
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a:Đặt (d1): y=2x-3
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) với trục Ox là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) với trục Oy là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2x-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2\cdot0-3=0-3=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Đặt (d2): \(y=-\dfrac{3}{4}x\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d2) với trục Ox là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-\dfrac{3}{4}x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d2) với trục Oy là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=-\dfrac{3}{4}x=-\dfrac{3}{4}\cdot0=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Đặt \(\left(d3\right):y=2x^2\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d3) với trục Ox là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2=0\\y=2x^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2=0\\y=2x^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2\cdot0^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d3) với trục Oy là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2x^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2\cdot0^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: Đặt (d4): \(y=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\)
ĐKXĐ: x<>2
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d4) với trục Ox là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\y=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d4) với trục Oy là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}=\dfrac{0+1}{0-2}=\dfrac{1}{-2}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e: Đặt (d5): \(y=x-2+\dfrac{1}{x}\)
ĐKXĐ: x<>0
Vì hàm số không đi qua điểm có hoành độ là x=0 nên (d5) sẽ không cắt trục Oy
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d5) với trục Ox là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x-2+\dfrac{1}{x}=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x+1=0\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
f: Đặt (d6): \(y=x^2+2x-5\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d6) với trục Oy là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=x^2+2x-5=0^2+2\cdot0-5=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ giao điểm của (d6) với trục Ox là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x^2+2x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x^2+2x+1-6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left(x+1\right)^2=6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x+1=\sqrt{6}\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x+1=-\sqrt{6}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=\sqrt{6}-1\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-\sqrt{6}-1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)

Câu 5:
a: Khi m=3 thì \(f\left(x\right)=\left(2\cdot3+1\right)x-3=7x-3\)
\(f\left(-3\right)=7\cdot\left(-3\right)-3=-21-3=-24\)
\(f\left(0\right)=7\cdot0-3=-3\)
b: Thay x=2 và y=3 vào f(x)=(2m+1)x-3, ta được:
\(2\left(2m+1\right)-3=3\)
=>2(2m+1)=6
=>2m+1=3
=>2m=2
=>m=1
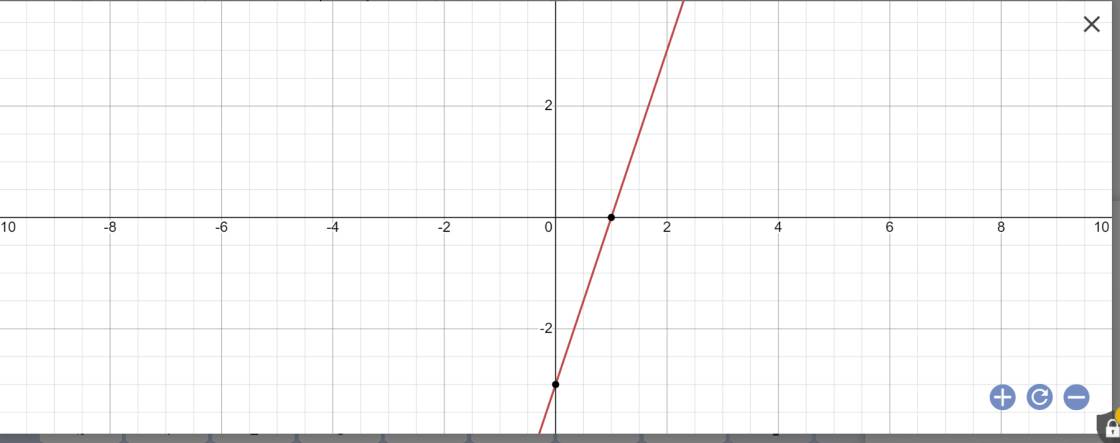
c: Thay m=1 vào hàm số, ta được:
\(y=\left(2\cdot1+1\right)x-3=3x-3\)
*Vẽ đồ thị
d: Để hàm số y=(2m+1)x-3 là hàm số bậc nhất thì \(2m+1\ne0\)
=>\(2m\ne-1\)
=>\(m\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
e: Để đồ thị hàm số y=(2m+1)x-3 song song với đường thẳng y=5x+1 thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m+1=5\\-3\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>2m+1=5
=>2m=4
=>m=2

*Bảng giá trị:
| x | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| y=2x-4 | -6 | -4 | -2 |
| y=3x+3 | 0 | 3 | 6 |
| y=-x | 1 | 0 | -1 |
*Vẽ đồ thị:
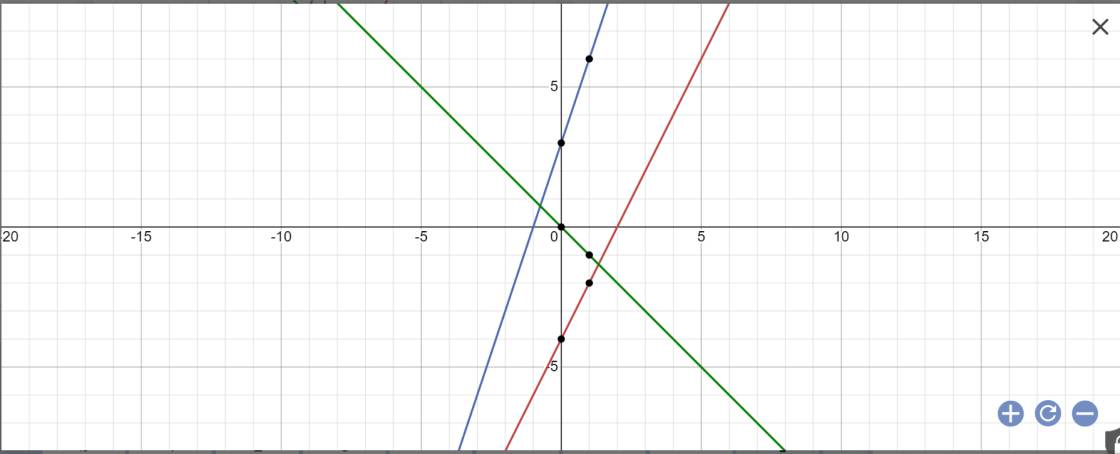


a: 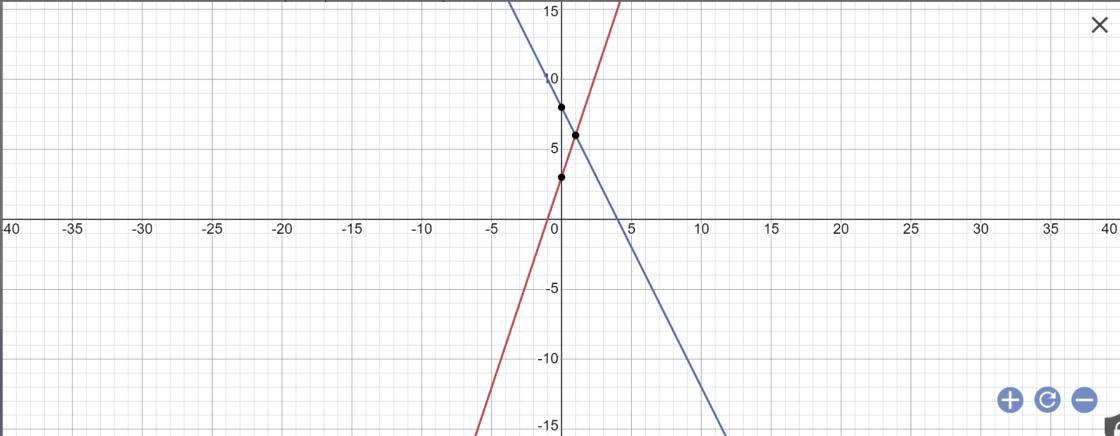
b: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+3=-2x+8\\y=-2x+8\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x=5\\y=-2x+8\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=-2+8=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(1;6)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\3x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-2x+8=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-2x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(1;6); B(-1;0); C(4;0)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(-1-1\right)^2+\left(0-6\right)^2}=2\sqrt{10}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(4-1\right)^2+\left(0-6\right)^2}=3\sqrt{5}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(4+1\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=5\)
Xét ΔABC có \(cosBAC=\dfrac{AB^2+AC^2-BC^2}{2\cdot BA\cdot AC}=\dfrac{40+45-25}{2\cdot2\sqrt{10}\cdot3\sqrt{5}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
=>\(sinBAC=\sqrt{1-\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)^2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AB\cdot AC\cdot sinBAC\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\cdot2\sqrt{10}\cdot3\sqrt{5}=15\)

mỗi đồ thị bạn chọn ra hai điểm rồi nối lại là xong.( hai điểm đó thay vào thỏa đẳng thức )