
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: (2x-10)(5x+25)=0
=>2x-10=0 hoặc 5x+25=0
=>x=5 hoặc x=-5
b: (x+15)(x-2)=0
=>x+15=0 hoặc x-2=0
=>x=-15 hoặc x=2
c: =>x(x-7)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=7

x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
⇔ x2 – 2x – 3x + 6 = 0
(Tách để xuất hiện nhân tử chung)
⇔ (x2 – 2x) – (3x – 6) = 0
⇔ x(x – 2) – 3(x – 2) = 0
⇔(x – 3)(x – 2) = 0
⇔ x – 3 = 0 hoặc x – 2 = 0
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3.
+ x – 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 2.
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {2; 3}.

- Bất phương trình a), c) là các bất phương trình bậc nhất một ẩn.
- Bất phương trình b) có a = 0 không thỏa mãn điều kiện a ≠ 0 nên không phải là bất phương trình bậc nhất một ẩn.
- Bất phương trình d) có mũ ở ẩn x là 2 nên không phải là bất phương trình bậc nhất một ẩn.

– x 2 + 5x – 6 = 0 ⇔ - x 2 + 2x + 3x – 6 = 0
⇔ - x(x – 2) + 3(x – 2) = 0 ⇔ (x – 2)(3 – x) = 0
⇔ x – 2 = 0 hoặc 3 – x = 0
x – 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 2
3 – x = 0 ⇔ x = 3
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 2 hoặc x = 3.
giải các Phương trình sau
a) (5x+3)(x2+1)(x-1)=0
b) (4x-1)(x-3)-(x-3)(5x+2)=0
c) (x+6)(3x-1)+x2-36 =0

a: =>(5x+3)(x-1)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-3/5
b: =>(x-3)(4x-1-5x-2)=0
=>(x-3)(-x-3)=0
=>x=-3 hoặc x=3
c: =>(x+6)(3x-1+x-6)=0
=>(x+6)(4x-7)=0
=>x=7/4 hoặc x=-6

2 x 2 + 5x + 3 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 2x + 3x + 3 = 0
⇔ 2x(x + 1) + 3(x + 1) = 0 ⇔ (2x + 3)(x + 1) = 0
⇔ 2x + 3 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
2x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -1,5
x + 1 = 0 ⇔ x = -1
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = -1,5 hoặc x = -1

(x – 1)( x 2 + 5x – 2) – ( x 3 – 1) = 0
⇔ (x – 1)( x 2 + 5x – 2) – (x – 1)( x 2 + x + 1) = 0
⇔ (x – 1)[( x 2 + 5x – 2) – ( x 2 + x + 1)] = 0
⇔ (x – 1)( x 2 + 5x – 2 – x 2 – x – 1) = 0
⇔ (x – 1)(4x – 3) = 0 ⇔ x – 1 = 0 hoặc 4x – 3 = 0
x – 1 = 0 ⇔ x = 1
4x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 0,75
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 1 hoặc x = 0,75

1.\(\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=x^2-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-3\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-3-x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
2.\(x^2+3x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.\(2x^2+5x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x+3x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+1\right)+3\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
4.\(x^3+x^2-12x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2+x-12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-4\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-3\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-3-x+2\right)=0\)
=>(x+2)(x-1)=0
=>x=-2 hoặc x=1
b: =>(x+1)(x+2)=0
=>x=-1 hoặc x=-2
c: =>(2x+3)(x+1)=0
=>x=-1 hoặc x=-3/2
d: =>x(x+4)(x-3)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{0;-4;3\right\}\)

3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
=> 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
=> x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2) = 0
=> (x - 3)(x - 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
=> 3x2 + 6x + x + 2 = 0
=> 3x(x + 2) + (x + 2) = 0
=> (3x + 1)(x + 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
1, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
2, \(x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)
3, \(3x^2+7x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
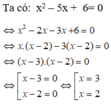
x2+5x+15= (x2+ 2 .x. 5/2 + 25/4) - 25/4 + 15 = (x - 5/2)2 - 25/4 + 60/4 = (x - 5/2)2 + 35/4 \(\ge\) 0 + 35/4 = 35/4 với mọi x
=> phương trình x2+5x+15= 0 vô nghiệm