Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1. Áp dụng quy tắc L'Hopital
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+1}-1}{f\left(0\right)-f\left(x\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x+1}}}{-f'\left(0\right)}=-\dfrac{1}{6}\)
2.
\(g'\left(x\right)=2x.f'\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\f'\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\\sqrt{x^2+4}=1\\\sqrt{x^2+4}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
2 pt cuối đều vô nghiệm nên \(g'\left(x\right)=0\) có đúng 1 nghiệm

1a.
\(y'=3x^2.f'\left(x^3\right)-2x.g'\left(x^2\right)\)
b.
\(y'=\dfrac{3f^2\left(x\right).f'\left(x\right)+3g^2\left(x\right).g'\left(x\right)}{2\sqrt{f^3\left(x\right)+g^3\left(x\right)}}\)
2.
\(f'\left(x\right)=\left(m-1\right)x^3+\left(m-2\right)x^2-2mx+3=0\)
Để ý rằng tổng hệ số của vế trái bằng 1 nên pt luôn có nghiệm \(x=1\), sử dụng lược đồ Hooc-ne ta phân tích được:
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(m-1\right)x^2+\left(2m-3\right)x-3\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\\left(m-1\right)x^2+\left(2m-3\right)x-3=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét (1), với \(m=1\Rightarrow x=-3\)
- Với \(m\ne1\Rightarrow\Delta=\left(2m-3\right)^2+12\left(m-1\right)=4m^2-3\)
Nếu \(\left|m\right|< \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\Rightarrow\) (1) vô nghiệm \(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=0\) có đúng 1 nghiệm
Nếu \(\left|m\right|>\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\) có 2 nghiệm \(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=0\) có 3 nghiệm

\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x^2-4\left|x\right|+2\right|=m\) (1) có 8 nghiệm phân biệt
Đặt \(x^2-4\left|x\right|+2=t\) (2)
Từ đồ thị của hàm \(y=x^2-4\left|x\right|+2\) ta thấy:
- Với \(t< -2\Rightarrow\) (2) vô nghiệm
- Với \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-2\\t>2\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\) (2) có 2 nghiệm
- Với \(-2< t< 2\Rightarrow\) (2) có 4 nghiệm
- Với \(t=2\Rightarrow\) (2) có 3 nghiệm
Khi đó (1) trở thành: \(\left|t\right|=m\) (3) có tối đa 2 nghiệm
\(\Rightarrow\)Phương trình đã cho có 8 nghiệm pb khi và chỉ khi (3) có 2 nghiệm t phân biệt thỏa mãn \(-2< t< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow0< m< 2\)
Không có phương án nào đúng

\(f\left(x\right)=x+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{x+1}\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=1+\dfrac{1-x}{2\sqrt{x}\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(f'\left(x\right)-1>0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1-x}{2\sqrt{x}\left(x+1\right)^2}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow0< x< 1\)

1.
\(f'\left(x\right)=3x^2-6mx+3\left(2m-1\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)-6x=3x^2-3.2\left(m+1\right)x+3\left(2m-1\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+2m-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-1>2m\left(x-1\right)\)
Do \(x>2\Rightarrow x-1>0\) nên BPT tương đương:
\(\dfrac{x^2-2x-1}{x-1}>2m\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2-2}{x-1}>2m\)
Đặt \(t=x-1>1\Rightarrow\dfrac{t^2-2}{t}>2m\Leftrightarrow f\left(t\right)=t-\dfrac{2}{t}>2m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)\) với \(t>1\) : \(f'\left(t\right)=1+\dfrac{2}{t^2}>0\) ; \(\forall t\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)\) đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)>f\left(1\right)=-1\Rightarrow\) BPT đúng với mọi \(t>1\) khi \(2m< -1\Rightarrow m< -\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2.
Thay \(x=0\) vào giả thiết:
\(f^3\left(2\right)-2f^2\left(2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow f^2\left(2\right)\left[f\left(2\right)-2\right]=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}f\left(2\right)=0\\f\left(2\right)=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đạo hàm 2 vế giả thiết:
\(-3f^2\left(2-x\right).f'\left(2-x\right)-12f\left(2+3x\right).f'\left(2+3x\right)+2x.g\left(x\right)+x^2.g'\left(x\right)+36=0\) (1)
Thế \(x=0\) vào (1) ta được:
\(-3f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+4f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12=0\) (2)
Với \(f\left(2\right)=0\) thế vào (2) \(\Rightarrow-12=0\) ko thỏa mãn (loại)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=2\)
Thế vào (2):
\(4f'\left(2\right)+8f'\left(2\right)-12=0\Leftrightarrow f'\left(2\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow A=3.2+4.1\)

\(f'\left(x\right)=x^2-4\sqrt{2}x+8=\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2=0\Rightarrow x=2\sqrt{2}\)

Trên các khoảng \(\left( { - \infty ;0} \right)\) và \(\left( {0; + \infty } \right)\), \(f\left( x \right) = \frac{{{x^2} - 2x}}{x}\) là hàm phân thức hữu tỉ nên liên tục trên từng khoảng \(\left( { - \infty ;0} \right)\) và \(\left( {0; + \infty } \right)\).
Ta có: \(f\left( 0 \right) = a\)
\(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} f\left( x \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} \frac{{{x^2} - 2x}}{x} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} \frac{{x\left( {x - 2} \right)}}{x} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} \left( {x - 2} \right) = 0 - 2 = - 2\)
Để hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right)\) liên tục trên \(\mathbb{R}\) thì hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right)\) phải liên tục tại điểm \({x_0} = 0\). Khi đó:
\(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} f\left( x \right) = f\left( 0 \right) \Leftrightarrow a = - 2\).
Vậy với \(a = - 2\) thì hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right)\) liên tục trên \(\mathbb{R}\).
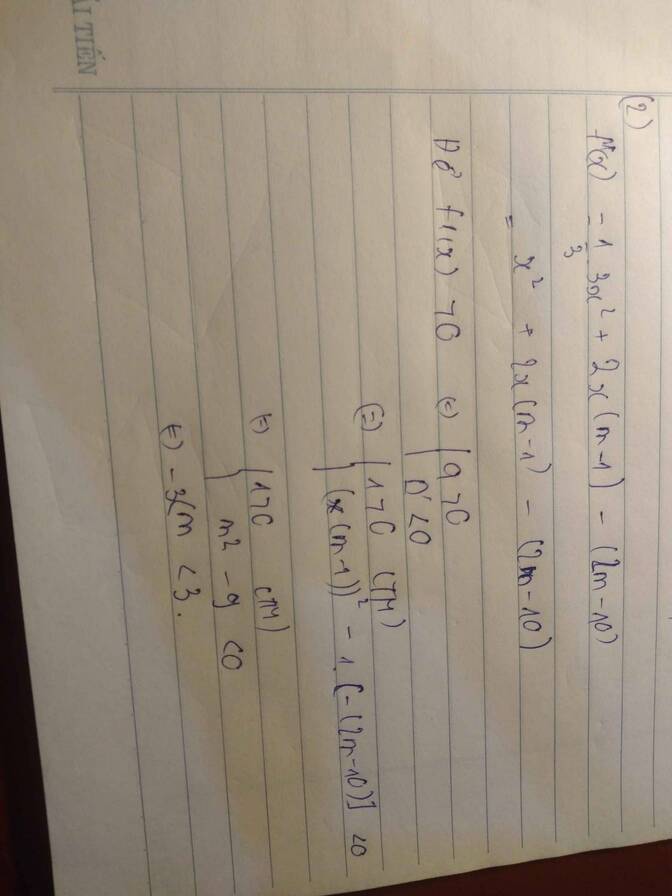
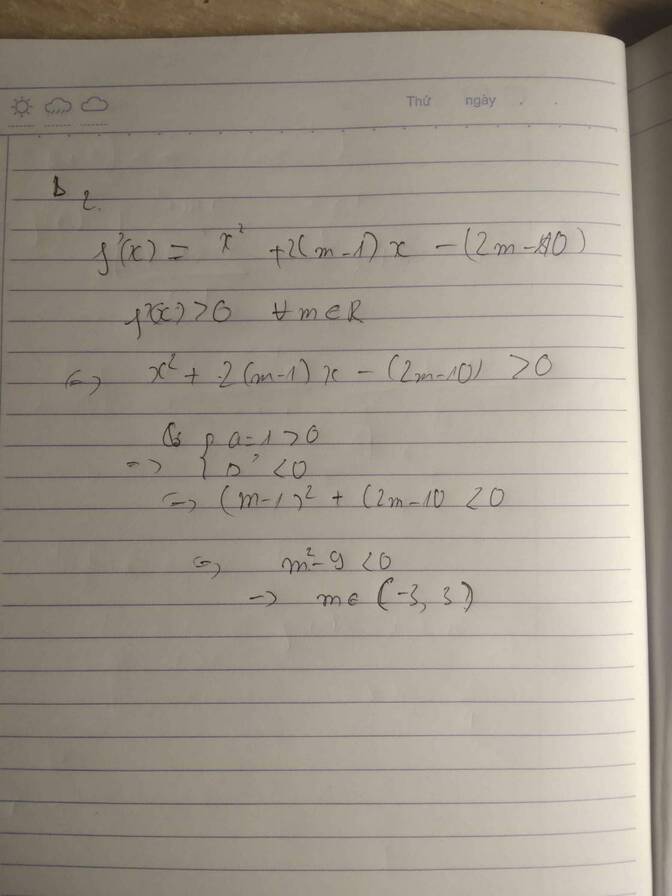

\(f'\left(x\right)=x^2+2\left(m-2\right)x+9\)
Để \(f'\left(x\right)\ge0\) \(\forall x\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\le0\Leftrightarrow\left(m-2\right)^2-9\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3\le m-2\le3\Leftrightarrow-1\le m\le5\)