tìm x biết x-1/7 + x-2/3 + x-3/5 + x-4/2 = 6
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bạn tự biểu diễn nha.
\(a,\dfrac{x-4}{6}+\dfrac{1}{2}>\dfrac{2x-5}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-4}{6}+\dfrac{3}{6}-\dfrac{2\left(2x-5\right)}{6}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-4+3-4x+10}{6}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x>-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 3\)
\(b,\dfrac{x+6}{5}-\dfrac{x-2}{3}< 2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(x+6\right)}{15}-\dfrac{5\left(x-2\right)}{15}-\dfrac{2.15}{15}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x+18-5x+10-30}{15}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x< 2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-1\)
\(c,x-\dfrac{x-1}{3}+\dfrac{x+2}{6}>\dfrac{2x}{5}+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{30x-10\left(x-1\right)+5\left(x+2\right)-2x.6-5.30}{30}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow30x-10x+10+5x+10-12x-150>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow13x>130\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>10\)

A B C D M N P Q
\(S_{BMN}=\dfrac{1}{2}xBMxBN=\dfrac{1}{2}x\dfrac{AB}{4}x\dfrac{BC}{2}=\dfrac{1}{16}xS_{ABCD}\)
\(S_{CPN}=\dfrac{1}{2}xCNxCP=\dfrac{1}{2}x\dfrac{BC}{2}x\dfrac{CD}{2}=\dfrac{1}{8}xS_{ABCD}\)
\(S_{DPQ}=\dfrac{1}{2}xPDxDQ=\dfrac{1}{2}x\dfrac{CD}{2}x\dfrac{AD}{3}=\dfrac{1}{12}xS_{ABCD}\)
\(S_{AMQ}=\dfrac{1}{2}xAMxAQ=\dfrac{1}{2}x\dfrac{3xAB}{4}x\dfrac{2xAD}{3}=\dfrac{1}{4}xS_{ABCD}\)
\(\Rightarrow S_{MNPQ}=S_{ABCD}-\left(S_{BMN}+S_{CPN}+S_{DPQ}+S_{AMQ}\right)\)
Bạn tự thay số rồi tính nốt nhé

3x + 8 = 35
3x =35 - 8
3x =27
x = 27 : 3
x = 9.
Vậy x = 9.
3x + 8 = 35
3x = 35 - 8
3x = 27
x = 27 : 3
x = 9
Vậy x = 9

( x + y ) - ( x - y ) = 64
=> x + y - x + y = 64
=> 2y = 64
=> y = 32
=> x + y >= 0, 64 > 0 => x - y >= 0 => x >= 32 => x = 32 ( ko chắc )
Vậy x = 32, y = 32

Lời giải:
Xét thừa số tổng quát:
\(1-\frac{1}{1+2+...+n}=\frac{(1+2+...+n)-1}{1+2+...+n}=\frac{\frac{n(n+1)}{2}-1}{\frac{n(n+1)}{2}}=\frac{n(n+1)-2}{n(n+1)}=\frac{(n-1)(n+2)}{n(n+1)}\)
Thay $n=2,3,....,$ ta được:
\(P=\frac{1.4}{2.3}.\frac{2.5}{3.4}.\frac{3.6}{4.5}....\frac{(n-1)(n+2)}{n(n+1)}\)
\(=\frac{[1.2.3....(n-1)][4.5.6..(n+2)]}{(2.3.4..n)[3.4.5...(n+1)]}\)
\(=\frac{1}{n}.\frac{n+2}{3}=\frac{n+2}{3n}\)
\(\frac{1}{P}=\frac{3n}{n+2}\in\mathbb{Z}\) khi mà $3n\vdots n+2$
$\Leftrightarrow 3(n+2)-6\vdots n+2$
$\Leftrightarrow 6\vdots n+2$
$\Rightarrow n+2\in\left\{6\right\}$ (do $n+2\geq 4$ với mọi $n\geq 2$)
$\Rightarrow n=4$


Nam mua quyển sách hết :
\(50000\times\left(100\%-10\%\right)=45000\) (đồng)
Số tiền mà quyển sách giảm đi là: 50000 x 10% = 5000 ( đồng )
Số tiền mà Nam mua quyển sách là : 50000 - 5000 = 45000 ( đồng )
Kết luận ...

\(VT=\dfrac{a}{1+a^2}+\dfrac{b}{1+b^2}=\dfrac{a}{ab+a+b+a^2}+\dfrac{b}{ab+a+b+b^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{a}{\left(a+b\right).\left(a+1\right)}+\dfrac{b}{\left(a+b\right).\left(b+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(a+b\right).\left(ab+a+ab+b\right)}{\left(a+b\right)^2.\left(a+1\right).\left(b+1\right)}=\dfrac{ab+1}{\left(a+b\right).\left(ab+a+b+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{ab+1}{2.\left(a+b\right)}\)(1)
\(VP=\dfrac{ab+1}{\sqrt{2\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)}}=\dfrac{ab+1}{\sqrt{2\left(a+b\right)^2.\left(a+1\right).\left(b+1\right)}}\)
\(=\dfrac{ab+1}{2\left(a+b\right)}\) (2)
Từ (1) (2) => ĐPCM
Giải
Với a,b > 0, ta có:
\(\dfrac{a}{1+a^2}+\dfrac{b}{1+b^2}=\dfrac{1+ab}{\sqrt{2\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)}}\)
Tương đương
\(\dfrac{a+ab^2+b+a^2b}{\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)}=\dfrac{1+ab}{\sqrt{2\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)}}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{a+b+ab\left(a+b\right)}{\sqrt{\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)}}=\dfrac{1+ab}{\sqrt{2\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)}}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(a+b\right)\left(ab+1\right)}{\sqrt{\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)}}=\dfrac{1+ab}{\sqrt{2}}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(a+b\right)}{\sqrt{\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
Mặt khác, \(\left(1+a^2\right)\left(1+b^2\right)=\left(a^2+a+b+ab\right)\left(b^2+a+b+ab\right)\\ =\left(a+b\right)\left(a+1\right)\left(a+b\right)\left(b+1\right)\\ =\left(a+b\right)^2\left[\left(a+1\right)\left(b+1\right)\right]\\ =\left(a+b\right)^2\left(a+b+ab+1\right)\\ =2\left(a+b\right)^2\)
Do đó phương trình đã cho tương đương:
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(a+b\right)}{\sqrt{2\left(a+b\right)^2}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\\\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(a+b\right)}{\sqrt{2}.\left(a+b\right)}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(a,b>0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(1\right)\)
Vì phương trình (1) đúng nên phương trình ban đầu cũng đúng
Suy ra điều phải chứng minh

Ta có: 151+152+...+175>175+175+...+175=2575=13
176+177+...+1100>1100+1100+...+1100=25100=14
=> S>13+14=712 (1)
Ta có: 151+152+...+175<150+150+...+150=2550=12
176+177+...+1100<175+175+...+175=2575=13
=> S<12+13=56 (2)
Từ (1) và (2) => 712 < S<56 ( đpcm )
Ta có:
- 1/51 > 1/75, 1/52 > 1/75 ...
=> 1/51 + 1/52 + ... + 1/75 > 1/75 + ... 1/75 = 25/75 = 1/3
- 1/76 > 1/100, 1/77 > 1/100 ...
=> 1/76 + 1/77 + ... + 1/100 > 1/100 + ... + 1/100 = 25/100 = 1/4
Từ đó : S = ( 1/51 + ... + 1/75 ) + ( 1/76 + ... + 1/100 ) > 1/3 + 1/3 = 7/12 (1)
- 1/51 < 1/50, 1/52 < 1/50 ...
=> 1/51 + 1/52 + ... + 1/75 < 1/50 + ... 1/50 = 25/50 = 1/2
- 1/76 < 1/75, 1/77 < 1/75...
=> 1/76 + 1/77 + ... + 1/100 < 1/75 + ... + 1/75 = 25/75 = 1/3
Từ đó : S = ( 1/51 + ... + 1/75 ) + ( 1/76 + ... + 1/100 ) < 1/2 + 1/3 = 5/6 (2)
từ (1) và (2) => 5/6 > S > 7/12
* Chúc bn học tốt !!!
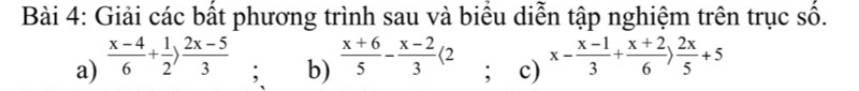

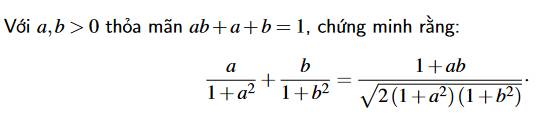
\(\dfrac{x-1}{7}+\dfrac{x-2}{3}+\dfrac{x-3}{5}+\dfrac{x-4}{2}=6\\ =>\left(\dfrac{x-1}{7}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x-2}{3}-2\right)+\left(\dfrac{x-3}{5}-1\right)+\left(\dfrac{x-4}{2}-2\right)=0\\ =>\dfrac{x-8}{7}+\dfrac{x-8}{3}+\dfrac{x-8}{5}+\dfrac{x-8}{2}=0\\ =>\left(x-8\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{7}+\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=0\\ =>x-8=0\\ =>x=8\)
chắc ko bro :)?