Giải phương trình: (x2 – 2x + 1) – 4 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 4\)
\(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(2+x\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2-x=0\\2+x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -2\)
a)\(x^2-2x+1< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2< 9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2-9< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1-3\right)\left(x-1+3\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4>0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 4\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>4\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lý)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 4\).
b) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(4-x^2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2-x\right)\left(x+2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2>0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2< 0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0\\x-2 >0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1< 0\\x-2< 0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x>2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x< 2\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x>2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (vô lí) hay \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x< 2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(x< -2\) hay \(1< x< 2\).
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne5\)
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-5}< 0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2< 0\\x-5>0\end{matrix}\right.hay\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2>0\\x-5< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>5\end{matrix}\right.\)(vô lí) hay
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>-2\\x< 5\end{matrix}\right.\) (có thể xảy ra)
-Vậy nghiệm của BĐT là \(-2< x< 5\)


3x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 3x2 + 3x - x - 1 = 0
=> 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1) = 0
=> (3x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
x2 - 5x + 6 = 0
=> x2 - 2x - 3x + 6 = 0
=> x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2) = 0
=> (x - 3)(x - 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
3x2 + 7x + 2 = 0
=> 3x2 + 6x + x + 2 = 0
=> 3x(x + 2) + (x + 2) = 0
=> (3x + 1)(x + 2) = 0
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x+1=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}}\)
=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{3}\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
1, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
2, \(x^2-5x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}}\)
3, \(3x^2+7x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+2=0\\3x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}}\)

\(a,x^2-10x=-25\)
\(< =>x^2-10x+25=0\)
\(< =>\left(x-5\right)^2=0< =>x=5\)
b, \(4x^2-4x=-1\)
\(< =>4x^2-4x+1=0\)
\(< =>\left(2x-1\right)^2=0< =>x=\frac{1}{2}\)

????
xin lỗi nha !
mình mới học lớp 3
mà bài này khó nắm

1) Ta có: \(x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
hay x=2
Vậy: S={2}

Lời giải:
PT $\Leftrightarrow (x^2-1)^3+(x^2+2)^3+(2x-1)^3-3(x^2-1)(x^2+2)(2x-1)=0$
Đặt $x^2-1=a; x^2+2=b; 2x-1=c$ thì pt trở thành:
$a^3+b^3+c^3-3abc=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b)^3+c^3-3ab(a+b)-3abc=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b+c)[(a+b)^2-c(a+b)+c^2]-3ab(a+b+c)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+b+c)(a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac)=0$
$\Rightarrow a+b+c=0$ hoặc $a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac=0$
Nếu $a+b+c=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-1+x^2+2+2x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2+2x=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0$ hoặc $x=-1$
Nếu $a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-b)^2+(b-c)^2+(c-a)^2=0$
$\Rightarrow a-b=b-c=c-a=0$ (dễ CM)
$\Leftrightarrow a=b=c$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=x^2+2=2x-1$ (vô lý)
Vậy..........
Akai Haruma Chị ơi chỗ
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a+b+c\right)\left(a^2+b^2+c^2-ab-bc-ac\right)=0\) từ chỗ trên chị tách làm sao ra được vế beeb phải vậy ạ

+ 2x2 + y2 – 8x + 2y – 1 = 0 không phải phương trình đường tròn vì hệ số của x2 khác hệ số của y2.
+ Phương trình x2 + y2 + 2x – 4y – 4 = 0 có :
a = –1; b = 2; c = –4 ⇒ a2 + b2 – c = 9 > 0
⇒ phương trình trên là phương trình đường tròn.
+ Phương trình x2 + y2 – 2x – 6y + 20 = 0 có :
a = 1; b = 3; c = 20 ⇒ a2 + b2 – c = –10 < 0
⇒ phương trình trên không là phương trình đường tròn.
+ Phương trình x2 + y2 + 6x + 2y + 10 = 0 có :
a = –3; b = –1; c = 10 ⇒ a2 + b2 – c = 0 = 0
⇒ phương trình trên không là phương trình đường tròn.
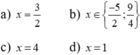
(x2 – 2x + 1) – 4 = 0
⇔ (x – 1)2 – 22 = 0
⇔ (x – 1 – 2)(x – 1 + 2) = 0
(Sử dụng hằng đẳng thức)
⇔ (x – 3)(x + 1) = 0
⇔ x – 3 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3.
+ x + 1 = 0 ⇔ x = -1.
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {-1; 3}.