfrac{7}{8}\right\}\)
1.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(5x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=5x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
2.
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-2x+16\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=x^2-2x+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
3.
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(4x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{2};x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Ta có: 5 x 4 – 7 x 2 – 2 = 3 x 4 – 10 x 2 – 3
⇔ 5 x 4 – 7 x 2 – 2 – 3 x 4 + 10 x 2 + 3 = 0
⇔ 2 x 4 + 3 x 2 + 1 = 0
Đặt m = x 2 . Điều kiện m ≥ 0
Ta có: 2 x 4 + 3 x 2 + 1 = 0 ⇔ 2 m 2 + 3m + 1 = 0
Phương trình 2 m 2 + 3m + 1 = 0 có hệ số a = 2, b = 3, c = 1 nên có dạng :
a – b + c = 0 suy ra m 1 = -1, m 2 = -1/2
Cả hai giá trị của m đều nhỏ hơn 0 nên không thỏa mãn điều kiện bài toán.
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.

2:
\(A=\dfrac{x_2-1+x_1-1}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3-2}{-7-3+1}=\dfrac{1}{-9}=\dfrac{-1}{9}\)
B=(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2
=3^2-2*(-7)
=9+14=23
C=căn (x1+x2)^2-4x1x2
=căn 3^2-4*(-7)=căn 9+28=căn 27
D=(x1^2+x2^2)^2-2(x1x2)^2
=23^2-2*(-7)^2
=23^2-2*49=431
D=9x1x2+3(x1^2+x2^2)+x1x2
=10x1x2+3*23
=69+10*(-7)=-1

Ta thấy x = 1 không phải nghiệm của phương trình nên nhân 2 vế của phương trình với x - 1 ta có:
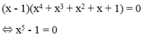
⇔ x = 1(KTM)
Vậy phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.
bạn ấn vào đúng 0 sẽ ra kết quả, mình làm bài này rồi dễ lắm