Trả lời các câu hỏi sau đây
1 : 2 + 4 = ?
2 : 45 + 32 = ?
3 : 6 - 3 = ?
4 : 79 - 52 = ?
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



S = 1/(1.4) + 1/(4.7) + 1/(7.10) + ... + 1/(94.97) + 1/(97.100)
= 1/3 . (1 - 1/4 + 1/4 - 1/7 + 1/7 - 1/10 + ... + 1/94 - 1/97 + 1/97 - 1/100)
= 1/3 . (1 - 1/100)
= 1/3 . 99/100
= 33/100
Em đăng câu hỏi đúng nội dung lớp học em nhé. Lớp 1 đã học phân số đâu. 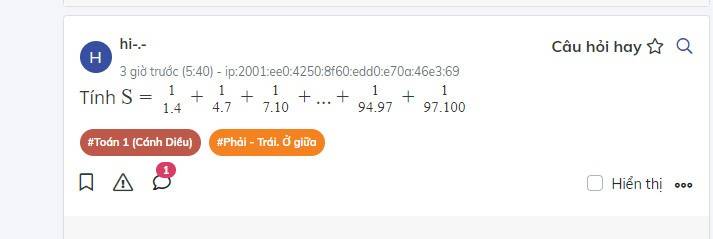



\(f\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=3.-2.\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=3-1=2\)

1=4,5
2=32,0444
3=2,5
4= -51,9437