
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


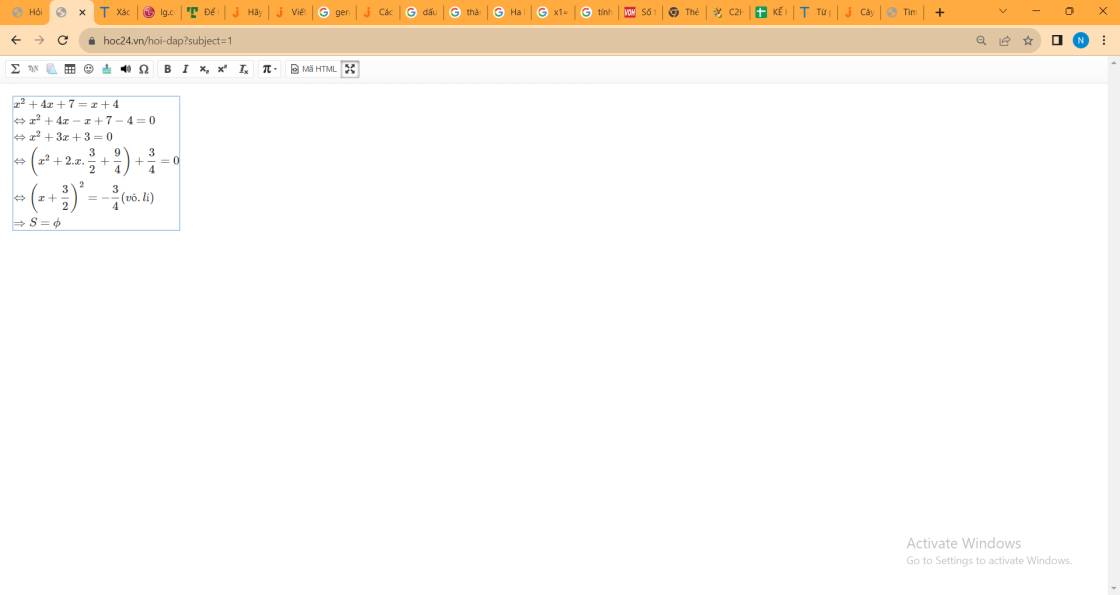
\(x^2+4x+7=x+4\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+4x-x+7-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+3x+3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2.x.\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)+\dfrac{3}{4}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2=-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(vô.lí\right)\\ \Rightarrow S=\phi\)

\(\left(x^2+2>0\right)\left(2x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)


ta có :
\(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x-1\right|=1+\left|\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|\left|x+1\right|-\left|x-1\right|-\left|x+1\right|+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\left|x-1\right|-1\right)\left(\left|x+1\right|-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|x-1\right|=1\\\left|x+1\right|=1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2,0,2\right\}\)

\(\dfrac{x}{2x-6}-\dfrac{x}{2x+2}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-1,x\ne3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{2\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x}{2\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x-3\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x\cdot2}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x-3\right)=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)
Phương trình có vô số nghiệm , trừ x = -1,x = 3
Vậy ...
\(\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< \dfrac{9x+1}{3}-\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\cdot\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< 12\cdot\dfrac{9x+1}{3}-12\cdot\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 4\left(9x+1\right)-3\left(8x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 36x+4-24x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 12x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-12x< 1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x< 0\)
Vậy S = {x | x \(\in R\)}

1. a = 3 thì phương trình trở thành:
\(\frac{x+3}{3-x}-\frac{x-3}{3+x}=\frac{-3\left[3.\left(-3\right)+1\right]}{\left(-3\right)^2}-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x+3\right)^2+\left(3-x\right)^2}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}=\frac{-3\left[-9+1\right]}{9}-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^2+6x+9+x^2-6x+9}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}=\frac{-3.\left(-8\right)}{9}-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2+18}{9-x^2}=\frac{24}{9}-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2+18}{9-x^2}+x^2=\frac{24}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2+18+9x^2-x^4}{9-x^2}=\frac{24}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{11x^2+18-x^4}{9-x^2}=\frac{24}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow99x^2+18-9x^4=216-24x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^4-123x^2+198=0\)
Đặt \(x^2=t\left(t\ge0\right)\)
Phương trình trở thành \(9t^2-123t+198=0\)
Ta có \(\Delta=123^2-4.9.198=8001,\sqrt{\Delta}=3\sqrt{889}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=\frac{123+3\sqrt{889}}{18}=\frac{41+\sqrt{889}}{6}\\t=\frac{123-3\sqrt{889}}{18}=\frac{41-\sqrt{889}}{6}\end{cases}}\)
Lúc đó \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=\frac{41+\sqrt{889}}{6}\\x^2=\frac{41-\sqrt{889}}{6}\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\pm\sqrt{\frac{41+\sqrt{889}}{6}}\\x=\pm\sqrt{\frac{41-\sqrt{889}}{6}}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy pt có 4 nghiệm \(S=\left\{\pm\sqrt{\frac{41+\sqrt{889}}{6}};\pm\sqrt{\frac{41-\sqrt{889}}{6}}\right\}\)

Ta có : 17 - 14(x + 1) = 13 - 4(x + 1) - 5(x - 3)
<=> 17 - 14x - 14 = 13 - 4x - 4 - 5x + 15
<=> -14x + 3 = -9x + 24
<=> -14x + 9x = 24 - 3
<=> -5x = 21
=> x = -4,2
Ta có : 5x + 3,5 + (3x - 4) = 7x - 3(x - 0,5)
<=> 5x + 3,5 + 3x - 4 = 7x - 3x + 1,5
<=> 8x - 0,5 = 4x + 1,5
=> 8x - 4x = 1,5 + 0,5
=> 4x = 2
=> x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
=>x^2+x-1=0
Δ=1^2-4*1*(-1)=1+4=5>0
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{5}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
là sao ôg