Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\Delta=2^2-4\left(m-5\right)\)
\(=4-4m+20=-4m+24\)
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm thì \(\Delta>=0\)
=>-4m+24>=0
=>-4m>=-24
=>m<=6
Theo Vi-et, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{-2}{1}=-2\\x_1\cdot x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_2^2-2x_1+m^2-11m+26=0\)
=>\(x_2^2+x_1\left(x_1+x_2\right)+m^2-11m+26=0\)
=>\(\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)+x_1x_2+m^2-11m+26=0\)
=>\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-x_1x_2+m^2-11m+26=0\)
=>\(\left(-2\right)^2-\left(m-5\right)+m^2-11m+26=0\)
=>\(4-m+5+m^2-11m+26=0\)
=>\(m^2-12m+35=0\)
=>(m-5)(m-7)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m-5=0\\m-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=5\left(nhận\right)\\m=7\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

1, Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-5\\x_1x_2=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=\left(x_1-2x_2\right)\left(2x_1-x_2\right)\\ =2x_1^2-4x_1x_2-x_1x_2+2x_1^2\\ =2\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)-5x_1x_2\\ =2\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\right]-5x_1x_2\\ =2\left(-5\right)^2-4.\left(-6\right)-5.\left(-6\right)\\ =104\)
2, Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5\\x_1x_2=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(B=x_1^3x_2+x_1x_2^3\\ =x_1x_2\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)\\ =\left(-3\right)\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\right]\\ =\left(-3\right)\left[5^2-2\left(-3\right)\right]\\ =-93\)

Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-4\right)\\x_1x_2=-m^2+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}+\dfrac{4}{x_1x_2}=1\)
Thay vào ta được : \(\dfrac{2\left(m-4\right)+4}{-m^2+4}=1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2m-4}{\left(2-m\right)\left(m+2\right)}=1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-2}{m+2}=1\Rightarrow-2=m+2\Leftrightarrow m=-4\)

a) ∆' = [-(m - 3)]² - (m² + 3)
= m² - 6m + 9 - m² - 3
= -6m + 6
Để phương trình đã cho có 2 nghiệm thì ∆' ≥ 0
⇔ -6m + 6 ≥ 0
⇔ 6m ≤ 6
⇔ m ≤ 1
Vậy m ≤ 1 thì phương trình đã cho luôn có 2 nghiệm
b) Theo định lý Viét, ta có:
x₁ + x₂ = 2(m - 3) = 2m - 6
x₁x₂ = m² + 3
Ta có:
(x₁ - x₂)² - 5x₁x₂ = 4
⇔ x₁² - 2x₁x₂ + x₂² - 5x₁x₂ = 4
⇔ x₁² + 2x₁x₂ + x₂² - 2x₁x₂ - 2x₁x₂ - 5x₁x₂ = 4
⇔ (x₁ + x₂)² - 9x₁x₂ = 4
⇔ (2m - 6)² - 9(m² + 3) = 4
⇔ 4m² - 24m + 36 - 9m² - 27 = 4
⇔ -5m² - 24m + 9 = 4
⇔ 5m² + 24m - 5 = 0
⇔ 5m² + 25m - m - 5 = 0
⇔ (5m² + 25m) - (m + 5) = 0
⇔ 5m(m + 5) - (m + 5) = 0
⇔ (m + 5)(5m - 1) = 0
⇔ m + 5 = 0 hoặc 5m - 1 = 0
*) m + 5 = 0
⇔ m = -5 (nhận)
*) 5m - 1 = 0
⇔ m = 1/5 (nhận)
Vậy m = -5; m = 1/5 thì phương trình đã cho có 2 nghiệm thỏa mãn yêu cầu
a: \(\Delta=\left[-2\left(m-3\right)\right]^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(m^2+3\right)\)
\(=\left(2m-6\right)^2-4\left(m^2+3\right)\)
\(=4m^2-24m+36-4m^2-12=-24m+24\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì \(\Delta>=0\)
=>-24m+24>=0
=>-24m>=-24
=>m<=1
b: Theo Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{-\left[-2\left(m-3\right)\right]}{1}=2\left(m-3\right)\\x_1\cdot x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m^2+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2-5x_1x_2=4\)
=>\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2-5x_2x_1=4\)
=>\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-9x_1x_2=4\)
=>\(\left(2m-6\right)^2-9\left(m^2+3\right)=4\)
=>\(4m^2-24m+36-9m^2-27-4=0\)
=>\(-5m^2-24m+5=0\)
=>\(-5m^2-25m+m+5=0\)
=>\(-5m\left(m+5\right)+\left(m+5\right)=0\)
=>(m+5)(-5m+1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m+5=0\\-5m+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-5\left(nhận\right)\\m=\dfrac{1}{5}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

x1+x2=2m-2
2x1-x2=2
=>3x1=2m và 2x1-x2=2
=>x1=2m/3 và x2=4m/3-2
x1*x2=-2m+1
=>8/9m^2-4/3m+2m-1=0
=>8/9m^2+2/3m-1=0
=>8m^2+6m-9=0
=>m=3/4 hoặc m=-3/2
\(x^2-2\left(m-1\right)x-2m+1=0\left(1\right)\)
Để phương trình (1) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta>0\Rightarrow\left[2\left(m-1\right)\right]^2-4\left(-2m+1\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m-1\right)^2+8m-4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4+8m-4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2>0\Leftrightarrow m\ne0\)
Vậy với \(\forall m\ne0\) thì phương trình (1) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt.
Theo định lí Viete cho phương trình (1) ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=-2m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có \(2x_1-x_2=2\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x_1+x_2\right)-2=3x_2\left(1'\right)\\\left(x_1+x_2\right)+2=3x_1\left(2'\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy (1') nhân cho (2') ta được:
\(\left[2\left(x_1+x_2\right)-2\right]\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)+2\right]=9x_1x_2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[2.2\left(m-1\right)-2\right]\left[2\left(m-1\right)+2\right]=9\left(-2m+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4m-6\right).2m=-18m+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8m^2+6m-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=\dfrac{3}{4}\\m=\dfrac{-3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thử lại ta có m=3/4 hay m=-3/2

\(\Delta'=m-1\ge0\Rightarrow m\ge1\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=m^2-m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=x_1^3+x_2^3-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)\)
\(=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^3-3x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)\)
\(=8m^3-3.2m\left(m^2-m+1\right)-4m\)
\(=2m^3+6m^2-10m\)
\(=2\left(m^3+3m^2-5m+1\right)-2\)
\(=2\left(m-1\right)\left[\left(m^2-1\right)+4m\right]-2\)
Do \(m\ge1\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-1\ge0\\\left(m^2-1\right)+4m>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(m-1\right)\left[\left(m^2-1\right)+4m\right]\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow A\ge-2\)
\(A_{min}=-2\) khi \(m=1\)

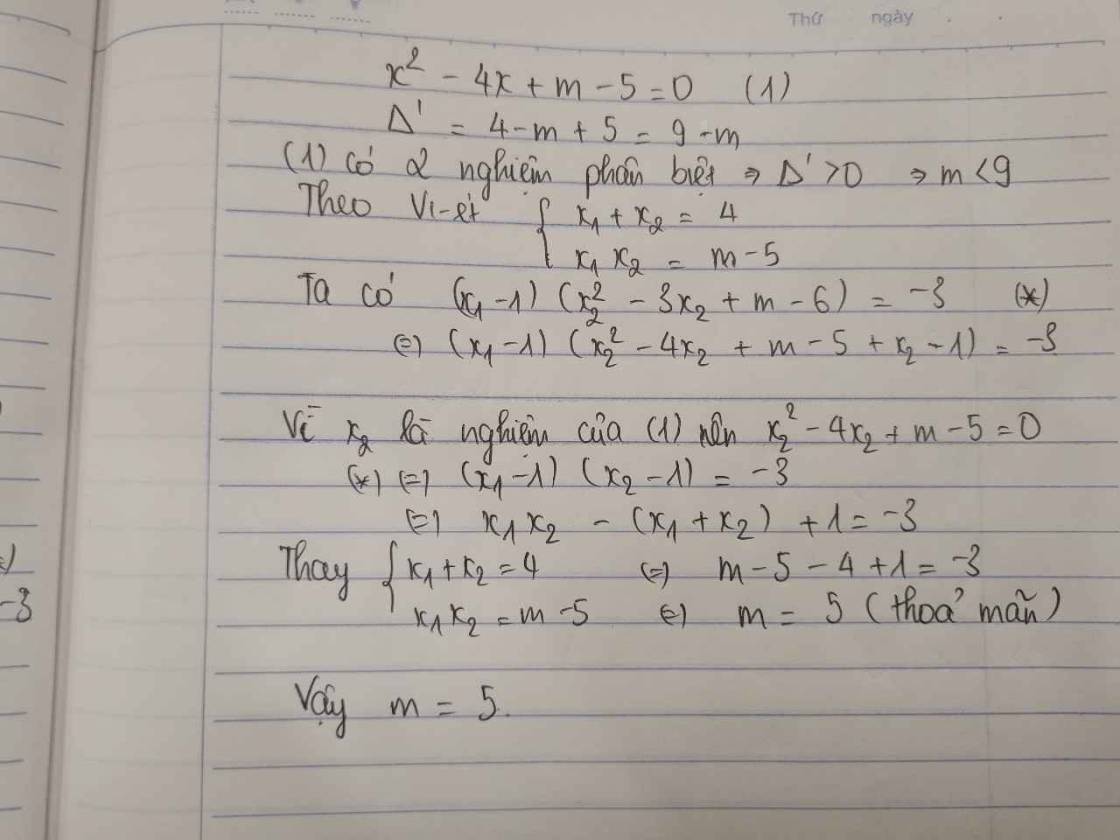

Moij người giúp mình với ạ mình đang cần gấp ạ