Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a: Thay x=-2 và y=2 vào hàm số, ta được:
4a=2
hay a=1/2
Bài 2:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+5y=3\\4x-12y=20\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}17y=-17\\x-3y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\3y=x-5=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}=1\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{3}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(x,y\right)=\left(2;\dfrac{10}{3}\right)\)

a, Hoành độ giao điểm tm pt
\(x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=0;x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Với x = 0 => y = 0
Với x = 1/2 => y = 1/4
Vậy (P) cắt (d) tại O(0;0) ; A(1/2;1/4)

Bạn tự vẽ nhé.
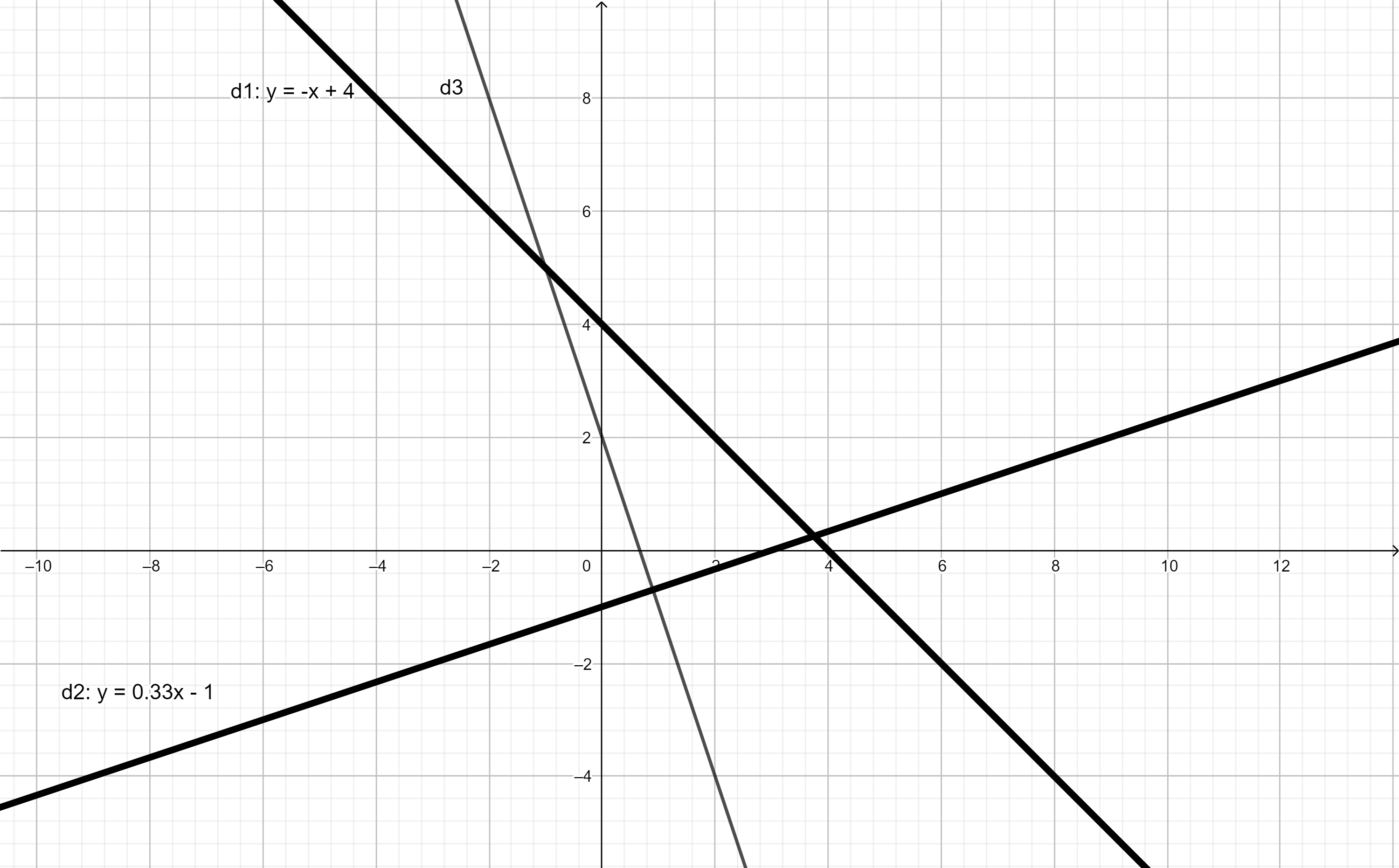
\(a,\) 2 đồ thị hàm số \(y=2x,y=-3x+5\) giao nhau khi và chỉ khi :
\(2x=-3x+5\\ \Leftrightarrow5x=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Thay \(x=1\) vào \(y=2x\Leftrightarrow y=2\)
Vậy giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là \(\left(1;2\right)\)
\(b,\) 2 đồ thị hàm số \(y=3x+2,y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+1\) giao nhau khi và chỉ khi :
\(3x+2=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7}{2}x=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{2}{7}\)
Thay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{7}\) vào \(y=3x+2\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{8}{7}\)
Vậy giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là \(\left(-\dfrac{2}{7};\dfrac{8}{7}\right)\)
\(c,\) 2 đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-2,y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\) giao nhau khi và chỉ khi :
\(\dfrac{3}{2}x-2=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Thay \(x=2\) vào \(y=\dfrac{3}{2}x-2\Rightarrow y=1\)
Vậy giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là \(\left(2;1\right)\)
\(d,\) 2 đồ thị hàm số \(y=-2x+5,y=x+2\) giao nhau khi và chỉ khi :
\(-2x+5=x+2\\ \Leftrightarrow-3x=-3\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Thay \(x=1\) vào \(y=x+2\Rightarrow y=3\)
Vậy giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là \(\left(1;3\right)\)


\(a,\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\dfrac{m-2}{m+3}}>0\)
Mà \(\sqrt{\dfrac{m-2}{m+3}}\ge0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\dfrac{m-2}{m+3}}\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne2;m\ne-3\)
\(b,y=m^2x-5mx-6m=x\left(m^2-5m\right)-6m\)
Đồng biến \(\Leftrightarrow m^2-5m>0\Leftrightarrow m\left(m-5\right)>0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m< 0\\m>5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,y=x\left(\dfrac{m+5}{m-2}-1\right)+\sqrt{m-2}=\dfrac{7}{m-2}x+\sqrt{m-2}\)
Đồng biến \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7}{m-2}>0\Leftrightarrow m-2>0\Leftrightarrow m>2\)

Bài 3:
\(A=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-4}{3\sqrt{x}-4}+\dfrac{x+22\sqrt{x}-32}{3x-10\sqrt{x}+8}+\dfrac{4+2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-4}{3\sqrt{x}-4}+\dfrac{x+22\sqrt{x}-32}{\left(3\sqrt{x}-4\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}+\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+4}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(2\sqrt{x}-4\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)+x+22\sqrt{x}-32+\left(2\sqrt{x}+4\right)\left(3\sqrt{x}-4\right)}{\left(3\sqrt{x}-4\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-8\sqrt{x}+8+x+22\sqrt{x}-32+6x-8\sqrt{x}+12\sqrt{x}-16}{\left(3\sqrt{x}-4\right)\cdot\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{9x+18\sqrt{x}-40}{\left(3\sqrt{x}-4\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{9x-12\sqrt{x}+30\sqrt{x}-40}{\left(3\sqrt{x}-4\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(3\sqrt{x}-4\right)\left(3\sqrt{x}+10\right)}{\left(3\sqrt{x}-4\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+10}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
Bài 2:
b: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{3}{2}=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\3-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>A(3;0)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{3}{2}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot0+\dfrac{3}{2}=1,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>B(0;1,5)
\(OA=\sqrt{\left(3-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{3^2+0^2}=3\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(1,5-0\right)^2}=1,5\)
Ox\(\perp\)Oy nên OA\(\perp\)OB
=>ΔOAB vuông tại O
=>\(S_{OAB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB=2.25\)
Bài 1:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(\sqrt{x^2+4x+4}=2\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)^2}=2\)
=>|x+2|=2
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=2\\x+2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: ĐKXĐ: x>=2
\(\sqrt{4x-8}-7\cdot\sqrt{\dfrac{x-2}{49}}=5\)
=>\(2\sqrt{x-2}-7\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x-2}}{7}=5\)
=>\(\sqrt{x-2}=5\)
=>x-2=25
=>x=27(nhận)

+) vẽ : tự vẽ nha
+) nhận xét là : 2 đường thẳng trên song song với nhau , vì 2 đường thẳng này có cùng hệ số góc .
Nếu có gì không đúng thì chỉ cho mk nhé
?