Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a.
$x^2-y^2-2x+2y=(x^2-y^2)-(2x-2y)=(x-y)(x+y)-2(x-y)=(x-y)(x+y-2)$
b.
$x^2(x-1)+16(1-x)=x^2(x-1)-16(x-1)=(x-1)(x^2-16)=(x-1)(x-4)(x+4)$
c.
$x^2+4x-y^2+4=(x^2+4x+4)-y^2=(x+2)^2-y^2=(x+2-y)(x+2+y)$
d.
$x^3-3x^2-3x+1=(x^3+1)-(3x^2+3x)=(x+1)(x^2-x+1)-3x(x+1)$
$=(x+1)(x^2-4x+1)$
e.
$x^4+4y^4=(x^2)^2+(2y^2)^2+2.x^2.2y^2-4x^2y^2$
$=(x^2+2y^2)^2-(2xy)^2=(x^2+2y^2-2xy)(x^2+2y^2+2xy)$
f.
$x^4-13x^2+36=(x^4-4x^2)-(9x^2-36)$
$=x^2(x^2-4)-9(x^2-4)=(x^2-9)(x^2-4)=(x-3)(x+3)(x-2)(x+2)$
g.
$(x^2+x)^2+4x^2+4x-12=(x^2+x)^2+4(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)^2-2(x^2+x)+6(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)(x^2+x-2)+6(x^2+x-2)=(x^2+x-2)(x^2+x+6)$
$=[x(x-1)+2(x-1)](x^2+x+6)=(x-1)(x+2)(x^2+x+6)$
h.
$x^6+2x^5+x^4-2x^3-2x^2+1$
$=(x^6+2x^5+x^4)-(2x^3+2x^2)+1$
$=(x^3+x^2)^2-2(x^3+x^2)+1=(x^3+x^2-1)^2$

a) Sắp xếp đa thức - 3 x 3 + 5 x 2 – 9x + 15 và -3x + 5.
Thực hiện phép chia thu được đa thức thương x 2 + 3.
b) Sắp xếp đa thức x 3 – 4 x 2 + 5x – 20.
Thực hiện phép chia thu được đa thức thương x 2 + 5.

x3 – 7x + 3 – x2 = x3 – x2 – 7x + 3
Thực hiện phép chia:
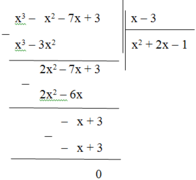
Vậy (x3 – x2 – 7x + 3) : (x – 3) = x2 + 2x – 1

a: Ta có: \(x^2-4y^2-2x-4y\)
\(=\left(x-2y\right)\left(x+2y\right)-2\left(x+2y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+2y\right)\left(x-2y-2\right)\)
c: Ta có: \(x^3+2x^2y-x-2y\)
\(=x^2\left(x+2y\right)-\left(x+2y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+2y\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
d: Ta có: \(3x^2-3y^2-2\cdot\left(x-y\right)^2\)
\(=3\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-2\cdot\left(x-y\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(3x+3y-2x+2y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+5y\right)\)
e: Ta có: \(x^3-4x^2-9x+36\)
\(=x^2\left(x-4\right)-9\left(x-4\right)\)
\(=\left(x-4\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)\)
f: Ta có: \(x^2-y^2-2x-2y\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-2\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(x-y-2\right)\)

a) Để thu gọn đa thức Px, ta sắp xếp các hạng tử theo lũy thừa giảm dần của biến x:
Px = x⁴ - 2x³ + x - 5 + / 3x / -2x + 2x³ = x⁴ + 2x³ - 2x³ + x + / 3x / -2x = x⁴ + (2x³ - 2x³) + (x + / 3x / -2x) = x⁴ + (x + / 3x / -2x)
Tương tự, để thu gọn đa thức Qx, ta sắp xếp các hạng tử theo lũy thừa giảm dần của biến x:
Qx = (2x² - x³) - (2 - x⁴ - x³) - 3x = -x³ + 2x² - 2 + x⁴ + x³ - 3x = x⁴ + (-x³ + x³) + 2x² - 3x - 2 = x⁴ + 2x² - 3x - 2
b) Để tính Ax = Px - Qx, ta trừ từng hạng tử của Qx từ Px:
Ax = (x⁴ + (x + / 3x / -2x)) - (x⁴ + 2x² - 3x - 2) = x⁴ + x + / 3x / -2x - x⁴ - 2x² + 3x + 2 = x⁴ - x⁴ + x + / 3x / -2x - 2x² + 3x + 2 = x + / 3x / -2x - 2x² + 3x + 2
c) Để chứng tỏ x = 1 là một nghiệm của đa thức Ax, ta thay x = 1 vào Ax và kiểm tra xem kết quả có bằng 0 hay không:
Ax = 1 + / 3(1) / -2(1) - 2(1)² + 3(1) + 2 = 1 + 3/2 - 2 + 3 + 2 = 6.5
Vì Ax không bằng 0 khi thay x = 1, nên x = 1 không phải là một nghiệm của đa thức Ax.
a: P(x)=x^4-2x^3+x+2x^3-2x-5+3x
=x^4-x+3x-5
=x^4+2x-5
Q(x)=2x^2-x^3-2+x^4+x^3-3x
=x^4+2x^2-3x-2
b: A(x)=P(x)-Q(x)
=x^4+2x-5-x^4-2x^2+3x+2
=-2x^2+5x-3
c: A(1)=-2+5-3=0
=>x=1 là nghiệm của A(x)

1: \(=\dfrac{-\left[\left(x+5\right)^2-9\right]}{\left(x+2\right)^2}=\dfrac{-\left(x+5-3\right)\left(x+5+3\right)}{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-\left(x+2\right)\left(x+8\right)}{\left(x+2\right)^2}=\dfrac{-\left(x+8\right)}{x+2}\)
2: \(=\dfrac{2x\left(x^2-4x+16\right)}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x^2-4x+16\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{x+4}\)
3: \(=\dfrac{5x\left(x^2+1\right)}{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}=\dfrac{5x}{x^2-1}\)
4: \(=\dfrac{3\left(x^2-4x+4\right)}{x\left(x^3-8\right)}=\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)^2}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x^2+2x+4\right)}\)
5: \(=\dfrac{2a\left(a-b\right)}{a\left(c+d\right)-b\left(c+d\right)}=\dfrac{2a\left(a-b\right)}{\left(c+d\right)\left(a-b\right)}=\dfrac{2a}{c+d}\)
6: \(=\dfrac{x\left(x-y\right)}{\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}\cdot\left(-1\right)=\dfrac{-x}{x+y}\)
7: \(=\dfrac{2\left(1-a\right)}{-\left(1-a^3\right)}=\dfrac{-2\left(1-a\right)}{\left(1-a\right)\left(1+a+a^2\right)}=-\dfrac{2}{1+a+a^2}\)
8: \(=\dfrac{x^4\left(x^3-1\right)}{\left(x^3-1\right)\left(x^3+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^4}{x^3+1}\)
9: \(=\dfrac{\left(x+2-x+2\right)\left(x+2+x-2\right)}{16x}=\dfrac{4\cdot2x}{16x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
10: \(=\dfrac{0.5\left(49x^2-y^2\right)}{0.5x\left(7x-y\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x}\cdot\dfrac{\left(7x-y\right)\left(7x+y\right)}{7x-y}\)
\(=\dfrac{7x+y}{x}\)

Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=2x^3-3x^2+x+a\)
Ta có: phép chia \(f\left(x\right)\) cho \(x+2\) có dư là \(R=f\left(-2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-2\right)=2.\left(-2\right)^3-3.\left(-2\right)^2+\left(-2\right)+a\)
\(f\left(-2\right)=2.\left(-8\right)-3.4-2+a\)
\(f\left(-2\right)=-16-12-2+a\)
\(f\left(-2\right)=-20+a\)
Để \(f\left(x\right)\) chia hết cho \(x+2\) thì \(R=0\) hay \(f\left(-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-20+a=0\Leftrightarrow a=20\)

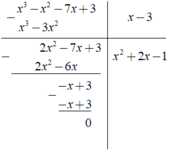
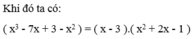

a) P(x) = – x6 – x4 – 4x3 + 3x2+ 5
Q(x) = 2x5 – x4 – x3 + x – 1
b) P(x) + Q(x) = – x6 + 2x5– 2x4 – 5x3 + 3x2+ x + 4
P(x) – Q(x) = – x6 – 2x5 – 3x3 + 3x2– x + 6
Thank you so much !!!