Giải phương trình phân thức sau: (2x/2x^2-3x+1)-(x/2x^2+x+1)=-3/2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Đáp số của bài toán đúng nhưng lời giải của bạn Hà chưa đầy đủ.
Lời giải của bạn Hà thiếu bước tìm điều kiện xác định và bước đối chiếu giá trị của x tìm được với điều kiện để kết luận nghiệm.
Trong bài toán trên thì điều kiện xác định của phương trình là:
x ≠ - 3/2 và x ≠ - 1/2
So sánh với điều kiện xác định thì giá trị x = - 4/7 thỏa mãn.
Vậy x = - 4/7 là nghiệm của phương trình.

1/ ( x-1) (2x+1) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-0,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
2/ x (2x-1) (3x+15) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x-1=0\\3x+15=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=0,5\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3/ (2x-6) (3x+4).x=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-6=0\\3x+4=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
4/ (2x-10)(x2+1)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-10=0\\x^2+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x^2=-1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
5/ (x2+3) (2x-1) =0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+3=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=-3\left(loại\right)\\x=0,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
6/ (3x-1) (2x2 +1)=0
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\2x^2+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\x^2=-0,5\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
1: Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
2: Ta có: \(x\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x+15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\2x-1=0\\3x+15=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
3: Ta có: \(\left(2x-6\right)\left(3x+4\right)x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-6=0\\3x+4=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) |3x| = x + 6 (1)
Ta có 3x = 3x khi x ≥ 0 và 3x = -3x khi x < 0
Vậy để giải phương trình (1) ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
+ ) Phương trình 3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x ≥ 0
Ta có: 3x = x + 6 ⇔ 2x = 6 ⇔ x = 3 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ ) Phương trình -3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x < 0
Ta có -3x = x + 6 ⇔ -4x + 6 ⇔ x = -3/2 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = -3/2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S = {3; -3/2}
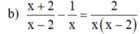
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ 2
Quy đồng mẫu hai vễ của phương trình, ta được:
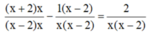
![]()
![]()
![]()
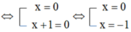
![]()
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {-1}
c) (x + 1)(2x – 2) – 3 > –5x – (2x + 1)(3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 2x + 2x – 2 – 3 > –5x – (6x – 2x2 + 3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 5 ≥ –5x – 6x + 2x2 – 3 + x
⇔ 10x ≥ 2 ⇔ x ≥ 1/5
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x ≥ 1/5}

Bạn coi lại đề xem có sai không chứ nghiệm giải ra xấu cực. Và phương trình không rút gọn hết nghe cũng rất vô lý.
dạ vâng,em cx không bt có sai ko do đây là đề của thầy em đưa,chắc cx có sai sót mong thầy bỏ qua

\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

1: Ta có: \(2x\left(x+3\right)-6\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+6x-6x+18=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+18=0\left(loại\right)\)
2: Ta có: \(2x^2\left(2x+3\right)+\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3=0\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
3: Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)-4x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(1-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
4: Ta có: \(2x\left(x-5\right)-3x+15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(2x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
5: Ta có: \(3x\left(x+4\right)-2x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
6: Ta có: \(x^2\left(2x-6\right)+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-6=0\)
hay x=3

1:
a: 2x-3=5
=>2x=8
=>x=4
b: (x+2)(3x-15)=0
=>(x-5)(x+2)=0
=>x=5 hoặc x=-2
2:
b: 3x-4<5x-6
=>-2x<-2
=>x>1

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;0\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+3x+x^2-3x+2=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-2\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: S={1}
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-7;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x+7}=\dfrac{6x+1}{2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=\left(6x+1\right)\left(x+7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-9x-4x+6=6x^2+42x+x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-13x+6-6x^2-43x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x=1\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{56}\)(nhận)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{56}\right\}\)
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x+4x-2-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-6x+7x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x\left(x-1\right)+7\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(6x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\6x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\6x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{7}{6}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{1;-\dfrac{7}{6}\right\}\)
d) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{2}{7}\)
Ta có: \(\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)-\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3-x+5\right)\cdot\dfrac{-4x+6}{2-7x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\cdot\left(-4x+6\right)=0\)(Vì \(2-7x\ne0\forall x\) thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\-4x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\-4x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-8;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)