
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

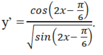

tham khảo:
a)\(y'=xsin2x+sin^2x\)
\(y'=sin^2x+xsin2x\)
b)\(y'=-2sin2x+2cosx\\ y'=2\left(cosx-sin2x\right)\)
c)\(y=sin3x-3sinx\)
\(y'=3cos3x-3cosx\)
d)\(y'=\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}-\dfrac{1}{sin^2x}\)
\(y'=\dfrac{sin^2x-cos^2x}{sin^2x.cos^2x}\)

\(a,y'=\left(f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)\right)'\)
\(=f'\left(g\left(x\right)\right).g'\left(x\right)\)
\(=e^{g\left(x\right)}.\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(=e^{x^2-x}.\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(b,y'=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(3^{sinx}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(e^{ln3.sinx}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(ln3.sinx\right).e^{ln3.sinx}\)
\(=ln3.cosx.3^{sinx}\)

Đáp án B
+ Xét hàm y = f(x) = cos (x + π)
TXĐ: D = R
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và f(-x) = cos (-x + π) = -cos x = cos (x + π) = f(x)
Do đó y = cos (x + π) là hàm số chẵn .
+ Xét hàm y = g(x) = tan2016x
TXĐ: D = R\{π/2 + kπ, k ∈ Z}
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và g(-x) = tan2016(-x) = (-tan x)2016 = tan2016x = g(x)
Do đó: y = tan2016x là hàm chẵn trên tập xác định của nó.
+Xét hàm y = cot2x
f(-x) = cot(-2x) = - cot 2x = -f(x) nên đây là hàm số lẻ.
+ Xét hàm số y = 1-sinx
f(-x) = 1- sin(-x) = 1+ sin x
Nên hàm số không chẵn không lẻ

a: \(y=u^2=\left(sinx\right)^2\)
b: \(y'\left(x\right)=\left(sin^2x\right)'=2\cdot sinx\cdot cosx\)
\(y'\left(u\right)=\left(u^2\right)'=2\cdot u\)
\(u'\left(x\right)=\left(sinx\right)'=cosx\)
=>\(y'\left(x\right)=y'\left(u\right)\cdot u'\left(x\right)\)

ĐKXĐ:
a. \(cos\left(x-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\Rightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
b. \(sin\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\ne k\pi\Rightarrow x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
c. \(\dfrac{1+x}{2-x}\ge0\Rightarrow-1\le x< 2\)

a) Đặt \(u = 3{\rm{x}}\) thì \(y = \sin u\). Ta có: \(u{'_x} = {\left( {3{\rm{x}}} \right)^\prime } = 3\) và \(y{'_u} = {\left( {\sin u} \right)^\prime } = \cos u\).
Suy ra \(y{'_x} = y{'_u}.u{'_x} = \cos u.3 = 3\cos 3{\rm{x}}\).
Vậy \(y' = 3\cos 3{\rm{x}}\).
b) Đặt \(u = \cos 2{\rm{x}}\) thì \(y = {u^3}\). Ta có: \(u{'_x} = {\left( {\cos 2{\rm{x}}} \right)^\prime } = - 2\sin 2{\rm{x}}\) và \(y{'_u} = {\left( {{u^3}} \right)^\prime } = 3{u^2}\).
Suy ra \(y{'_x} = y{'_u}.u{'_x} = 3{u^2}.\left( { - 2\sin 2{\rm{x}}} \right) = 3{\left( {\cos 2{\rm{x}}} \right)^2}.\left( { - 2\sin 2{\rm{x}}} \right) = - 6\sin 2{\rm{x}}{\cos ^2}2{\rm{x}}\).
Vậy \(y' = - 6\sin 2{\rm{x}}{\cos ^2}2{\rm{x}}\).
c) Đặt \(u = \tan {\rm{x}}\) thì \(y = {u^2}\). Ta có: \(u{'_x} = {\left( {\tan {\rm{x}}} \right)^\prime } = \frac{1}{{{{\cos }^2}x}}\) và \(y{'_u} = {\left( {{u^2}} \right)^\prime } = 2u\).
Suy ra \(y{'_x} = y{'_u}.u{'_x} = 2u.\frac{1}{{{{\cos }^2}x}} = 2\tan x\left( {{{\tan }^2}x + 1} \right)\).
Vậy \(y' = 2\tan x\left( {{{\tan }^2}x + 1} \right)\).
d) Đặt \(u = 4 - {x^2}\) thì \(y = \cot u\). Ta có: \(u{'_x} = {\left( {4 - {x^2}} \right)^\prime } = - 2{\rm{x}}\) và \(y{'_u} = {\left( {\cot u} \right)^\prime } = - \frac{1}{{{{\sin }^2}u}}\).
Suy ra \(y{'_x} = y{'_u}.u{'_x} = - \frac{1}{{{{\sin }^2}u}}.\left( { - 2{\rm{x}}} \right) = \frac{{2{\rm{x}}}}{{{{\sin }^2}\left( {4 - {x^2}} \right)}}\).
Vậy \(y' = \frac{{2{\rm{x}}}}{{{{\sin }^2}\left( {4 - {x^2}} \right)}}\).