Tìm x nguyên để M= X2/X-3 nhận giá trị nguyên
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Chắc là \(M=\dfrac{4x+1}{x^2+3}\) đúng không nhỉ?
\(M=\dfrac{-\left(x^2+3\right)+x^2+4x+4}{x^2+3}=-1+\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x^2+3}\ge-1\)
\(M=\dfrac{12x+3}{3\left(x^2+3\right)}=\dfrac{4\left(x^2+3\right)-4x^2+12x-9}{3\left(x^2+3\right)}=\dfrac{4}{3}-\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right)^2}{3\left(x^2+3\right)}\le\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow-1\le M\le\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Mà M nguyên \(\Rightarrow M=\left\{-1;0;1\right\}\)
- Với \(M=-1\Rightarrow\dfrac{4x+1}{x^2+3}=-1\Rightarrow\left(x+2\right)^2=0\Rightarrow x=-2\)
- Với \(M=0\Rightarrow\dfrac{4x+1}{x^2+3}=0\Rightarrow4x+1=0\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
- Với \(M=1\Rightarrow\dfrac{4x+1}{x^2+3}=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+2=0\Rightarrow x=2\pm\sqrt{2}\)
Vậy \(x=\left\{-2;-\dfrac{1}{4};2-\sqrt{2};2+\sqrt{2}\right\}\) thì M nguyên


đề bài ĐKXĐ như nào bạn tự xét gtri thỏa mãn nhé
\(P=\frac{x^2}{x-1}=\frac{x^2-x+x-1+1}{x-1}=\frac{x\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)+1}{x-1}=x+1+\frac{1}{x-1}\)
Vì x nguyên nên x + 1 nguyên
Để P nguyên thì 1/x-1 nguyên ( đến đây quá dễ rồi:)) )
Như trên ta có : \(P=x+1+\frac{1}{x-1}=\left[\left(x-1\right)+\frac{1}{x-1}\right]+2\)
Vì x > 1, áp dụng bất đẳng thức AM-GM ta có :
\(P\ge2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\cdot\frac{1}{x-1}}+2=4\). Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> x = 2
Vậy GTNN của P = 4 <=> x=2

a) Ta có: \(M=\dfrac{8x+1}{4x-5}=\dfrac{8x-10+11}{4x-5}=\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)+11}{4x-5}=2+\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\)
Để M nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(2+\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow11⋮4x-5\)
Vì \(x\in Z\) nên \(4x-5\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow4x-5\inƯ\left(11\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm11\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;\pm1,5;4\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{1;4\right\}\) thỏa mãn \(x\in Z\).
b) Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{5}{4-x}\). ĐK: \(x\ne4\)
Nếu 4 - x < 0 thì x > 4 \(\Rightarrow A>0\)
4 - x > 0 thì x < 4 \(\Rightarrow A< 0\)
Để A đạt GTLN thì 4 - x là số nguyên dương nhỏ nhất
\(\Rightarrow4-x=1\Rightarrow x=3\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{5}{4-3}=5\)
Vậy MaxA = 5 tại x = 3
c) \(B=\dfrac{8-x}{x-3}\). ĐK: \(x\ne3\).
Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{8-x}{x-3}=\dfrac{-\left(x-8\right)}{x-3}=\dfrac{-\left(x-3\right)+5}{x-3}=\dfrac{5}{x-3}-1\)
Để B đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất thì \(\dfrac{5}{x-3}-1\) nhỏ nhất
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}\) nhỏ nhất
Nếu x - 3 > 0 thì x > 3 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}>0\)
x - 3 < 0 thì x < 3 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}< 0\)
Để \(\dfrac{5}{x-3}\) nhỏ nhất thì x - 3 là số nguyên âm lớn nhất
\(\Rightarrow x-3=-1\Rightarrow x=2\)
\(\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{8-2}{2-3}=-6\)
Vậy MaxB = -6 tại x = 2.
Mình làm sai câu a...
Ta có: \(M=\dfrac{8x+1}{4x-1}=\dfrac{8x-2+3}{4x-1}=\dfrac{2\left(4x-1\right)+3}{4x-1}=2+\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\)
Để M nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(2+\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
Vì \(4x-1\in Z\) nên \(4x-1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{\pm0,5;0;1\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;1\right\}\) thỏa mãn \(x\in Z\).

a)
Để A nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow x^3+x⋮x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-1+x+1⋮x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)+x+1⋮x-1\left(1\right)\)
Vì x nguyên \(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-1\in Z\\x^2+x+1\in Z\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)⋮x-1\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) \(\Rightarrow x+1⋮x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1+2⋮x-1\)
Mà \(x-1⋮x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow2⋮x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-1;0;2;3\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-1;0;2;3\right\}\)
b) Để B nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+5⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-8x+10⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2-x\right)-\left(6x-3\right)-\left(x-7\right)⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-1\right)-3\left(2x-1\right)-\left(x-7\right)⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x-7\right)⋮2x-1\left(1\right)\)
Vì x nguyên \(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x-1\in Z\\x-3\in Z\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)⋮2x-1\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và(2) \(\Rightarrow x-7⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-14⋮2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1-13⋮2x-1\)
Mà \(2x-1⋮2x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow13⋮2x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-1\inƯ\left(13\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm13\right\}\)
Làm nốt nha các phần còn lại bạn cứ dựa bài mình mà làm

a: Khi x=5 thì A=5/(5+3)=5/8
b: \(C=A+B=\dfrac{x}{x+3}+\dfrac{2}{x-3}+\dfrac{3-5x}{x^2-9}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-3x+2x+6+3-5x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-6x+9}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)
c: Để C nguyên thì x+3-6 chia hết cho x+3
=>\(x+3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;3;-3;6;-6\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{-2;-4;-1;-5;0;-6;-9\right\}\)

c) Để A nhận giá trị nguyên khi và chỉ khi:
![]()
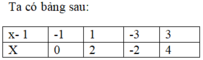
Kết hợp với điều kiện, tập hợp các giá trị của x nguyên để A nguyên là: {0; 2; -2; 4}.

a: \(P=\dfrac{x^2-x-18+2x+6-4x+12}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-3x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{x}{x+3}\)
b: P=2/3
=>x/(x+3)=2/3
=>3x=2x+6
=>x=6(nhận)
c: P nguyên
=>x chia hết cho x+3
=>x+3-3 chia hết cho x+3
=>x+3 thuộc {1;-1;2;-2}
=>x thuộc {-2;-4;-1;-5}

\(M=\frac{x^2}{x-3}=\frac{x^2-3x+3x-9+9}{x-3}=\frac{x\left(x-3\right)+3\left(x-3\right)+9}{x-3}=\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)+9}{x-3}=x+3+\frac{9}{x-3}\)
Vì x nguyên nên x + 3 nguyên
Để M nguyên thì 9/x+3 nguyên
hay x + 3 thuộc Ư(9) *bạn tự tính tiếp*