Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(x-5=\frac{1}{3\left(x+2\right)}\left(đkxđ:x\ne-2\right)\)
\(< =>3\left(x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)=1\)
\(< =>3\left(x^2-3x-10\right)=1\)
\(< =>x^2-3x-10=\frac{1}{3}\)
\(< =>x^2-3x-\frac{31}{3}=0\)
giải pt bậc 2 dễ r
\(\frac{x}{3}+\frac{x}{4}=\frac{x}{5}-\frac{x}{6}\)
\(< =>\frac{4x+3x}{12}=\frac{6x-5x}{30}\)
\(< =>\frac{7x}{12}=\frac{x}{30}< =>12x=210x\)
\(< =>x\left(210-12\right)=0< =>x=0\)

a: 11x+4=-3/2
=>\(11x=-\dfrac{3}{2}-4=-\dfrac{11}{2}\)
=>\(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b: \(x^2-9+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3+2\right)=0\)
=>(x-3)(x+5)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: \(\dfrac{x-3}{5}+\dfrac{1+2x}{3}=6\)
=>\(\dfrac{3\left(x-3\right)+5\left(2x+1\right)}{15}=6\)
=>\(3x-9+10x+5=90\)
=>13x-4=90
=>13x=94
=>\(x=\dfrac{94}{13}\)
d: \(\dfrac{2}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{3x-11}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)(ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;2\right\}\))
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)-\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{3x-11}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>3x-11=2x-4-x-1
=>3x-11=x-5
=>2x=6
=>x=3(nhận)

Câu 1 :
a, \(\frac{3\left(2x+1\right)}{4}-\frac{5x+3}{6}=\frac{2x-1}{3}-\frac{3-x}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{6x+3}{4}+\frac{3-x}{4}=\frac{2x-1}{3}+\frac{5x+3}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{5x+6}{4}=\frac{9x+1}{6}\Leftrightarrow\frac{30x+36}{24}=\frac{36x+4}{24}\)
Khử mẫu : \(30x+36=36x+4\Leftrightarrow-6x=-32\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{32}{6}=\frac{16}{3}\)
tương tự
\(\frac{19}{4}-\frac{2\left(3x-5\right)}{5}=\frac{3-2x}{10}-\frac{3x-1}{4}\)
\(< =>\frac{19.5}{20}-\frac{8\left(3x-5\right)}{20}=\frac{2\left(3-2x\right)}{20}-\frac{5\left(3x-1\right)}{20}\)
\(< =>95-24x+40=6-4x-15x+5\)
\(< =>-24x+135=-19x+11\)
\(< =>5x=135-11=124\)
\(< =>x=\frac{124}{5}\)

a: Ta có: \(4x-2\left(1-x\right)=5\left(x-4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-2+2x=5x-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-18\)
b: Ta có: \(\dfrac{x}{6}+\dfrac{1-3x}{9}=\dfrac{-x+1}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x+4\left(1-3x\right)=3\left(-x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x+4-12x=-3x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x=-1\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
c: Ta có: \(\left(x+2\right)^2-3\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

TK
https://lazi.vn/edu/exercise/giai-phuong-trinh-4x-5-x-1-2-x-x-1-7-x-2-3-x-5
a: \(\Leftrightarrow4x-5=2x-2+x\)
=>4x-5=3x-2
=>x=3(nhận)
b: =>7x-35=3x+6
=>4x=41
hay x=41/4(nhận)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14}{3\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{x+2}{x-4}=\dfrac{-3}{2\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{28}{6\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{6\left(x+2\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{-9}{6\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5\left(x-4\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow28-6x-12=-9-5x+20\)
=>-6x+16=-5x+11
=>-x=-5
hay x=5(nhận)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=16\)
hay x=4(nhận)

Bài 1:
a) (5x-4)(4x+6)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x-4=0\\4x+6=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}5x=4\\4x=-6\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{4}{5}\\y=\frac{-3}{2}\end{cases}}}\)
b) (x-5)(3-2x)(3x+4)=0
<=> x-5=0 hoặc 3-2x=0 hoặc 3x+4=0
<=> x=5 hoặc x=\(\frac{3}{2}\)hoặc x=\(\frac{-4}{3}\)
c) (2x+1)(x2+2)=0
=> 2x+1=0 (vì x2+2>0)
=> x=\(\frac{-1}{2}\)
bài 1:
a) (5x - 4)(4x + 6) = 0
<=> 5x - 4 = 0 hoặc 4x + 6 = 0
<=> 5x = 0 + 4 hoặc 4x = 0 - 6
<=> 5x = 4 hoặc 4x = -6
<=> x = 4/5 hoặc x = -6/4 = -3/2
b) (x - 5)(3 - 2x)(3x + 4) = 0
<=> x - 5 = 0 hoặc 3 - 2x = 0 hoặc 3x + 4 = 0
<=> x = 0 + 5 hoặc -2x = 0 - 3 hoặc 3x = 0 - 4
<=> x = 5 hoặc -2x = -3 hoặc 3x = -4
<=> x = 5 hoặc x = 3/2 hoặc x = 4/3
c) (2x + 1)(x^2 + 2) = 0
vì x^2 + 2 > 0 nên:
<=> 2x + 1 = 0
<=> 2x = 0 - 1
<=> 2x = -1
<=> x = -1/2
bài 2:
a) (2x + 7)^2 = 9(x + 2)^2
<=> 4x^2 + 28x + 49 = 9x^2 + 36x + 36
<=> 4x^2 + 28x + 49 - 9x^2 - 36x - 36 = 0
<=> -5x^2 - 8x + 13 = 0
<=> (-5x - 13)(x - 1) = 0
<=> 5x + 13 = 0 hoặc x - 1 = 0
<=> 5x = 0 - 13 hoặc x = 0 + 1
<=> 5x = -13 hoặc x = 1
<=> x = -13/5 hoặc x = 1
b) (x^2 - 1)(x + 2)(x - 3) = (x - 1)(x^2 - 4)(x + 5)
<=> x^4 - x^3 - 7x^2 + x + 6 = x^4 + 4x^3 - 9x^2 - 16x + 20
<=> x^4 - x^3 - 7x^2 + x + 6 - x^4 - 4x^3 + 9x^2 + 16x - 20 = 0
<=> -5x^3 - 2x^2 + 17x - 14 = 0
<=> (-x + 1)(x + 2)(5x - 7) = 0
<=> x - 1 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0 hoặc 5x - 7 = 0
<=> x = 0 + 1 hoặc x = 0 - 2 hoặc 5x = 0 + 7
<=> x = 1 hoặc x = -2 hoặc 5x = 7
<=> x = 1 hoặc x = -2 hoặc x = 7/5

a, làm tương tự với phần b bài nãy bạn đăng
b, \(\left(x+1\right)^2-5=x^2+11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1-5=x^2+11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-10=0\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = { 5 } ( kết luận như thế với các phần sau nhé ! )
c, \(3\left(3x-1\right)=3x+5\Leftrightarrow9x-3-3x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-8=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}\)
d, \(3x\left(2x-3\right)-3\left(3+2x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-9x-9-6x^2=0\Leftrightarrow-9x=9\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
e, khai triển nó ra rút gọn rồi giải thôi nhé! ( tự làm )
f, \(\left(x-1\right)^2-x\left(x+1\right)+3\left(x-2\right)+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1-x^2+x+3x-6+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{0}{2}\)vô lí
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm

a) Ta có: \(7-\left(2x+4\right)=-\left(x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7-2x-4=-x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+3+x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=-7\)
hay x=7
Vậy: S={7}
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{2+x}{5}-0.5x=\dfrac{1-2x}{4}+0.25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4\left(2+x\right)}{20}-\dfrac{0.5x\cdot20}{20}=\dfrac{5\left(1-2x\right)}{20}+\dfrac{20\cdot0.25}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(2+x\right)-10x=5\left(1-2x\right)+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8+4x-10x=5-10x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+8=-10x+10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+8+10x-10=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=2\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
d) Ta có: \(\dfrac{x-1}{59}+\dfrac{x-2}{58}+\dfrac{x-3}{57}=\dfrac{x-59}{1}+\dfrac{x-58}{2}+\dfrac{x-57}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{59}-1+\dfrac{x-2}{58}-1+\dfrac{x-3}{57}-1=\dfrac{x-59}{1}-1+\dfrac{x-58}{2}-1+\dfrac{x-57}{3}-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-60}{59}+\dfrac{x-60}{58}+\dfrac{x-60}{57}=\dfrac{x-60}{1}+\dfrac{x-60}{2}+\dfrac{x-60}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-60\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{59}+\dfrac{1}{58}+\dfrac{1}{57}\right)-\left(x-60\right)\left(1+\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-60\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{59}+\dfrac{1}{58}+\dfrac{1}{57}-1-\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=0\)
mà \(\dfrac{1}{59}+\dfrac{1}{58}+\dfrac{1}{57}-1-\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{3}\ne0\)
nên x-60=0
hay x=60
Vậy: S={60}

bạn đăng tách cho mn cùng giúp nhé
Bài 1 :
a, \(\Leftrightarrow11-x=12-8x\Leftrightarrow7x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{7}\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x^2+4x+4\right)-8x^2=2\left(x^3-8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+8x^2+8x-8x^2=2x^3-16\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow3-2x=-x-4\Leftrightarrow x=7\)
d, \(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+12x-8+9x^2-1=x^3+3x^2+3x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+12x-9=3x^2+3x+1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{10}{9}\)
e, \(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x-3=2x^2+9x-5\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
f, \(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+3x-1-x^3-2x^2-x=10x-5x^2-11x-22\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-5x^2+2x-1=-5x^2-x-22\Leftrightarrow3x=-21\Leftrightarrow x=-7\)

=) vào ngay quả bảng phá dấu GTTĐ, cay thế :<
a, \(3x+\frac{2x}{3}-3=\frac{5}{2}x-2\Leftrightarrow\frac{18x+4x-18}{6}=\frac{15x-12}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow22x-18=15x-12\Leftrightarrow7x=6\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{6}{7}\)
Vậy pt có nghiệm x = 6/7
b, \(\frac{3\left(2x+1\right)}{4}-\frac{5x+3}{6}+\frac{x+1}{3}=\frac{x+7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{9\left(2x+1\right)-2\left(5x+3\right)+4\left(x+1\right)}{12}=\frac{x+7}{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow18x+9-10x-6+4x+4=x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+7=x+7\Leftrightarrow11x=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy pt có nghiệm là x = 0
c, \(\frac{3x}{x-3}-\frac{x-3}{x+3}=2\)ĐK : \(x\ne\pm3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-3\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{2\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow3x^2+9x-x^2+6x-9=2\left(x^2-9\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+15x-9=2x^2-18\Leftrightarrow15x+9=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{9}{15}=-\frac{3}{5}\)
Vậy pt có nghiệm là x = -3/5
d, Sửa đề : \(\frac{x+10}{2003}+\frac{x+6}{2007}+\frac{x+2}{2011}+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+10}{2003}+1+\frac{x+6}{2007}+1+\frac{x+2}{2011}+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2013}{2003}+\frac{x+2013}{2007}+\frac{x+2013}{2011}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2013\right)\left(\frac{1}{2003}+\frac{1}{2007}+\frac{1}{2011}\ne0\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=-2013\)
Vậy pt có nghiệm là x = -2013
e, \(4\left(x+5\right)-3\left|2x-1\right|=10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+20-3\left|2x-1\right|=10\Leftrightarrow-3\left|2x-1\right|=-10-4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|=\frac{10+4x}{3}\)
ĐK : \(\frac{10+4x}{3}\ge0\Leftrightarrow10+4x\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge-\frac{10}{4}=-\frac{5}{2}\)
TH1 : \(2x-1=\frac{10+4x}{3}\Rightarrow6x-3=10+4x\Leftrightarrow2x=13\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{13}{2}\)( tm )
TH2 : \(2x-1=\frac{-10-4x}{3}\Rightarrow6x-3=-10-4x\Leftrightarrow10x=-7\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{7}{10}\)( tm )
f, để mình xem lại đã, quên cách phá GTTĐ rồi :v :>

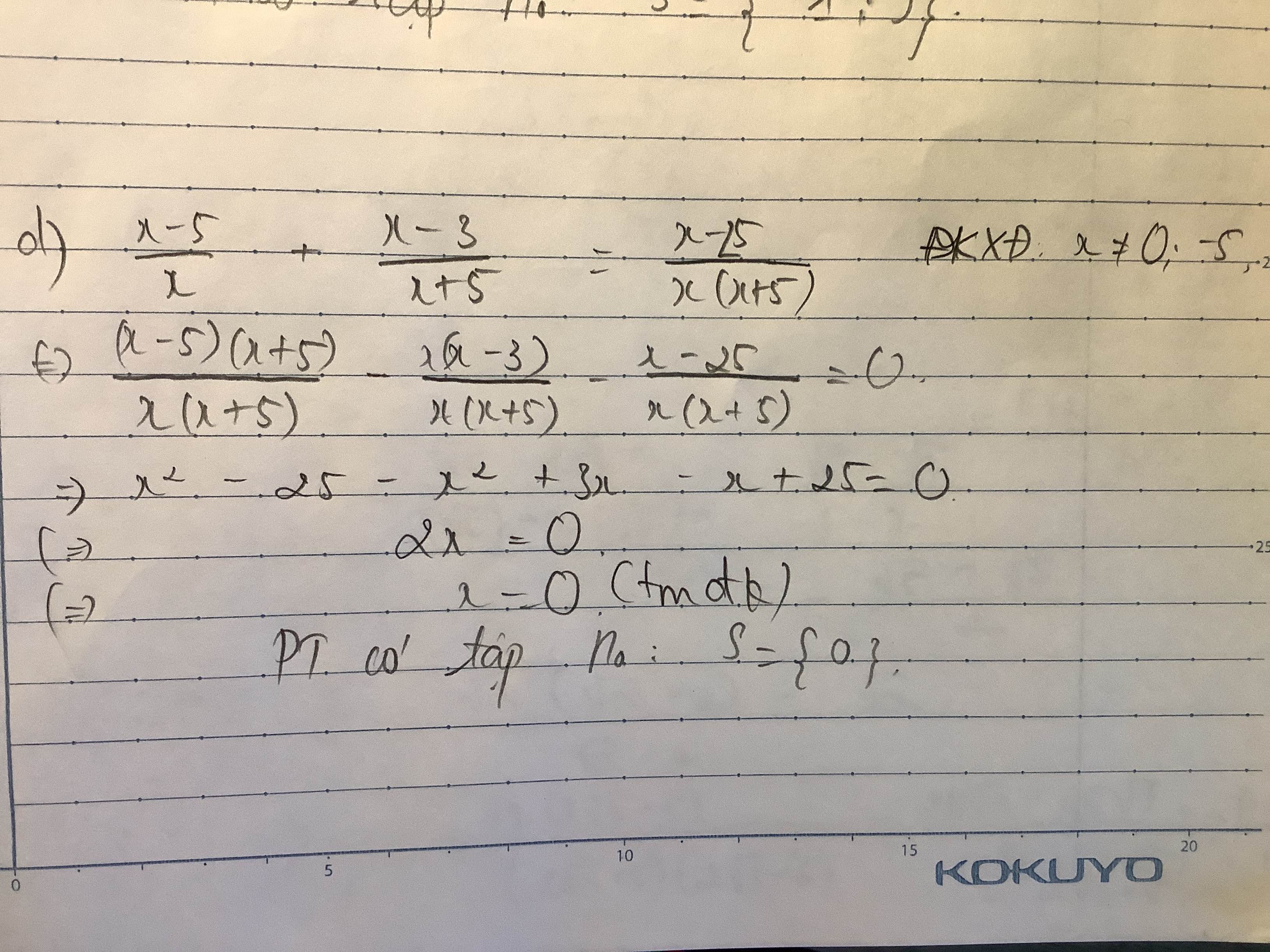

a) (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1) – 2x = x(x – 1)(x + 1)
⇔ x3 – 1 – 2x = x(x2 – 1)
⇔ x2 – 1 – 2x = x3 – x
⇔ -2x + x = 1 ⇔ - x = 1 ⇔ x = -1
Tập nghiệm của phương trình: S = { -1}
b) x2 – 3x – 4 = 0
⇔ x2 – 4x + x – 4 = 0 ⇔ x(x – 4) + (x – 4) = 0
⇔ (x – 4)(x + 1) = 0 ⇔ x – 4 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
⇔ x = 4 hoặc x = -1
Tập nghiệm của phương trình: S = {4; -1}
c) ĐKXĐ : x – 1 ≠ 0 và x2 + x + 1 ≠ 0 (khi đó : x3 – 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1) ≠ 0)
⇔ x ≠ 1
Quy đồng mẫu thức hai vế:
Khử mẫu, ta được: 2x2 + 2x + 2 – 3x2 = x2 – x
⇔ -2x2 + 3x + 2 = 0 ⇔ 2x2 – 3x – 2 = 0
⇔ 2x2 – 4x + x – 2 = 0 ⇔ 2x(x – 2) + (x – 2) = 0
⇔ (x – 2)(2x + 1) = 0 ⇔ x – 2 = 0 hoặc 2x + 1 = 0
⇔ x = 2 hoặc x = -1/2(thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Tập nghiệm của phương trình : S = {2 ; -1/2}
d) ĐKXĐ : x – 5 ≠ 0 và x – 1 ≠ 0 (khi đó : x2 – 6x + 5 = (x – 5)(x – 1) ≠ 0)
Quy đồng mẫu thức hai vế :
Khử mẫu, ta được : x – 1 – 3 = 5x – 25 ⇔ -4x = -21
⇔ x = 21/4 (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
Tập nghiệm của phương trình : S = {21/4}