
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(A=-5x^3+9x^3-2x^2-2x^2+x-x+1\)
\(=4x^3-4x^2+1\)
\(B=-4x^3+2x^3-2x^2+2x^2+6x-9x-2\)
\(=-2x^3-3x-2\)
\(C=x^3-6x^2+2x-4\)
b: \(A\left(x\right)+B\left(x\right)-C\left(x\right)\)
\(=4x^3-4x^2+1-2x^3-3x-2+x^3-6x^2+2x-4\)
\(=3x^3-10x^2-x-4\)

câu 4: b, đề bài là tính giá trị của A tại x =-1/2;y=-1
Tk
Bài 2
a) F(x)-G(x)+H(x)= \(x^3-2x^2+3x+1-\left(x^3+x-1\right)+\left(2x^2-1\right)\)
= \(x^3-2x^2+3x+1-x^3-x+1+2x^2-1\)
= \(x^3-x^3-2x^2+2x^2+3x-x+1+1-1\)
= 2x + 1
b) 2x + 1 = 0
2x = -1
x=\(\dfrac{-1}{2}\)

`P(x)=\(4x^2+x^3-2x+3-x-x^3+3x-2x^2\)
`= (x^3-x^3)+(4x^2-2x^2)+(-2x-x+3x)+3`
`= 2x^2+3`
`Q(x)=`\(3x^2-3x+2-x^3+2x-x^2\)
`= -x^3+(3x^2-x^2)+(-3x+2x)+2`
`= -x^3+2x^2-x+2`
`P(x)-Q(x)-R(x)=0`
`-> P(X)-Q(x)=R(x)`
`-> R(x)=P(x)-Q(x)`
`-> R(x)=(2x^2+3)-(-x^3+2x^2-x+2)`
`-> R(x)=2x^2+3+x^3-2x^2+x-2`
`= x^3+(2x^2-2x^2)+x+(3-2)`
`= x^3+x+1`
`@`\(\text{dn inactive.}\)
a: P(x)-Q(x)-R(x)=0
=>R(x)=P(x)-Q(x)
=2x^2+3+x^3-2x^2+x-2
=x^3+x+1

a: \(M\left(x\right)=2x^2+3\)
\(N\left(x\right)=3x^3-2x^2+x\)
b: \(M\left(x\right)+N\left(x\right)=3x^3+x+3\)
\(M\left(x\right)-N\left(x\right)=2x^2+3-3x^3+2x^2-x=-3x^3+2x^2-x+3\)

a) Ta có:
B = (A + B) – A
= (x3 + 3x + 1) – (x4 + x3 – 2x – 2)
= x3 + 3x + 1 – x4 - x3 + 2x + 2
= – x4 + (x3 – x3) + (3x + 2x) + (1 + 2)
= – x4 + 5x + 3.
b) C = A - (A – C)
= x4 + x3 – 2x – 2 – x5
= – x5 + x4 + x3 – 2x – 2.
c) D = (2x2 – 3) . A
= (2x2 – 3) . (x4 + x3 – 2x – 2)
= 2x2 . (x4 + x3 – 2x – 2) + (-3) .(x4 + x3 – 2x – 2)
= 2x2 . x4 + 2x2 . x3 + 2x2 . (-2x) + 2x2 . (-2) + (-3). x4 + (-3) . x3 + (-3). (-2x) + (-3). (-2)
= 2x6 + 2x5 – 4x3 – 4x2 – 3x4 – 3x3 + 6x + 6
= 2x6 + 2x5 – 3x4 + (-4x3 – 3x3) – 4x2+ 6x + 6
= 2x6 + 2x5 – 3x4 – 7x3 – 4x2+ 6x + 6.
d) P = A : (x+1) = (x4 + x3 – 2x – 2) : (x + 1)
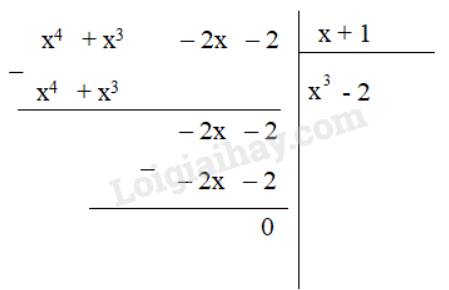
Vậy P = x3 - 2
e) Q = A : (x2 + 1)
Nếu A chia cho đa thức x2 + 1 không dư thì có một đa thức Q thỏa mãn
Ta thực hiện phép chia (x4 + x3 – 2x – 2) : (x2 + 1)
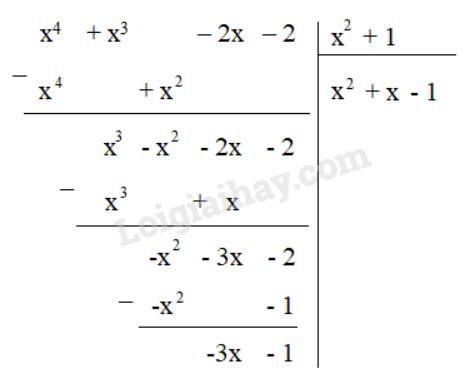
Do phép chia có dư nên không tồn tại đa thức Q thỏa mãn

Ta có
P ( x ) = 2 x 3 − 3 x + x 5 − 4 x 3 + 4 x − x 5 + x 2 − 2 = x 5 − x 5 + 2 x 3 − 4 x 3 + x 2 + ( 4 x − 3 x ) − 2 = − 2 x 3 + x 2 + x − 2 Và Q ( x ) = x 3 − 2 x 2 + 3 x + 1 + 2 x 2 = x 3 + − 2 x 2 + 2 x 2 + 3 x + 1 = x 3 + 3 x + 1
Khi đó
M ( x ) = P ( x ) + Q ( x ) = − 2 x 3 + x 2 + x − 2 + x 3 + 3 x + 1 = − 2 x 3 + x 2 + x − 2 + x 3 + 3 x + 1 = − 2 x 3 + x 3 + x 2 + ( x + 3 x ) − 2 + 1 = − x 3 + x 2 + 4 x − 1
Bậc của M ( x ) = - x 3 + x 2 + 4 x - 1 l à 3
Chọn đáp án C

Lời giải:
a.
$P(x)=2x^4+(x^3-5x^3)+2x^2+(-2x+x)+1$
$=2x^4-4x^3+2x^2-x+1$
b)
$P(0)=2.0^4-4.0^3+2.0^2-0+1=1$
$P(1)=2-4+2-1+1=0$
c.
$P(1)=0$ (theo phần b) nên $x=1$ là nghiệm của đa thức $P(x)$
$P(-1)=2+4+2+1+1=10\neq 0$ nên $x=-1$ không là nghiệm của đa thức $P(x)$

\(P\left(x\right)=x^3-3x-x^2+1;Q\left(x\right)=2x^2-x^3+x-5\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}P\left(x\right)+Q\left(x\right)=x^2-2x-4\\P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=2x^3-3x^2-4x+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(P\left(x\right)+Q\left(x\right)=x^2-2x-4=\left(x-1\right)^2-5=0\)
Nghiệm \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{5}+1\\x=-\sqrt{5}+1\end{matrix}\right.\)

c. Ta có h(x) = 0 ⇒ 5x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = -1/5
Vậy nghiệm của đa thức h(x) là x = -1/5 (1 điểm)
\(M\left(x\right)=x^3-2x^2+2x-1=\left(x^3-x^2\right)-\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-x\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\\left(x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\right)+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\ge\frac{3}{4}>0\Rightarrow vn\end{cases}}\)
Vậy đa thức M(x) có 1 nghiệm duy nhất x = 1