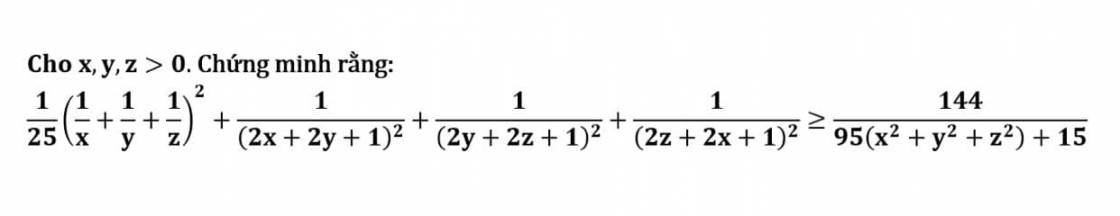
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


`\sqrt{[-3]/[(5x-1)^2]}` có nghĩa `<=>[-3]/(5x-1)^2 >= 0`
Mà `-3 < 0` và `(5x-1)^2 >= 0 AA x`
`=>` Không có gtrị nào để căn thức có nghĩa
`\sqrt{7/[(4-3x)^2]}` có nghĩa `<=>7/[(4-3x)^2] >= 0`
Mà `7 > 0`
`=>(4-3x)^2 > 0<=>4-3x \ne 0<=>x \ne 4/3`
`\sqrt{9/[(3x+1)^2]}` có nghĩa `<=>9/[(3x+1)^2] >= 0`
Mà `9 > 0`
`=>(3x+1)^2 > 0<=>3x+1 \ne 0<=>x \ne [-1]/3`

Consider the first equation:
\(x+5y=7\Leftrightarrow x=7-5y\)
We can see that as long as \(y\) is an integer, \(x\) will also be an integer. This means the given equation has an infinite amount of integer roots of \(\left(x;y\right)\) such that \(x=7-5y\)
Now consider the second equation:
\(2x+5y=10\Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{10-2x}{5}\) (1)
Because \(y\) is an integer, \(\dfrac{10-2x}{5}\) must also be an integer. Therefore, \(10-2x⋮5\)
Since \(10⋮5\), \(2x⋮5\).
We have \(\left(2,5\right)=1\), so \(x⋮5\). Thus, \(x=5k\) (\(k\) is an integer)
From this, we subtitute that in (1) to get \(y=\dfrac{10-2.5k}{5}=\dfrac{10-10k}{5}=2-2k\)
As long as \(k\) is an integer, \(y\) and \(x\) will also be an integer. Therefore, the given equation has an infinite amount of integer roots such that \(y=-\dfrac{2}{5}x+2\)


What is the question? (find the min, max value/ factor/ simplify, etc.)



Lời giải:
Áp dụng BĐT Cauchy-Schwarz:
\(\text{VT}\geq \frac{1}{25}.\frac{81}{(x+y+z)^2}+\frac{1}{(2x+2y+1)^2}+\frac{1}{(2y+2z+1)^2}+\frac{1}{(2z+2x+1)^2}\)
\(=\frac{9^2}{25(x+y+z)^2}+\frac{1}{(2x+2y+1)^2}+\frac{1}{(2y+2z+1)^2}+\frac{1}{(2z+2x+1)^2}\)
\(\geq \frac{(9+1+1+1)^2}{25(x+y+z)^2+\sum (2x+2y+1)^2}=\frac{144}{25(x+y+z)^2+\sum (2x+2y+1)^2}\)
\(=\frac{144}{25.3(x^2+y^2+z^2)+\sum (2x+2y+1)^2}\)
Ta cần cm $\sum (2x+2y+1)^2\leq 20(x^2+y^2+z^2)+15$
$\Leftrightarrow 8(x^2+y^2+z^2)+8(xy+yz+xz)+8(x+y+z)+3\leq 20(x^2+y^2+z^2)+15$
$\Leftrightarrow 3(x^2+y^2+z^2)+3\geq 2(xy+yz+xz)+2(x+y+z)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-y)^2+(y-z)^2+(z-x)^2+(x-1)^2+(y-1)^2+(z-1)^2\geq 0$ (luôn đúng với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}^+$)
Do đó ta có đpcm
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi $x=y=z=1$