Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 4:
a. Ta thấy: $x^2-x+2=(x-\frac{1}{2})^2+1,75>0$ với mọi $x$.
Do đó để $B=\frac{x^2-x+2}{x-3}<0$ thì $x-3<0$
$\Leftrightarrow x<3$
b.
$B=\frac{x(x-3)+2(x-3)+8}{x-3}=x+2+\frac{8}{x-3}$
Với $x$ nguyên, để $B$ nguyên thì $x-3$ phải là ước của 8.
$\Rightarrow x-3\in\left\{\pm 1; \pm 2; \pm 4; \pm 8\right\}$
$\Rightarrow x\in \left\{4; 2; 5; 1; -1; 7; 11; -5\right\}$
Bài 5:
\(\frac{\frac{x}{x-y}-\frac{y}{x+y}}{\frac{y}{x-y}+\frac{x}{x+y}}=\frac{\frac{x(x+y)-y(x-y)}{(x-y)(x+y)}}{\frac{y(x+y)+x(x-y)}{(x-y)(x+y)}}\)
\(=\frac{x(x+y)-y(x-y)}{y(x+y)+x(x-y)}=\frac{x^2+y^2}{x^2+y^2}=1\)

a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-3;2\right\}\)
b: \(A=\dfrac{x^2-4-5+x+3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+x-6}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}\)
c: Để A=3/4 thì 4x-8=3x+6
=>x=14
d: Để A nguyên thì \(x-2\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{3;1;4;0;6;-2\right\}\)

a) Điều kiện : \(x\ne2;x\ne3\)
\(B=\frac{2x-9}{x^2-5x+6}-\frac{x+3}{x-2}-\frac{2x+4}{3-x}=\frac{2x-9}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\frac{x+3}{x-2}+\frac{2x+4}{x-3}\)
\(=\frac{2x-9-\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)+2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\frac{2x-9-x^2+9+2x^2-8}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\frac{x^2+2x-8}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\frac{x+4}{x-3}\)
b) Điều kiện \(x\in Z;x\ne2;x\ne3\)
Có \(B=\frac{x+4}{x-3}\in Z\), mà x+4 và x-3 nguyên do x nguyên, nên
\(x+4⋮x-3\Leftrightarrow7⋮x-3\), do đó \(x-3\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{1;7;-1;-7\right\}\Rightarrow x\in\left\{4;10;2;-4\right\}\)
mà do x khác 2 (điều kiện) nên ta kết luận \(x\in\left\{4;10;-4\right\}\)

Trả lời:
a, \(ĐK:x\ne\frac{1}{3}\)
\(A=\frac{3x+1-1}{1-3x}:\frac{3x-9x^2}{3x-1}=\frac{3x}{1-3x}\cdot\frac{3x-1}{3x-9x^2}=\frac{3x.\left(3x-1\right)}{\left(1-3x\right)\left(3x-9x^2\right)}=\frac{3x\left(3x-1\right)}{\left(1-3x\right)3x\left(1-3x\right)}\)
\(=\frac{3x\left(3x-1\right)}{3x\left(1-3x\right)^2}=\frac{3x\left(3x-1\right)}{3x\left(3x-1\right)^2}=\frac{1}{3x-1}\)
b, \(5x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(5x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\5x+3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-\frac{3}{5}\end{cases}}}\)
Thay x = 0 vào A, ta có :
\(A=\frac{1}{3.0-1}=\frac{1}{-1}=-1\)
Thay x = - 3/5 vào A, ta có :
\(A=\frac{1}{3.\left(-\frac{3}{5}\right)-1}=\frac{1}{-\frac{9}{5}-1}=\frac{1}{-\frac{14}{5}}=-\frac{5}{14}\)
c, \(A=\frac{x}{x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{3x-1}=\frac{x}{x-1}\)\(\left(ĐK:x\ne\frac{1}{3};x\ne1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-1}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{x\left(3x-1\right)}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=3x^2-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-x-x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x^2-\frac{2}{3}x+\frac{1}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{2}{3}x+\frac{1}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2.x.\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{9}+\frac{2}{9}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{3}\right)^2+\frac{2}{9}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{3}\right)^2=-\frac{2}{9}\) (vô lí)
Vậy không tìm được x thỏa mãn đề bài.
d, \(\frac{6}{A}=\frac{6}{\frac{1}{3x-1}}=6\left(3x-1\right)=18x-6\)
Vậy x thuộc Z thì 6/A thuộc Z

\(A=\left(3x+1-\frac{1}{1-3x}\right):\left(\frac{3x-9x^2}{3x-1}\right)=\left(\frac{1-9x^2-1}{1-3x}\right):\left(\frac{3x\left(1-3x\right)}{3x-1}\right)=-\frac{9x}{1-3x}:\left(-3x\right)=\frac{3}{1-3x}\)
b. Với \(5x^2+3x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(5x+3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-\frac{3}{5}\end{cases}}\) nhưng mà ở trên ta cần có điều kiện x#0 nên
\(x=-\frac{3}{5}\Rightarrow A=\frac{3}{1-3\times\left(-\frac{3}{5}\right)}=\frac{15}{14}\)
c.\(A=\frac{x}{x-1}=\frac{3}{1-3x}\Leftrightarrow x-3x^2=3x-3\Leftrightarrow3x^2+2x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt{10}}{3}\)
d.\(\frac{6}{A}=2\times\left(1-3x\right)\) nguyên nên \(1-3x=-\frac{k}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{k+2}{6}\) với k là số nguyên

a: \(B=\dfrac{3x\left(2x-3\right)-4\left(2x+3\right)-4x^2+23x+12}{\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{2x+3}{x+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{6x^2-9x-8x-12-4x^2+23x+12}{2x-3}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+6x}{\left(2x-3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x+3}=\dfrac{2x}{2x-3}\)
b: 2x^2+7x+3=0
=>(2x+3)(x+2)=0
=>x=-3/2(loại) hoặc x=-2(nhận)
Khi x=-2 thì \(A=\dfrac{2\cdot\left(-2\right)}{-2-3}=\dfrac{-4}{-7}=\dfrac{4}{7}\)
d: |B|<1
=>B>-1 và B<1
=>B+1>0 và B-1<0
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2x+2x-3}{2x-3}>0\\\dfrac{2x-2x+3}{2x-3}< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3< 0\\\dfrac{4x-3}{2x-3}>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{3}{4}\)

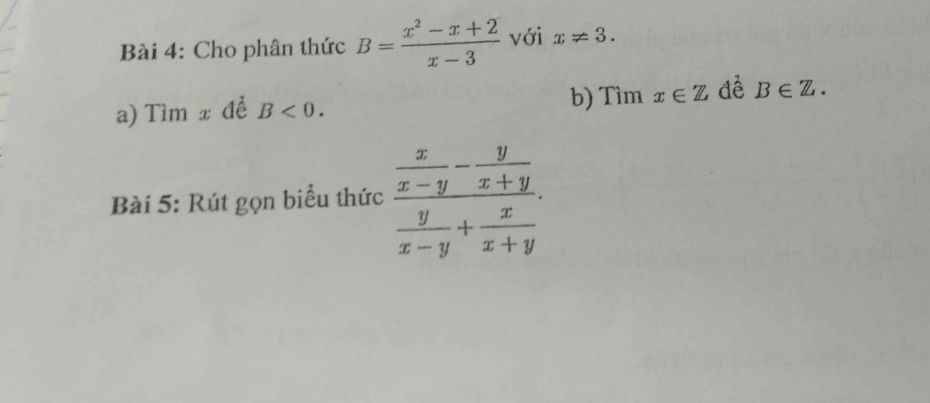
a: \(B=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{x-2}{x-4}\)
Để B>=0 thì x-4>0 hoặc x-2<=0
=>x>4 hoặc x<=2
b: Để B là số nguyên thì x-4+2 chia hết cho x-4
\(\Leftrightarrow x-4\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{5;6;2\right\}\)