Cho A=(x^3/x^2-4)-(x/x-2)-(2/x+2) Tìm giá trị của x để A nhận giá trị dương!
Giup nha!
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) C được xác định <=> x khác +- 2
b) Ta có : \(C=\dfrac{x^3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-x^2-2x-2x+4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=x-1\)
Để C = 0 thì x - 1 = 0 <=> x = 1 (tm)
c) Để C nhận giá trị dương thì x - 1 > 0 <=> x > 1
Kết hợp với ĐK => Với x > 1 và x khác 2 thì C nhận giá trị dương

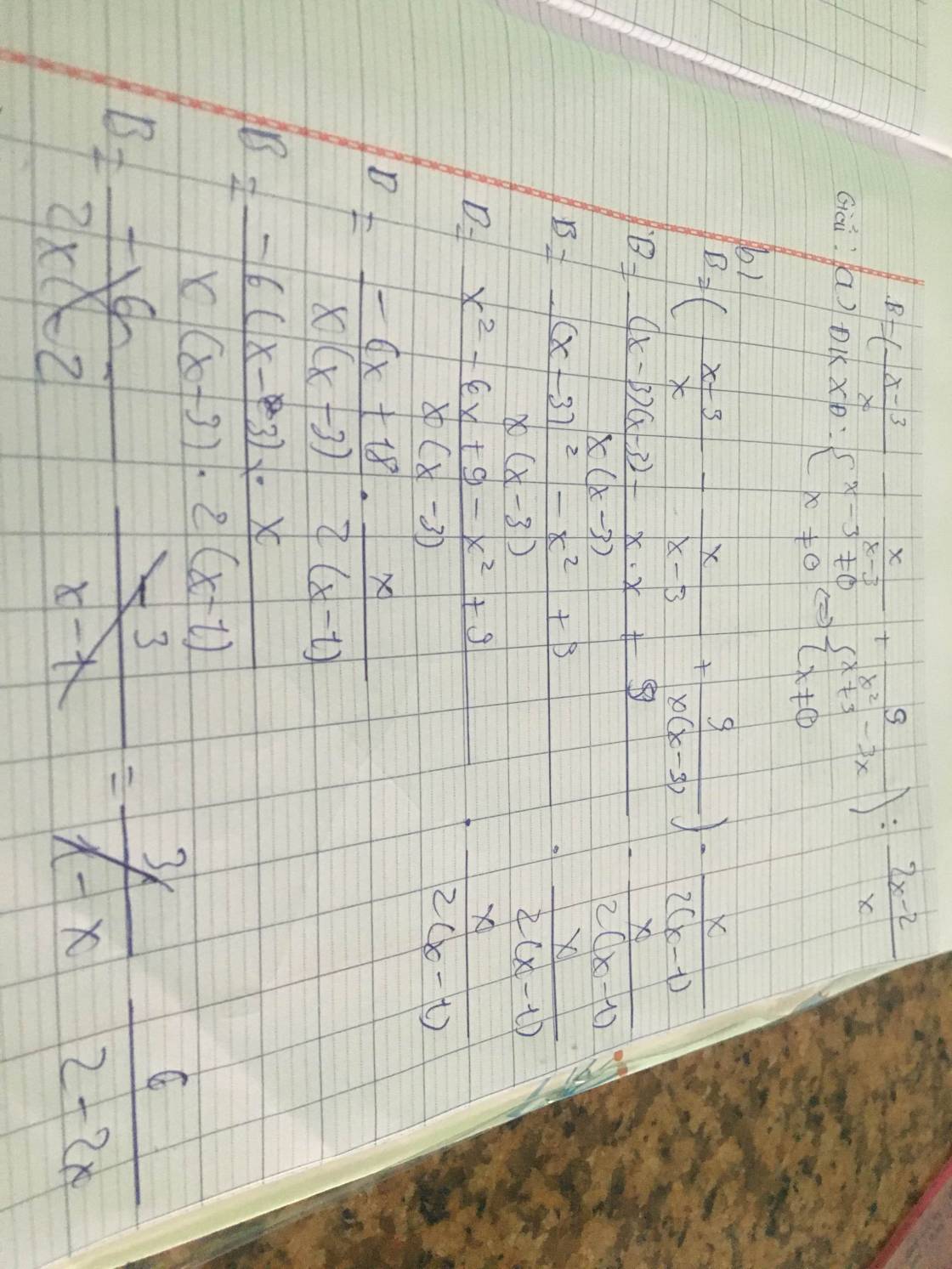 c/
c/
Ta có : B=2=>6/2-2x
<=>6=4-4x
<=>6-4=-4x
<=>-4x=2
<=>x=2/-4=-1/2
d/ĐKXĐ:2-2x≠0
<=>2(1-x)≠0<=>-2(x-1)≠0
<=>x≠1
Để giá trị của biểu thức B nguyên thì 2-2x là Ư(6)
=>2-2x ∈ Ư(6)={±1;±2;±3;±6) Nếu 2-2x=1=> -2x=-1=>x=1/2( thoả mãng)
Rồi còn nhiêu bạn tự xét trường hợp y trang cách làm ở trênn nnhan :;)).À sẽ có mấy cái trường hợp nó giống ĐKXĐ thì bạn ghi trong ngoặc ko thoã mãn nhan.


\(a)\) Ta có :
\(A=\frac{6x+9}{3x+2}=\frac{6x+4+5}{3x+2}=\frac{6x+4}{3x+2}+\frac{5}{3x+2}=\frac{2\left(3x+2\right)}{3x+2}+\frac{5}{3x+2}=2+\frac{5}{3x+2}\)
Để A có giá trị nguyên thì \(\frac{5}{3x+2}\) phải nguyên hay \(5\) chia hết cho \(3x+2\)\(\Rightarrow\)\(\left(3x+2\right)\inƯ\left(5\right)\)
Mà \(Ư\left(5\right)=\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
Suy ra :
| \(3x+2\) | \(1\) | \(-1\) | \(5\) | \(-5\) |
| \(x\) | \(\frac{-1}{3}\) | \(-1\) | \(1\) | \(\frac{-7}{3}\) |
Mà \(x\) là số nguyên nên \(x\in\left\{-1;1\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-1;1\right\}\)
Chúc bạn học tốt ~
\(b)\) Ta có bất đẳng thức giá trị tuyệt đối như sau :
\(\left|x\right|+\left|y\right|\ge\left|x+y\right|\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(xy\ge0\)
Áp dụng vào ta có :
\(A=\left|x\right|+\left|8-x\right|\ge\left|x+8-x\right|=\left|8\right|=8\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(x\left(8-x\right)\ge0\)
Trường hợp 1 :
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\8-x\ge0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\x\le8\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}0\le x\le8}\)
Trường hợp 2 :
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x\le0\\8-x\le0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\le0\\x\ge8\end{cases}}}\) ( loại )
Vậy GTNN của \(A=8\) khi \(0\le x\le8\)
Chúc bạn học tốt ~

a: \(P=\left(\dfrac{-\left(x+3\right)}{x-3}+\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}+\dfrac{4x^2}{x^2-9}\right):\dfrac{2x+1-x-3}{x+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x^2-6x-9+x^2-6x+9+4x^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x^2-12x}{x-3}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{4x}{x-2}\)
b: \(2x^2-5x+2=0\)
=>(x-2)(2x-1)=0
=>x=1/2
Thay x=1/2 vào P, ta được:
\(P=\left(4\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\right):\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-2\right)=2:\dfrac{-3}{2}=\dfrac{-4}{3}\)

a, ĐKXĐ: x2-4≠0 ⇔ x≠±2
b, \(\dfrac{x^2-4x+4}{x^2-4}\)=\(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)=\(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}\)
c, |x|=3
TH1: x≥0 thì x=3 (TMĐK)
TH1: x<0 thì x=-3 (TMĐK)
Thay x=3 và biểu thức ta có:
\(\dfrac{3-2}{3+2}\)=\(\dfrac{1}{5}\)
Thay x=-3 và biểu thức ta có:
\(\dfrac{-3-2}{-3+2}\)=5

`a)ĐK:x^2-4 ne 0<=>x^2 ne 4`
`<=>x ne 2,x ne -2`
`b)A=(x^2-4x+4)/(x^2-4)`
`=(x-2)^2/((x-2)(x+2))`
`=(x-2)/(x+2)`
`c)|x|=3`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=3\\x=-3\end{array} \right.\)
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}A=\dfrac{3-2}{3+2}=\dfrac15\\x=\dfrac{-3-2}{-3+2}=5\end{array} \right.\)
`d)A=2`
`=>x-2=2(x+2)`
`<=>x-2=2x+4`
`<=>x=-6`
a, ĐKXĐ: \(x^2-4\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\pm2\)
b, Ta có: \(\dfrac{x^2-4x+4}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}\) (*)
c, \(\left|x\right|=3\Rightarrow x=\pm3\)
_ Thay x = 3 vào (*), ta được: \(\dfrac{3-2}{3+2}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
_ Thay x = -3 vào (*), ta được: \(\dfrac{-3-2}{-3+2}=5\)
d, Có: \(\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=2\left(x+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=2x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-6\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy...

\(a,ĐK:\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\\sqrt{x}+2\ne0\\\sqrt{x}-2\ne0;4-x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\x\ne4\end{cases}}\)
Rút gọn :
\(A=\frac{4}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-2}+\frac{5\sqrt{x}-6}{4-x}\)
\(A=\frac{4}{\sqrt{x}+2}+\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\frac{5\sqrt{x}-6}{x-4}\)
\(A=\frac{4\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}+\frac{2\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}-\frac{5\sqrt{x}-6}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(A=\frac{4\sqrt{x}-8+2\sqrt{x}+4-5\sqrt{x}+6}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(A=\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(b,\)Để A nhận giá tri nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\) nguyên
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-2\inƯ\left(1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}-2=1\\\sqrt{x}-2=-1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}=3\\\sqrt{x}=1\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=9\\x=1\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy A có giá tri nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{1;9\right\}\)

`a)(2sqrtx-9)/(x-5sqrtx+6)-(sqrtx+3)/(sqrtx-2)-(2sqrtx+1)/(3-sqrtx)(x>=0,x ne 4,x ne 9)`
`=(2sqrtx-9)/(x-5sqrtx+6)-(sqrtx+3)/(sqrtx-2)+(2sqrtx+1)/(sqrtx-3)`
`=(2sqrtx-9+(sqrtx-3)(sqrtx+3)+(2sqrtx+1)(sqrtx-2))/(x-5sqrtx+6)`
`=(2sqrtx-9+x-9+2x-3sqrtx-2)/(x-5sqrtx+6)`
`=(3x-sqrtx-20)/