
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


con A bn bấm nhầm đúng ko mik sửa lại nhé
A= 20142 - 4018. 1014 + 10142
= (2014 - 1014)2
= 10002
= 1000000
B= 9x2 - 6x + 2013
= 9x2 - 6x + 1 + 2012
= (3x - 1)2 + 2012
thay x = \(\dfrac{200001}{3}\)vào biểu thức B ta có:
B = (3.\(\dfrac{200001}{3}\)- 1)2 + 2012
= (200001 - 1)2 + 2012
= 2000002 + 2012
= 40000002012
mik chỉ làm đc đến đây thôi nhưng mong bn ủng hộ! ![]()
![]()
![]()

Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ 3.
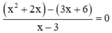
Suy ra: (x2 + 2x) – (3x + 6) = 0
⇔ x(x + 2) – 3(x + 2) = 0
⇔ (x – 3)(x + 2) = 0
⇔ x – 3 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3 (Không thỏa mãn đkxđ)
+ x + 2 = 0 ⇔ x = -2 (Thỏa mãn đkxđ).
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-2}.

Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ -7; x ≠ 3/2.
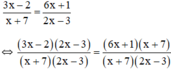
Suy ra: (3x – 2)(2x – 3) = (6x + 1)(x + 7)
⇔ 6x2 – 9x – 4x + 6 = 6x2 + 42x + x + 7
⇔ - 4x - 9x - 42x - x = 7 - 6
⇔ - 56x = 1
⇔ x = -1/56 (thỏa mãn đkxđ)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-1/56}.

2x(6x – 1) > (3x – 2)(4x + 3)
⇔ 12x2 – 2x > 12x2 – 8x + 9x – 6
⇔ 12x2 – 2x – 12x2 + 8x – 9x > -6 (Chuyển vế, đổi dấu)
⇔ -3x > -6
⇔ x < 2 (Chia cả hai vế cho -3 < 0, BPT đổi chiều)
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm x < 2.

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;0\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+3x+x^2-3x+2=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-2\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: S={1}
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-7;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x+7}=\dfrac{6x+1}{2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=\left(6x+1\right)\left(x+7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-9x-4x+6=6x^2+42x+x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-13x+6-6x^2-43x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x=1\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{56}\)(nhận)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{56}\right\}\)
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x+4x-2-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-6x+7x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x\left(x-1\right)+7\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(6x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\6x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\6x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{7}{6}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{1;-\dfrac{7}{6}\right\}\)
d) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{2}{7}\)
Ta có: \(\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)-\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3-x+5\right)\cdot\dfrac{-4x+6}{2-7x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\cdot\left(-4x+6\right)=0\)(Vì \(2-7x\ne0\forall x\) thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\-4x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\-4x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-8;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)


a: 5-3x=6x+7
=>-3x-6x=7-5
=>-9x=2
=>\(x=-\dfrac{2}{9}\)
b: \(\dfrac{3x-2}{6}-5=3-\dfrac{2\left(x+7\right)}{4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{3x-2}{6}+\dfrac{x+7}{2}=8\)
=>\(\dfrac{3x-2+3\left(x+7\right)}{6}=8\)
=>3x-2+3x+14=48
=>6x+12=48
=>6x=36
=>\(x=\dfrac{36}{6}=6\)
c: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(5x+3\right)=\left(3x-8\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
=>\(\left(x-1\right)\left(5x+3\right)-\left(3x-8\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
=>(x-1)(5x+3-3x+8)=0
=>(x-1)(2x+11)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+11=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{11}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: \(\left(2x-1\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)^2=0\)
=>\(\left(2x-1-x-3\right)\left(2x-1+x+3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x-4\right)\left(3x+2\right)=0\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\3x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
