giải phương trình
a , x2 - 7x + 6 = 0
b, 2x2 - 3x -5 = 0
c, 4x2 - 12x + 5 = 0
d, x4 - x3 + 2x2 - x +1 = 0
mik cần gấp
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Đặt \(x^2=a\left(a\ge0\right)\)
Ta có: \(2x^4-7x^2+4=0\)
Suy ra: \(2a^2-7a+4=0\)
\(\Delta=49-4\cdot2\cdot4=49-32=17\)
Vì \(\Delta>0\) nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a_1=\dfrac{7-\sqrt{17}}{4}\left(nhận\right)\\a_2=\dfrac{-7+\sqrt{17}}{4}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Suy ra: \(x^2=\dfrac{7-\sqrt{17}}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\dfrac{\sqrt{7-\sqrt{17}}}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{\sqrt{7-\sqrt{17}}}{2};-\dfrac{\sqrt{7-\sqrt{17}}}{2}\right\}\)

Bài 2:
a: =>2x^2-4x+1=x^2+x+5
=>x^2-5x-4=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{41}}{2}\)
b: =>11x^2-14x-12=3x^2+4x-7
=>8x^2-18x-5=0
=>x=5/2 hoặc x=-1/4

a: =>2x^2+9x-6x-27=0
=>x(2x+9)-3(2x+9)=0
=>(2x+9)(x-3)=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=-9/2
b: =>-10x^2+6x-5x+3=0
=>-2x(5x-3)-(5x-3)=0
=>(5x-3)(-2x-1)=0
=>x=-1/2 hoặc x=5/3
c: =>-x^3+2x^2-x^2+4=0
=>-x^2(x-2)-(x-2)(x+2)=0
=>(x-2)(-x^2-x-2)=0
=>x-2=0
=>x=2
d: =>(x^3+8)-4x(x+2)=0
=>(x+2)(x^2-2x+4)-4x(x+2)=0
=>(x+2)(x^2-6x+4)=0
=>x=-2 hoặc \(x=3\pm\sqrt{5}\)

a) 3 x 2 − 7 x − 10 ⋅ 2 x 2 + ( 1 − 5 ) x + 5 − 3 = 0
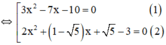
+ Giải (1):
3 x 2 – 7 x – 10 = 0
Có a = 3; b = -7; c = -10
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (1) có hai nghiệm x 1 = - 1 v à x 2 = - c / a = 10 / 3 .
+ Giải (2):
2 x 2 + ( 1 - √ 5 ) x + √ 5 - 3 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 1 - √5; c = √5 - 3
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
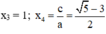
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 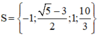
b)
x 3 + 3 x 2 - 2 x - 6 = 0 ⇔ x 3 + 3 x 2 - ( 2 x + 6 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x + 3 ) - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0 ⇔ x 2 - 2 ( x + 3 ) = 0
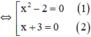
+ Giải (1): x 2 – 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 = 2 ⇔ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2.
+ Giải (2): x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -3.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-3; -√2; √2}
c)
x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 , 6 x 2 + x ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = x ⋅ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) ⇔ x 2 − 1 ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) − x ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) = 0 ⇔ ( 0 , 6 x + 1 ) x 2 − 1 − x = 0
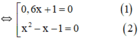
+ Giải (1): 0,6x + 1 = 0 ⇔ 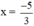
+ Giải (2):
x 2 – x – 1 = 0
Có a = 1; b = -1; c = -1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm 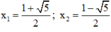
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 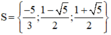
d)
x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 = x 2 − x + 5 2 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 2 − x 2 − x + 5 2 = 0 ⇔ x 2 + 2 x − 5 − x 2 − x + 5 ⋅ x 2 + 2 x − 5 + x 2 − x + 5 = 0 ⇔ ( 3 x − 10 ) 2 x 2 + x = 0
⇔ (3x-10).x.(2x+1)=0
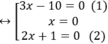
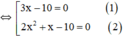
+ Giải (1): 3x – 10 = 0 ⇔ 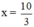
+ Giải (2):
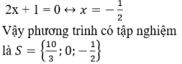

a) Ta có: \(36x^3-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\left(9x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=\dfrac{-1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(3x\left(x-2\right)+x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{-1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(\text{5x(x-2)+(2-x)=0}\)
\(\Rightarrow5x\left(x-2\right)-\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\5x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\text{x(2x-5)-10x+25=0}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(2x-5\right)-5\left(2x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x-5\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=0\\2x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=2,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\dfrac{25}{16}-4x^2+4x-1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{9}{16}-4x^2+4x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-4x^2+4x+\dfrac{9}{16}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-4x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{16}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(-4x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)+\left(\dfrac{9}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{16}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2}x\left(8x+1\right)+\dfrac{9}{16}\left(8x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{16}\right)\left(8x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{9}{16}=0\\8x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9}{8}\\x=\dfrac{-1}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a, \(x^4-x^2-2=0\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^2+x^2-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-2\right)+\left(x^2-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1>0\right)\left(x^2-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{2}\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=0;x=-1\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1>0\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
d, \(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x-4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3};x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
a)
/ \(x^4+x^2-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2\right)^2-x^2+2x^2-2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-1\right)+2\left(x^2-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2=0\\x+1=0\\x-1-0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Ta có: \(x^3+x^2+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+1>0\forall x\)
nên x+1=0
hay x=-1
Vậy: S={-1}
b) Ta có: \(x^3-6x^2+11x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-5x^2+5x+6x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-5x\left(x-1\right)+6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-5x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={1;2;3}
c) Ta có: \(x^3-x^2-21x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+2x^2-6x-15x+45=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-3\right)+2x\left(x-3\right)-15\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+2x-15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+5x-3x-15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2\cdot\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={3;-5}
d) Ta có: \(x^4+2x^3-4x^2-5x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^3+4x^3-8x^2+4x^2-8x+3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x-2\right)+4x^2\cdot\left(x-2\right)+4x\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+4x^2+4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+3x^2+x^2+4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left[x^2\left(x+3\right)+\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+x+1>0\forall x\)
nên (x-2)(x+3)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={2;-3}

a) \(x^3-x^2+3x-3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)+3\left(x-1\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x-1\right)>0\)
Mà: \(x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
b) \(x^3+x^2+9x+9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x+1\right)+9\left(x+1\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+9\right)\left(x+1\right)< 0\)
Mà: \(x^2+9>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -1\)
d) \(4x^3-14x^2+6x-21< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(2x-7\right)+3\left(2x-7\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2+3\right)\left(2x-7\right)< 0\)
Mà: \(2x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-7< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x< 7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{7}{2}\)
d) \(x^2\left(2x^2+3\right)+2x^2>-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4+3x^2+2x^2+3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4+5x^2+3>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(2x^2+3\right)>0\)
Mà:
\(x^2+1>0\forall x\)
\(2x^2+3>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in R\)
a: =>x^2(x-1)+3(x-1)>0
=>(x-1)(x^2+3)>0
=>x-1>0
=>x>1
b: =>x^2(x+1)+9(x+1)<0
=>(x+1)(x^2+9)<0
=>x+1<0
=>x<-1
c: 4x^3-14x^2+6x-21<0
=>2x^2(2x-7)+3(2x-7)<0
=>2x-7<0
=>x<7/2
d: =>x^2(2x^2+3)+2x^2+3>0
=>(2x^2+3)(x^2+1)>0(luôn đúng)

a: ta có: \(x^2+3x-\left(2x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(5x+20-x^2-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(5-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
a, <=> (x-1).(x-6) = 0
<=> x=1 hoặc x=6
b, <=> (x+1).(2x-5) = 0
<=> x=-1 hoặc x=5/2
c, <=> (2x-5).(2x-1) = 0
<=> x=5/2 hoặc x=1/2
d, <=> (x^2-x+1).(x^2+1) = 0
=> pt vô nghiệm vì x^2-x+1 và x^2+1 đều > 0
Tk mk nha
a) x2 - 7x + 6 = 0
<=> x2 - 6x - x + 6 = 0
<=>( x - 6 ) ( x - 1 ) = 0
<=> x - 6 = 0 hoặc x - 1 = 0
1. x - 6 = 0
<=> x = 6
2. x - 1 = 0
<=> x = 1
Vậy ......
b) 2x2 - 3x - 5 = 0
<=> 2x2 + 2x - 5x - 5 = 0
<=> ( x + 1 ) ( 2x - 5 ) = 0
<=> x + 1 = 0 hoặc 2x - 5 = 0
1. x + 1 = 0
<=> x = -1
2. 2x - 5 = 0
<=> x = 2.5
Vậy ............
c) 4x2 - 12x + 5 = 0
<=> 4x2 - 2x - 10x + 5 = 0
<=> 2x ( 2x - 1 ) - 5( 2x - 1 ) = 0
<=> ( 2x - 1 ) ( 2x - 5 ) = 0
<=> 2x - 1 = 0 hoặc 2x - 5 = 0
1. 2x - 1 = 0
<=> x = 0.5
2. 2x - 5 = 0
<=> x = 2.5
Vậy ....................
d) x4 - x3 + 2x2 - x + 1 = 0