
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(\sqrt{x^2+6x+9}=\sqrt{11+6\sqrt{2}}\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(x+3\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(3+\sqrt{2}\right)^2}\)
=>\(\left|x+3\right|=\left|3+\sqrt{2}\right|=3+\sqrt{2}\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=3+\sqrt{2}\\x+3=-3-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{2}\\x=-6-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=4\\x+2y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-2y=8\\x+2y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-2y+x+2y=8-3\\2x-y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x=5\\y=2x-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2\cdot1-4=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x+20}-3\sqrt{x+5}+\dfrac{4}{3}\sqrt{9x+45}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x+5}-3\sqrt{x+5}+4\sqrt{x+5}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{x+5}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+5=4\)
hay x=-1
b: Ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{x-1}-\dfrac{3}{2}\sqrt{9x-9}+24\sqrt{\dfrac{x-1}{64}}=-17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{x-1}-\dfrac{9}{2}\sqrt{x-1}+3\sqrt{x-1}=-17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=289\)
hay x=290

Đặt \(\sqrt[3]{6x-9}=a\Rightarrow-9=a^3-6x\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(x^3=6a+a^3-6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-a^3+6\left(x-a\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-a\right)\left(x^2+a^2-ax\right)+6\left(x-a\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-a\right)\left(x^2+a^2-ax+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=a\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt[3]{6x-9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-3x+3\right)=0\)

a,\(\sqrt{\left(3x-1\right)^2}=5=>|3x-1|=5=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=5\\3x-1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\sqrt{4x^2-4x+1}=3=\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}=3=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=3\\2x-1=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, \(\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}+3x=4=>|x-3|=4-3x\)
TH1: \(|x-3|=x-3< =>x\ge3=>x-3=4-3x=>x=1,75\left(ktm\right)\)
TH2 \(|x-3|=3-x< =>x< 3=>3-x=4-3x=>x=0,5\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy x=0,5...
d, đk \(x\ge-1\)
=>pt đã cho \(< =>9\sqrt{x+1}-6\sqrt{x+1}+4\sqrt{x+1}=12\)
\(=>7\sqrt{x+1}=12=>x+1=\dfrac{144}{49}=>x=\dfrac{95}{49}\left(tm\right)\)
a) Ta có: \(\sqrt{\left(3x-1\right)^2}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|3x-1\right|=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=5\\3x-1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=6\\3x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x^2-4x+1}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=3\\2x-1=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=4\\2x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Ta có: \(\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}+3x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-3\right|=4-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=4-23x\left(x\ge3\right)\\x-3=23x-4\left(x< 3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+23x=4+3\\x-23x=4+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{24}\left(loại\right)\\x=\dfrac{-4}{22}=\dfrac{-2}{11}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đặt: \(\sqrt{x+9}=v;\sqrt{x+6}=u\)
Ta có: \(v+5u=5+vu\)
\(\Leftrightarrow v+5u-5-uv=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-v\left(u-1\right)+5\left(u-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5-v\right)\left(u-1\right)\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5-v=0\Leftrightarrow5=\sqrt{x+9}\Leftrightarrow x=16\left(N\right)\\u-1=0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+6}=1\Leftrightarrow x=-5\left(L\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) ĐKXĐ:\(x>=-6\)
\(S=\left\{16\right\}\)
Đặt:\(\sqrt{x+9}=v;\sqrt{x+6}=u\)
Ta có: \(v+5u=5+vu\Leftrightarrow-v\left(u-1\right)+5\left(u-1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left(5-v\right)\left(u-1\right)\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5-v=0\Leftrightarrow5=\sqrt{x+9}\Leftrightarrow x=16\left(N\right)\\u-1=0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+6}=1\Leftrightarrow x=-5\left(N\right)\end{matrix}\right.ĐKXĐ:x>=-6\)
\(S=\left\{16,-5\right\}\)
Câu trên mình quên -5>-6

\(\sqrt{10\left(x-3\right)}=\sqrt{26}\)
\(\Rightarrow10\left(x-3\right)=26\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3=2.6\)
\(\Rightarrow x=3+2,6=5,6\)
\(\sqrt{3x^2}=x+2\Rightarrow3x^2=x^2+4x+4\)
\(\Rightarrow3x^2-x^2-4x-4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^2-4x-4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-2x-2=0\)
\(a=1;b=-2;c=-2;b'=-1\)
\(\Delta'=b'^2-ac=\left(-1\right)^2-1.\left(-2\right)=3>0\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệp phân biệt
\(x_1=\frac{-b'+\sqrt{\Delta'}}{a}=\frac{-\left(-1\right)+\sqrt{3}}{1}=1+\sqrt{3}\)
\(x_2=\frac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta'}}{a}=\frac{-\left(-1\right)-\sqrt{3}}{1}=1-\sqrt{3}\)
\(\sqrt{x^2+6x+9}=3x-6\)
\(x^2+6x+9=9x^2-36x+36\)
\(9x^2-x^2-36x-6x+36-9=0\)
\(8x^2-42x+27=0\)
\(a=8;b=-42;c=27;b'=-21\)
\(\Delta'=b'^2-ac=\left(-21\right)^2-8.27=225>0\)
Phương trình có 2 nghiệp phân biệt
\(x_1=\frac{-b'+\sqrt{\Delta'}}{a}=\frac{-\left(-21\right)+\sqrt{225}}{8}=\frac{21+15}{8}=\frac{36}{8}=\frac{9}{2}\)
\(x_2=\frac{-b'-\sqrt{\Delta'}}{a}=\frac{-\left(-21\right)-\sqrt{225}}{8}=\frac{21-15}{8}=\frac{6}{8}=\frac{3}{4}\)
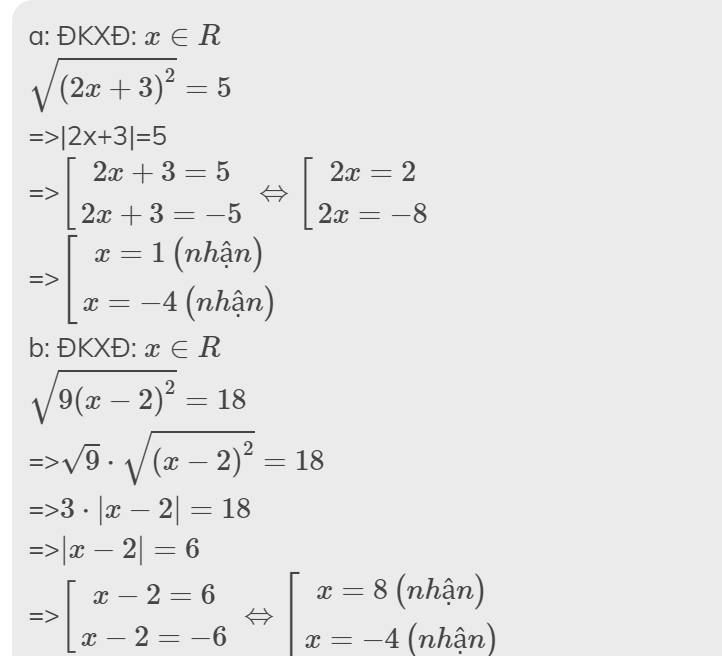
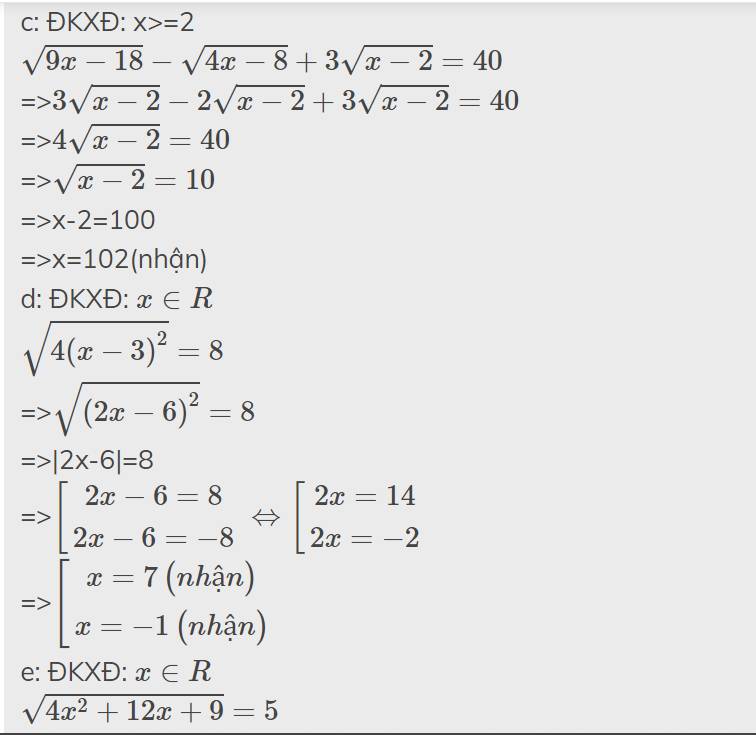
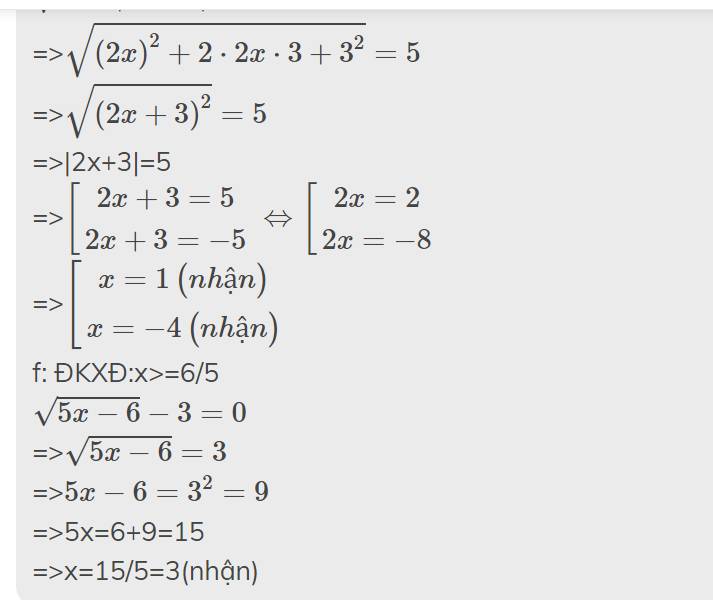
Đặt: \(\sqrt[3]{6x-9}=t\Leftrightarrow t^3=6x-9\)
Ta có hệ:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x^3=6t-9\\t^3=6x-9\end{cases}}\)
=> \(x^3-t^3=-6\left(x-t\right)\)
<=> \(\left(x-t\right)\left(x^2+xt+t^2+6\right)=0\)
<=> x = t
vì \(x^2+xt+\frac{1}{4}t^2+\frac{3}{4}t^2+6=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}t\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}t^2+6>0\)
Với x = t ta có: \(\sqrt[3]{6x-9}=x\Leftrightarrow x^3=6x-9\)
<=> x = -3 thử lại thỏa mãn
Kết luận:...