
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge0\)
\(\left(x^2-x-m\right)\sqrt{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2-x-m=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giả sử (1) có nghiệm thì theo Viet ta có \(x_1+x_2=1>0\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm dương nếu có nghiệm
Do đó:
a. Để pt có 1 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\left(1\right)\) vô nghiệm
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta=1+4m< 0\Leftrightarrow m< -\dfrac{1}{4}\)
b. Để pt có 2 nghiệm pb
TH1: (1) có 1 nghiệm dương và 1 nghiệm bằng 0
\(\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
TH2: (1) có 2 nghiệm trái dấu
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2=-m< 0\Leftrightarrow m>0\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge0\)
c. Để pt có 3 nghiệm pb \(\Leftrightarrow\) (1) có 2 nghiệm dương pb
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta=1+4m>0\\x_1x_2=-m>0\\\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{4}< m< 0\)

\(1,\\ a,ĐK:m\ne1\\ \Delta=49+48\left(m-1\right)=48m+1\\ \text{PT vô nghiệm }\Leftrightarrow48m+1< 0\Leftrightarrow m< -\dfrac{1}{48}\\ \text{PT có nghiệm kép }\Leftrightarrow48m+1=0\Leftrightarrow m=-\dfrac{1}{48}\\ \text{PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt }\Leftrightarrow48m+1>0\Leftrightarrow m>-\dfrac{1}{48};m\ne1\)
\(b,\Delta=4\left(m-1\right)^2+4\left(2m+1\right)=4m^2+8>0,\forall m\\ \text{Vậy PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt với mọi m}\\ 2,\\ \text{PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt }\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta=4\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(m^2-1\right)>0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2+8m+4-4m^2+4>0\\ \Leftrightarrow8m+8>0\\ \Leftrightarrow m>-1\)

\(x^3-x^2+2mx-2m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)+2m\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+2m\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x^2=-2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để pt có 3 nghiệm \(\Rightarrow-2m>0\Rightarrow m< 0\)
a. Do vai trò 3 nghiệm như nhau, ko mất tính tổng quát giả sử \(x_1=1\) và \(x_2;x_3\) là nghiệm của \(x^2+2m=0\)
Để pt có 3 nghiệm pb \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2m>0\\-2m\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< 0\\m\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó: \(x_2+x_3=0\Rightarrow x_1+x_2+x_3=1\ne10\) với mọi m
\(\Rightarrow\) Không tồn tại m thỏa mãn yêu cầu
b.
Giả sử pt có 3 nghiệm, khi đó \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_2=-\sqrt{-2m}< 0< 1\\x_3=\sqrt{-2m}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Luôn có 1 nghiệm của pt âm \(\Rightarrow\) không tồn tại m thỏa mãn
Em coi lại đề bài

(m-1)x2-2mx+m-2=0(m\(\ne1\) )
\(\Delta\)'=\(m^2-\left(m-2\right)\left(m-1\right)\)
=\(m^2-m^2+m+2m-2\)
=3m-2
Để pt có nghiệm 2 ngiệm trái dấu thì \(\Delta\) ' =3m-2>0\(\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Viet, ta có
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{2m}{m-1}\\x_1.x_2=\dfrac{m-2}{m-1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để PT có 2 nghiệm trái dấu thì x1x2<0\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m-2}{m-1}< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-2< 0\\m-1>0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-2>0\\m-1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< 2\\m>1\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>2\\m< 1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow1< m< 2\)
Vậy 1<m<2 thì pt có 2 nghiệm trái dấu
câu b
.Với m=1\(\Rightarrow-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left(l\right)\)
.Với \(m\ne1\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta\)'=3m-2\(\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge\dfrac{2}{3}\)

a, \(\sqrt{2x^2-2x+m}=x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2-2x+m=x^2+2x+1\\x+1\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-4x+m-1=0\left(1\right)\\x\ge-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi phương trình \(\left(1\right)\) có nghiệm \(x\ge-1\) chỉ có thể xảy ra các trường hợp sau
TH1: \(x_1\ge x_2\ge-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta'\ge0\\\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{2}\ge-1\\1.f\left(-1\right)\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5-m\ge0\\2\ge-1\\m+4\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4\le m\le5\)
TH2: \(x_1\ge-1>x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5-m\ge0\\m+4< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\) vô nghiệm
Vậy \(-4\le m\le5\)

Đặt $x^2=a$. Khi đó pt có dạng :
$a^2-(2m+2)a+4=0$ (1)
Xét $\Denlta' = m^2+2m+1-4$
$ = m^2+2m-3=(m-1).(m+3)$
Để pt ban đầu có 4 nghiệm nghiệm thì pt (1) phải có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Nên $(m-1).(m+3) > 0 $
$.....$


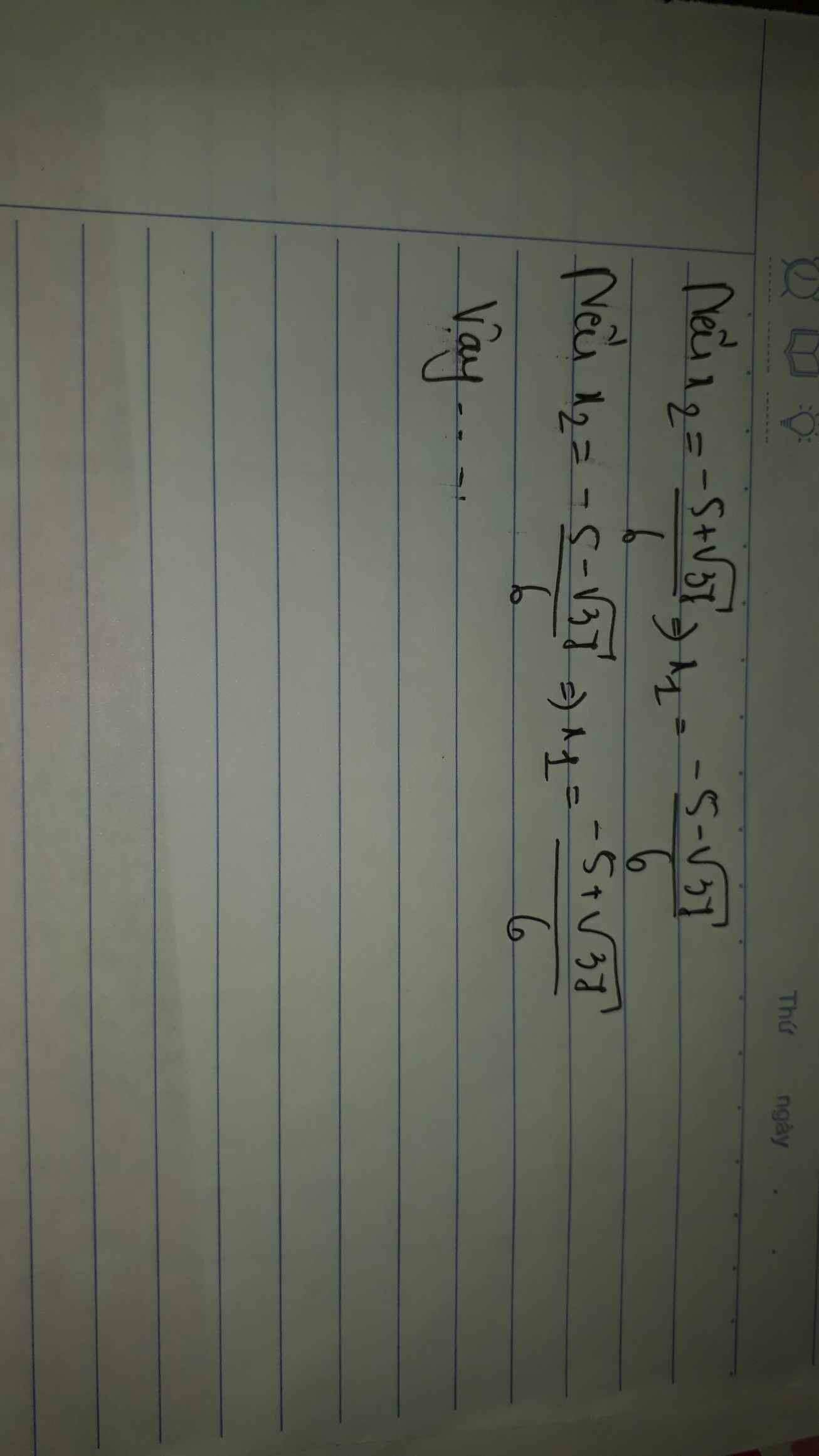
Lời giải:$|x^2-2|x|+m|=1$
$\Rightarrow x^2-2|x|=\pm 1$
\(\Leftrightarrow \left[\begin{matrix} m=1-x^2+2|x|=2-(|x|-1)^2(*)\\ m=-1-x^2+2|x|=-(|x|-1)^2(**)\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH1: $m\leq 0$ thì:
Từ (*) suy ra $|x|=1+\sqrt{2-m}\Rightarrow x=\pm (1+\sqrt{2-m})$ (2 nghiệm phân biệt)
Từ (**) suy ra $|x|=1\pm \sqrt{-m}$. PT này cũng có ít nhất 2 nghiệm phân biệt $x=\pm (1+\sqrt{-m})$
Kéo theo PT ban đầu có ít nhất 4 nghiệm phân biệt (loại)
TH2: $m>2$ thì hiển nhiên PT (*); (**) đều vô nghiệm (loại)
TH3: $2\geq m>0$ thì:
(**) hiển nhiên vô nghiệm
(*) $\Rightarrow |x|=1\pm \sqrt{2-m}$.
Với $|x|=1+\sqrt{2-m}$ thì $x=\pm (1+\sqrt{2-m})$ (2 nghiệm phân biệt)
Do đó để pt chỉ có 2 nghiệm pb thì trường hợp $|x|=1-\sqrt{2-m}$ vô nghiệm hoặc $1-\sqrt{2-m}=1+\sqrt{2-m}$ Điều này xảy ra khi 1-\sqrt{2-m}<0$ hoặc $m=2$
$\Rightarrow 0< m<1$ hoặc $m=2$
Ở TH3 còn trường hợp \(1+\sqrt{2-m}=1-\sqrt{2-m}\Leftrightarrow m=2\)
thì pt cũng cho 2 nghiệm phân biệt