Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(f\left(0\right)=-1\Rightarrow f'\left(0\right)+2=0\Leftrightarrow f'\left(0\right)=-2\)
\(\int\limits^1_0f\left(x\right)dx=\int\limits^1_0\dfrac{f'\left(x\right)-x.e^{3x}}{2}dx=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits^1_0f'\left(x\right)dx-\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits^1_0x.e^{3x}dx=\dfrac{1}{2}f\left(x\right)|^1_0-\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits^1_0xe^{3x}dx\)
\(I_1=\int xe^{3x}dx\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=x\\dv=e^{3x}dx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=dx\\v=\dfrac{1}{3}e^{3x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I_1=\dfrac{1}{3}xe^{3x}-\dfrac{1}{3}\int e^{3x}dx=\dfrac{1}{3}xe^{3x}-\dfrac{1}{9}e^{3x}\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{2}f\left(1\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}f\left(0\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{3}xe^{3x}-\dfrac{1}{9}e^{3x}\right)|^1_0\)
Èo, tắc chỗ f(1) rồi, vậy đành phải biến đổi để tìm f(x) luôn vậy, hmm
Thử nhân 2 vế với \(e^{2x}\) xem nào:
\(e^{2x}f'\left(x\right)-2e^{2x}f\left(x\right)=x.e^{5x}\Leftrightarrow\left(e^{2x}.f\left(x\right)\right)'=x.e^{5x}\)
Lay nguyen ham 2 ve:
\(e^{2x}.f\left(x\right)=\int x.e^{5x}dx\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=u\\dv=e^{5x}dx\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}dx=du\\v=\dfrac{1}{5}e^{5x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow e^{2x}.f\left(x\right)=\int x.e^{5x}dx=\dfrac{1}{5}x.e^{5x}-\dfrac{1}{5}\int e^{5x}dx=\dfrac{1}{5}xe^{5x}-\dfrac{1}{25}e^{5x}+C\)
\(f\left(0\right)=-1\Leftrightarrow f\left(0\right)=-\dfrac{1}{25}+C=-1\Leftrightarrow C=-\dfrac{24}{25}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{5}xe^{5x}-\dfrac{1}{25}e^{5x}-\dfrac{24}{25}}{e^{2x}}\)
Vậy là xong rồi \(\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=...\) , thay vô \(I=\dfrac{1}{2}f\left(1\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(-1\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{3}xe^{3x}-\dfrac{1}{9}e^{3x}\right)|^1_0\) là được nha :)
Nguyên tắc:
\(g\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)+h\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=p\left(x\right)\)
Đầu tiên luôn biến đổi để \(f'\left(x\right)\) đứng riêng biệt 1 mình:
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)+\dfrac{h\left(x\right)}{g\left(x\right)}.f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{p\left(x\right)}{g\left(x\right)}\) (1)
Cần thêm/bớt, nhân/chia sao cho biến về dạng:
\(\left[u\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)\right]'=q\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f'\left(x\right).u\left(x\right)+u'\left(x\right).f\left(x\right)=q\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f'\left(x\right)+\dfrac{u'\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}.f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{q\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}\)
Chỉ quan tâm vế trái, khi đó ta sẽ thấy hàm đằng trước \(f\left(x\right)\) chính là \(\dfrac{u'\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}\)
Đồng nhất \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{u'\left(x\right)}{u\left(x\right)}=-2\)
Lấy nguyên hàm 2 vế \(\Rightarrow ln\left|u\left(x\right)\right|=-2x\Rightarrow u\left(x\right)=e^{-2x}\)
Do đó, ở bài toán ban đầu ta cần nhân 2 vế của (1) với \(u\left(x\right)=e^{-2x}\) nghĩa là:
\(f'\left(x\right)-2f\left(x\right)=x.e^{3x}\Leftrightarrow e^{-2x}.f'\left(x\right)-2e^{-2x}.f\left(x\right)=x.e^x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[e^{-2x}.f\left(x\right)\right]'=x.e^x\)
Nguyên hàm 2 vế: \(\Rightarrow e^{-2x}.f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)e^x+C\)
Thay \(x=0\Rightarrow1.f\left(0\right)=-1+C\Rightarrow C=0\)
\(\Rightarrow e^{-2x}.f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)e^x\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)e^{3x}\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\limits^1_0\left(x-1\right)e^{3x}dx=...\)

Chọn C.
Đặt t = f ( x ) → d t = f ' x d x . Đổi cận: x = 2016 → t = f ( 2016 ) = a x = 2017 → t = f ( 2017 ) = b
Khi đó
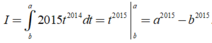

Chọn A
Cách 1: Từ đồ thị hàm số của ![]() ta thấy
ta thấy ![]() có hai cực trị dương nên hàm số
có hai cực trị dương nên hàm số ![]() lấy đối xứng phần đồ thị hàm số bên phải trục tung qua trục tung ta được bốn cực trị, cộng thêm giao điểm của đồ thị hàm số
lấy đối xứng phần đồ thị hàm số bên phải trục tung qua trục tung ta được bốn cực trị, cộng thêm giao điểm của đồ thị hàm số ![]() với trục tung nữa ta được tổng cộng là
với trục tung nữa ta được tổng cộng là ![]() cực trị.
cực trị.

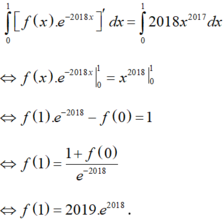
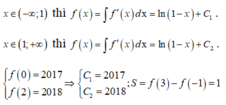
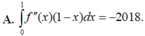
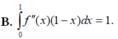
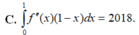
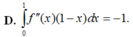

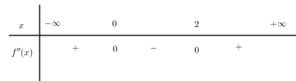
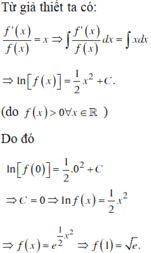

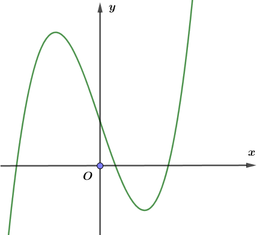
Chọn A