Cho các hàm số :
f\(_1\)(x)=3.x^2 f\(_2\)(x)=-5x f\(_3\)(x)=\(\dfrac{3}{x}\)
f\(_4\)(x)=x^3 f\(_5\)(x)=\(^{x^4+x^2}\)
a) Tính f\(_1\)(\(\dfrac{1}{3}\)) ; f\(_2\)(\(\dfrac{1}{5}\)) ; f\(_3\)(3) ; f\(_4\)(-1) ; f\(_5\)(1)
b) Tính f\(_1\)(0) + f\(_2\)(5) + f\(_3\)(3) + f\(_4\)(-2) + f\(_5\)(2)
c) So sánh f1(x) và f1(-x) ;f2(-x) và -f2(x). Trong các hàm số trên hàm số nào cũng có tính chất này.
d) Tìm x để f\(_5\)(x)=0 ; f\(_5\)(x)=-1
Giúp mk nha mn @Nguyễn Trần Thành Đạt

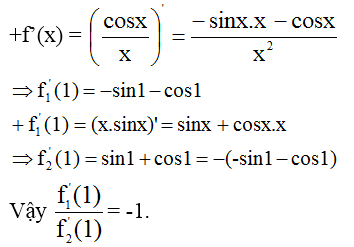
mk sửa có dấu phẩy sau các chứ f trên đấu bài nha.
giúp mk đi mn
@Nguyễn Huy Tú